Introduction
Since the release of GPT models by OpenAI, such as GPT 4o, the landscape of Natural Language Processing has been changed entirely and moved to a new notion called Generative AI. Large Language Models are at the core of it, which can understand complex human queries and generate relevant answers to them. The next step to this LLM is the multimodality. That is the ability to understand data other than text. This can include images, audio, and videos. Some of the multimodels have recently been released, both open source and closed sources, like the Gemini from Google, LlaVa, and GPT 4v. Recently a newer multi-model has been announced by OpenAI called the GPT 4o (Omni). In this article, we will be creating a multimodal chatbot with this OpenAI GPT 4o

Learning Objectives
- Understand GPT-4o and its capabilities in text, audio, and image generation
- Learn how to create helper functions for processing user input (images and audio) for GPT-4o
- Build a multimodal chatbot using Chainlit that interacts with GPT-4o
- Implement functionalities for handling text, image, and audio inputs in the chatbot
- Recognize the benefits of using a gpt 4o multimodal approach for chatbot interactions
- Explore potential applications of GPT-4o’s multimodal capabilities
This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Table of contents
What is GPT 4o?
The recently announced OpenAI’s GPT-4o marks a big leap in AI for its speed, accuracy, and ability to understand and generate text, audio, and images. This “multilingual” model can translate languages, write creative content, analyze or generate speech with varying tones, and even describe real-world scenes or create images based on your descriptions. Beyond its impressive capabilities, GPT-4o integrates seamlessly with ChatGPT, allowing real-time conversations where it can identify visual information and ask relevant questions. This ability to interact across modalities paves the way for a more natural and intuitive way of interacting with computers, potentially assisting visually impaired users and creating new artistic mediums. GPT-4o stands out as a groundbreaking next-gen model that pushes the boundaries of AI
Also read: The Omniscient GPT-4o + ChatGPT is HERE!
Creating the Helper Functions
In this section, we will begin writing the code for the gpt 4o multimodal Chatbot using GPT-4o. The first step would be to download the necessary libraries that we will need for this code to work. To do this, we run the below command
pip install openai chainlitRunning this will install the OpenAI library. This will let us work with the different OpenAI models, which include the text generation models like the GPT 4o and GPT 3.5, the image generation models like the DallE-3, and the Speech2Text models like the Whisper.
We install chainlit for creating the UI. Chainlit library lets us create quick chatbots completely in Python without writing Javascript, HTML, or CSS. Before beginning with the chatbot, we need to create some helper functions. The first one is for images. We cannot directly provide images of the model. We need to encode them to base64 and then give it. For this,
Code
import base64
def image2base64(image_path):
with open(image_path, "rb") as img:
encoded_string =, base64.b64encode(img.read())
return encoded_string.decode("utf-8")
- First, we import the base64 library for encoding. Then, we create a function named image_2_base64() to take an image_path as input.
- Next, we open the image with the provided path in read-bytes mode. Then, we call the b64encode() method from the base64 library, which encodes the image to base64.
- The encoded data is in bytes, so we need to convert it to the Unicode format the model expects to pass this Image along with the user query.
- Hence, we call the decode() method, which takes in the base64-encoded bytes and returns a Unicode string by decoding them with UTF-8 encoding.
- Finally, we return the base64 encoded string, which can be joined with text to be sent to the GPT-4o model
- On a high level, what we do is, we convert the image to “Base 64 encoded bytes” and “Base 64 encoded bytes” to “Base 64 encoded string”
The gpt 4o multimodal chat even expects audio inputs. So, we even need to process the audio before sending it to the model. For this, we work with the Speech-to-text model from OpenAI.
Code
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
def audio_process(audio_path):
audio_file = open(audio_path, "rb")
transcription = client.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-1", file=audio_file
)
return transcription.text- We start by importing the OpenAI class from the OpenAI function. Make sure that an OpenAI API key is present in a .env file
- Next, we instantiate an OpenAI object and store this object in the variable client
- Now, we create a function called the audio_process(), which expects an audio path for the input
- Then we open the file in read mode and store the resulting bytes in the variable audio_file
- We then call the client.audio.transcriptions.create() function and give the audio_file to this function. Along with this, we even tell the model name we want to work with for speech-to-text conversion. Here we give it “whisper-1”
- Calling the above function will pass the audio_file contents to that model and the respective transcripts are stored in the transcription variable
- We then finally return to the text part, which is the actual transcription of the audio from this function
We cannot expect what type of message the user will ask the model. The user may sometimes just send plain text, sometimes may include an image, and sometimes may include an audio file. So, based on that, we need to alter the message that we will send to the OpenAI model. For this, we can write another function that will provide different user inputs to the model.
Code
def append_messages(image_url=None, query=None, audio_transcript=None):
message_list = []
if image_url:
message_list.append({"type": "image_url", "image_url": {"url": image_url}})
if query and not audio_transcript:
message_list.append({"type": "text", "text": query})
if audio_transcript:
message_list.append({"type": "text", "text": query + "\n" + audio_transcript})
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": message_list}],
max_tokens=1024,
)
return response.choices[0]- We create a function called append_messages(), where we define three parameters. One is image_url, the second is the user query, and the final one is the audio transcript
- Then, we create an empty message_list variable by assigning an empty list
- Next, we check if an image_url is provided, and if it is, then we create a dictionary with the key “type” and value “image_url,” and the other key is the “image_url” and to this, we pass another dictionary by giving the image_url with which the function was called. This is the format that OpenAI expects for sending the image
- Then, we check if a query is provided and no audio_transcript. Then we just append another dictionary to the messag_list with key-value pairs that we see in the code
- Finally, we check if an audio_transcript is provided to the function, and if it is, then we combine it in the user query and append it to the message list
- Then we call the client.chat.completions.create() function, where we pass the model, which here is the GPT-4o, and the message_list that we have created earlier and store the result in the response variable
- We have even set the max_tokens to 1024. Apart from these, we can even give extra parameters like temperature, top_p and top_k
- Finally, we store to return the response generated by the GPT 4 Omni by returning the response.choices[0]
With this, we have done with creating the helper functions. We will be calling these helper functions later to pass user queries, audio, and image data and get the responses back
Also read: Here’s How You Can Use GPT 4o API for Vision, Text, Image & More.
Building the Chatbot UI
Now, we will be building the UI part of the Chatbot. This can be built very easily with the Chainlit library. The code we will write will be in the same file where our helper functions are defined.
Code
import chainlit as cl
@cl.on_message
async def chat(msg: cl.Message):
images = [file for file in msg.elements if "image" in file.mime]
audios = [file for file in msg.elements if "audio" in file.mime]
if len(images) > 0:
base64_image = image2base64(images[0].path)
image_url = f"data:image/png;base64,{base64_image}"
elif len(audios) > 0:
text = audio_process(audios[0].path)
response_msg = cl.Message(content="")
if len(images) == 0 and len(audios) == 0:
response = append_messages(query=msg.content)
elif len(audios) == 0:
response = append_messages(image_url=image_url, query=msg.content)
else:
response = append_messages(query=msg.content, audio_transcript=text)
response_msg.content = response.message.content
await response_msg.send()- We start by importing the chainlit library. Then we create a decorate @cl.on_message(), which tells that the function below it gets run when a user types in a message
- Chainlit library expects an async function. Hence, we define an async function called chat, which accepts a variable called cl.Message. Whatever the user types in or provides audio or images, everything is stored in the cl.Message
- msg.elements contains a list of types of messages the user sends. These can be plain text user queries or a user query with an image or an audio
- Hence, we check if there are some images or audio files present in the user message and store them in images and audio variable
- Now, we check with an if block, if images are present, then we convert them to base64 string and store them in the image_url variable in a format that the GPT-4o model expects
- We even check if audio is present, and if it is, then we process that audio by calling the audio_process() function, which returns the audio transcription and is stored in the variable called text
- Then we create a message placeholder response_img by giving it an empty message
- Then again, we check for some images or audio. If both are not present, we only send the user query to the append_message function, and if even one audio/images are present, then we even pass them to the append_messages function
- Then, we store the result from the model in the response variable, and we append it to the placeholder message variable response_msg that we created earlier
- Finally, we call the response_msg.send(), which will display the response in the UI
Also read: What Can You Do With GPT-4o? | Demo
Final Code
from openai import OpenAI
import base64
import chainlit as cl
client = OpenAI()
def append_messages(image_url=None, query=None, audio_transcript=None):
message_list = []
if image_url:
message_list.append({"type": "image_url", "image_url": {"url": image_url}})
if query and not audio_transcript:
message_list.append({"type": "text", "text": query})
if audio_transcript:
message_list.append({"type": "text", "text": query + "\n" + audio_transcript})
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": message_list}],
max_tokens=1024,
)
return response.choices[0]
def image2base64(image_path):
with open(image_path, "rb") as img:
encoded_string = base64.b64encode(img.read())
return encoded_string.decode("utf-8")
def audio_process(audio_path):
audio_file = open(audio_path, "rb")
transcription = client.audio.transcriptions.create(
model="whisper-1", file=audio_file
)
return transcription.text
@cl.on_message
async def chat(msg: cl.Message):
images = [file for file in msg.elements if "image" in file.mime]
audios = [file for file in msg.elements if "audio" in file.mime]
if len(images) > 0:
base64_image = image2base64(images[0].path)
image_url = f"data:image/png;base64,{base64_image}"
elif len(audios) > 0:
text = audio_process(audios[0].path)
response_msg = cl.Message(content="")
if len(images) == 0 and len(audios) == 0:
response = append_messages(query=msg.content)
elif len(audios) == 0:
response = append_messages(image_url=image_url, query=msg.content)
else:
response = append_messages(query=msg.content, audio_transcript=text)
response_msg.content = response.message.content
await response_msg.send()
To execute this, type chainlit run app.py assuming that the code resides in a file named app.py. After executing this command, the localhost:8000 port will become active, and we will see the image below
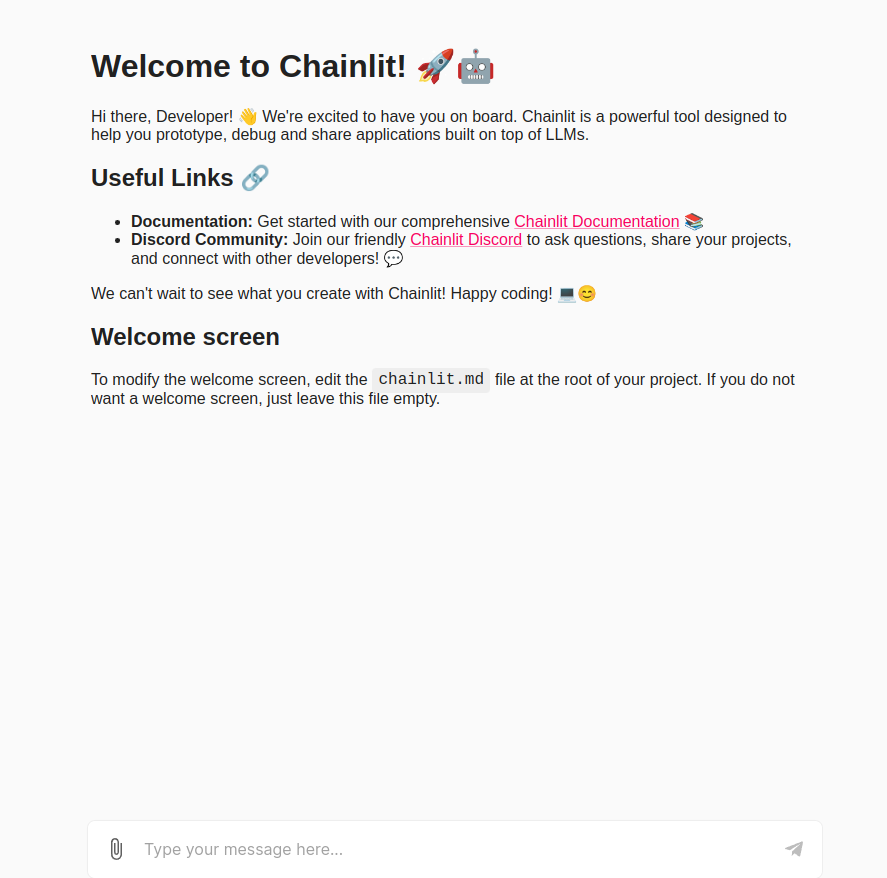
Now let us type in just a normal text query and see the output generated
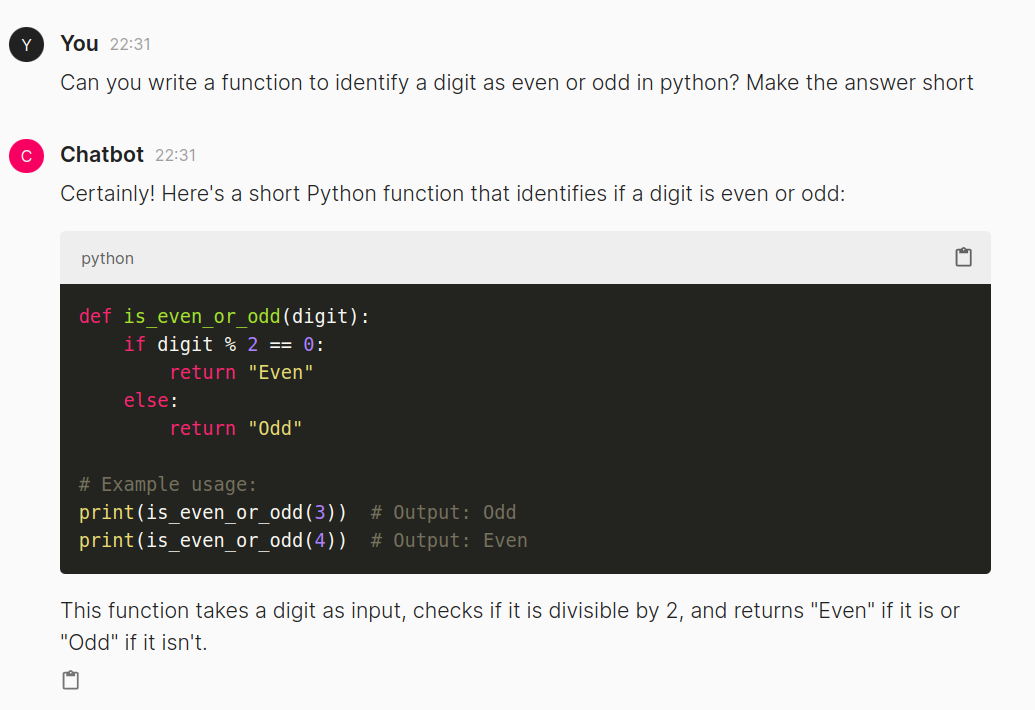
We see that the GPT-4o successfully generated an output for the user query. We observe that the code is being highlighted here, and we can copy and paste it quickly. This is all managed by Chainlit, which handles the underlying HTML, CSS, and Javascript. Next, let us try giving an image and asking about it the model.
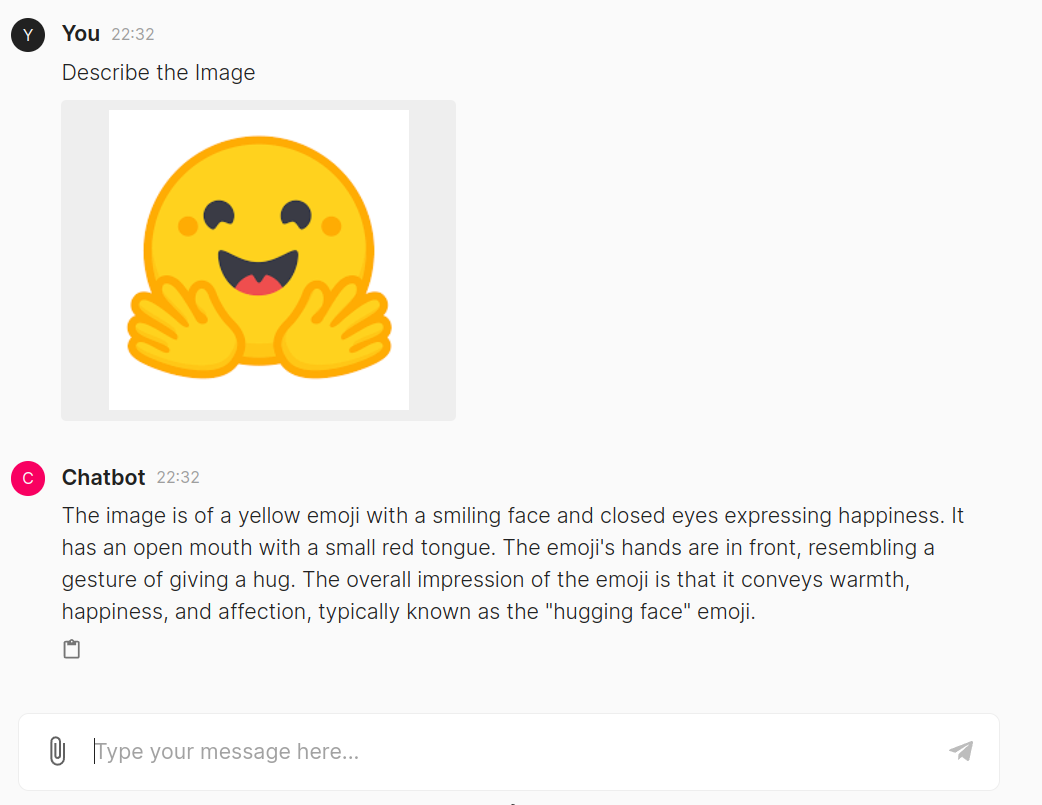
Here, the model has responded well to the image we uploaded. The system identified the image as an emoji and provided information about its identity and usage. Now, let us pass an audio file and test it
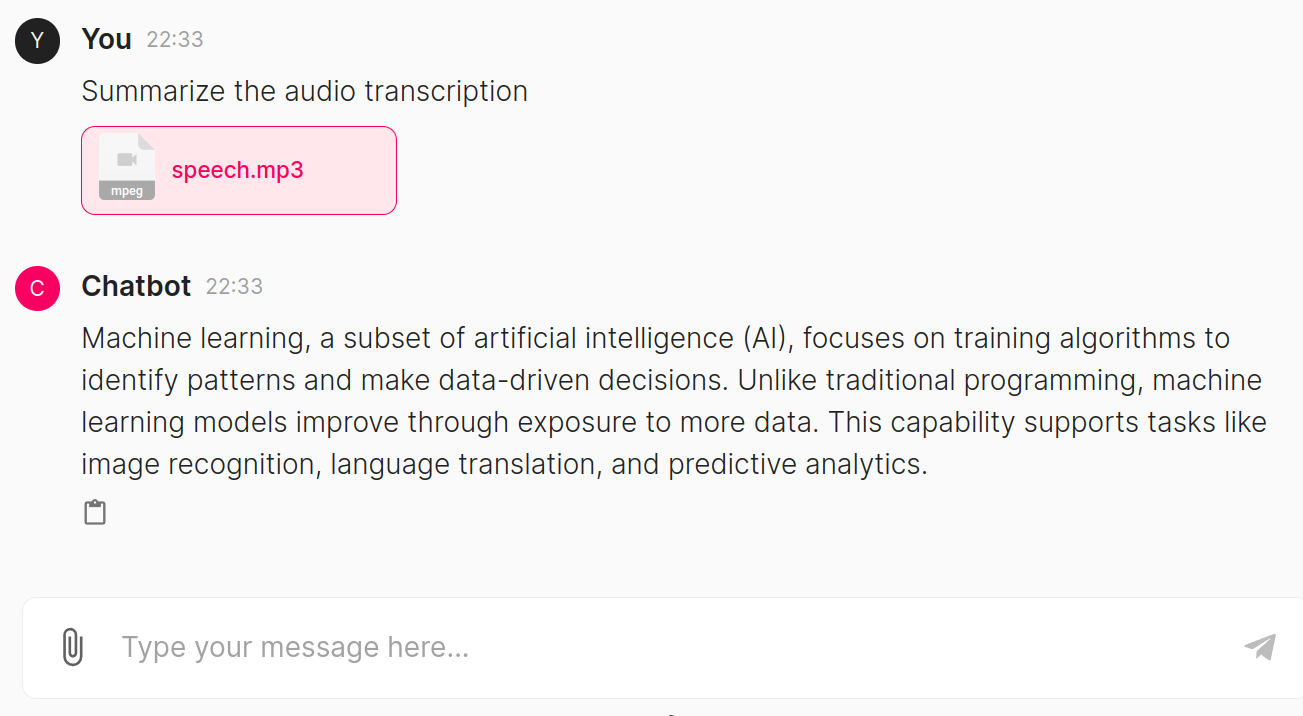
The speech.mp3 audio contains information about Machine Learning, so we asked the model to summarize its contents. The model generated a summary that is relevant to the content present in the audio file.
Also read: Building a MultiModal Chatbot with Gemini and Gradio
Conclusion
In conclusion, developing a multimodal chatbot using OpenAI’s GPT-4o (Omni) marks a great feat in AI technology, ushering in a new era of interactive experiences. Here, we’ve explored seamlessly integrating text, images, and audio inputs into conversations with the chatbot, leveraging the capabilities of GPT-4o. This innovative approach enhances user engagement and opens doors to different practical applications, from aiding visually impaired users to creating new artistic mediums. By combining the power of language understanding with multimodal capabilities, GPT-4o shows its potential to revolutionize how we interact with AI systems
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o represents a big moment in AI, offering text, audio, and image understanding and generation in just a single model
- Integration of multimodal functionality into chatbots gives more natural and intuitive interactions, increasing user engagement and experience
- Helper functions play a crucial role in preprocessing inputs, like encoding images to base64 and transcribing audio files, before feeding them into the model
- The append_messages function dynamically adjusts input formats based on User Queries, thus taking in plain text, images, and audio transcripts
- Chainlit library simplifies the development of chatbot interfaces, handling underlying HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, making UI creation easy
The media shown in this article are not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. GPT-4o is a groundbreaking AI model developed by OpenAI that can understand and generate text, audio, and images.
A. GPT-4o sets itself apart by integrating text, audio, and image understanding and generation in a single model.
A. GPT-4o can translate languages, create different forms of creative content, analyze or generate speech with different tones, and describe real-world scenes or create images based on descriptions.
A. The multimodal chatbot works with GPT-4o’s capabilities to understand and respond to user queries, including text, images, or audio inputs.
A. The necessary libraries for building the chatbot include OpenAI for accessing GPT-4o, Chainlit for creating the UI, and base64 for encoding images.
A. Chainlit simplifies the development of chatbot interfaces by managing underlying HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, making UI creation quick and efficient.





