What if collaborating with AI could feel as natural as working with a teammate? That’s what OpenAI’s new feature, Canvas, is for! Launched on the 4th day of the 12 Days of OpenAI series, Canvas is now available for all ChatGPT users. Whether you’re crafting a compelling story, debugging complex code, or exploring new ideas, Canvas brings a side-by-side workspace that adapts seamlessly to your needs. Let’s dive into what makes this tool special.
Canvas—a new way to work with ChatGPT to draft, edit, and get feedback on writing & code—is now available to all users in our 4o model.
— OpenAI (@OpenAI) December 10, 2024
It’s fully rolled out on web and the ChatGPT desktop app for Windows. pic.twitter.com/1MVvmXphZM
Table of contents
How to Access Canvas?
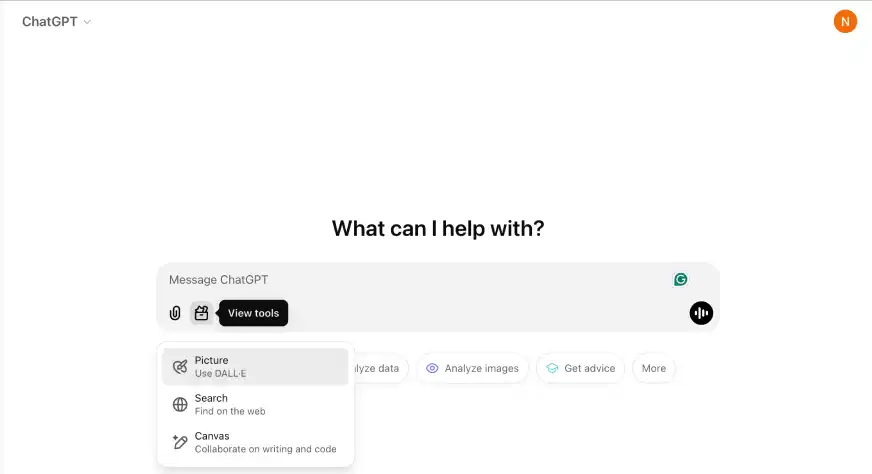
- Log into your ChatGPT account via the web interface.
- In the chat composer, click on the tools icon to view all available tools.
- Choose Canvas from the list. This will open a new workspace where you can start creating content or coding.
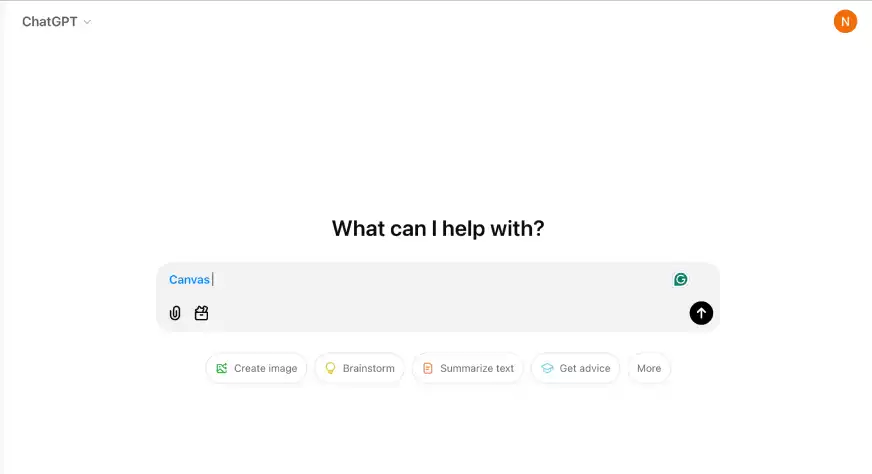
Key Features of Canvas
- Wide Accessibility: Canvas is now integrated directly into ChatGPT’s main interface and is accessible to all users, regardless of their subscription plan.
- Python Code Execution: Users can now run Python code directly within Canvas, complete with text or graphical outputs, ensuring a seamless coding experience.
- Integration with Custom GPTs: Canvas is now fully compatible with custom GPTs, empowering developers to utilize this tool’s potential in their tailored AI models.
I will be exploring these features in the next section.
Let’s use ChatGPT Canvas
To help you get started, here are some practical hands-on examples of how you can use Canvas:
Wide Accessibility
Canvas introduces a split-view format that allows users to work simultaneously with the chat and the document. This eliminates the clutter of edits and revisions in the chat feed, enabling clearer and more structured interaction.
Example
I evaluated my article content with ChatGPT and used the wide accessibility option. After pasting my content in the message window, I expanded the screen:
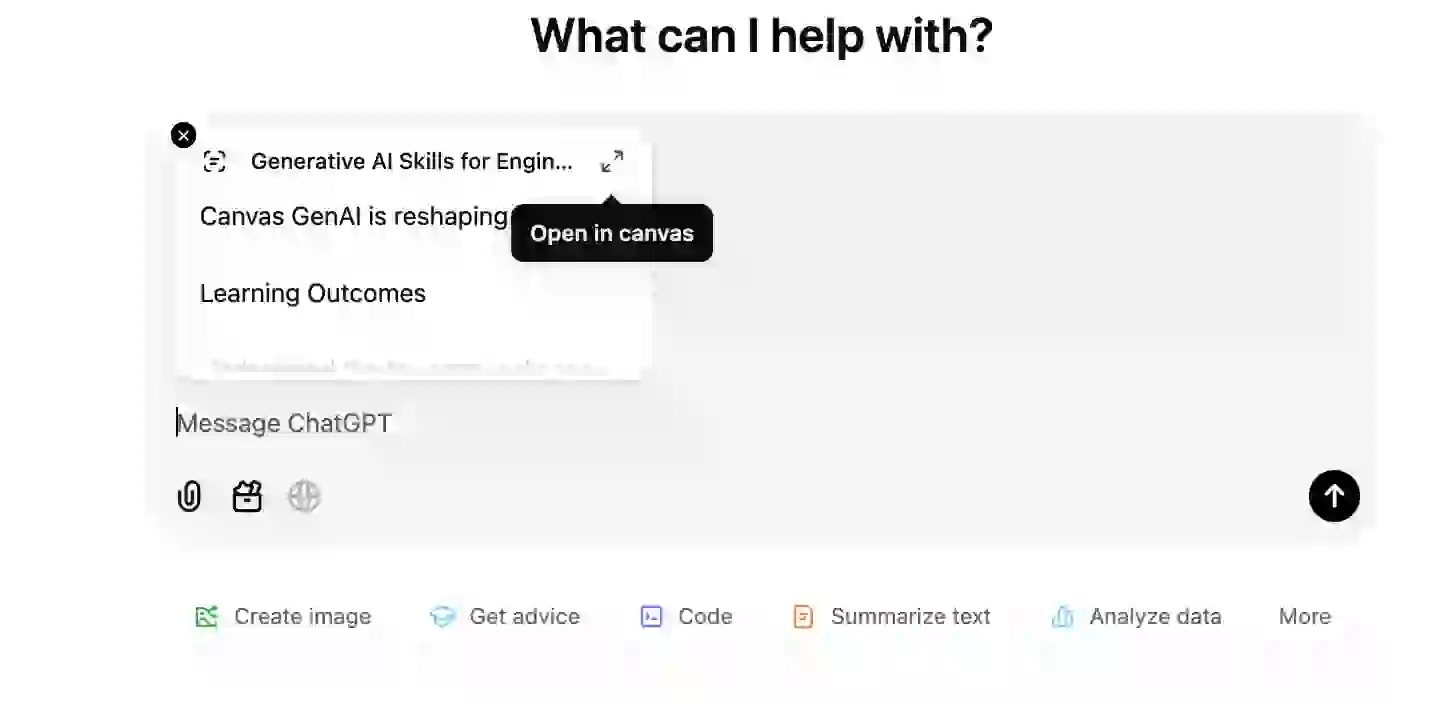
This is how the expanded screen looks:
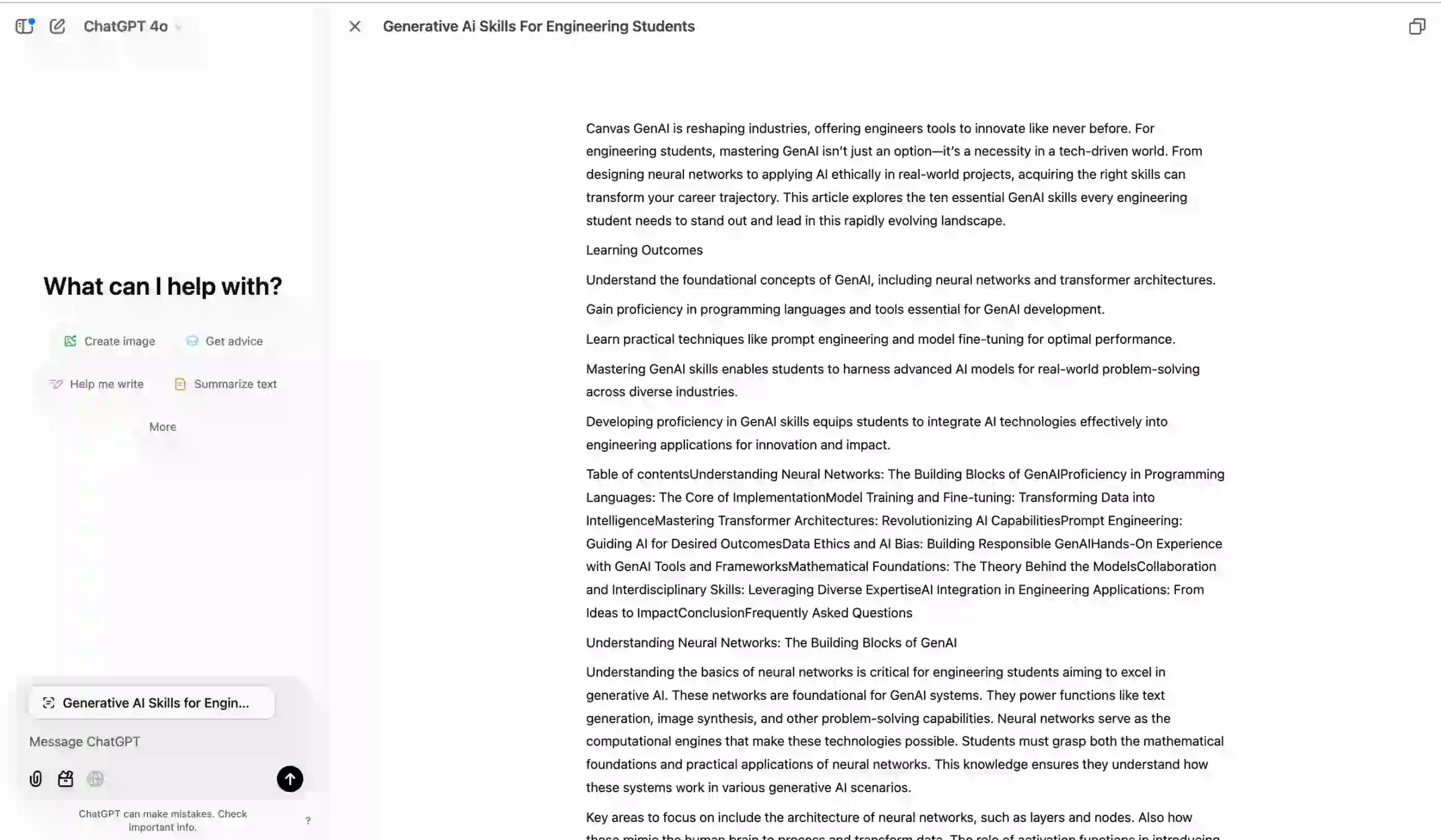
Editing Tool
You can edit documents directly within Canvas, apply formatting, and even receive suggestions from ChatGPT in real-time. It’s quite simple to use: copy the article content, paste it in the message box, open it in Canvas mode, and select the editing mode. Add prompts based on the feedback you need, and Canvas will suggest edits.
Example
I used a blog on “Generative AI Skills for Engineering Students” and gave Canvas the following prompt:
Think like an editor and add suggestions on how to divide this content into different headings. As this article is going on my blog, suggest what keywords can be added to improve its searchablity.
Output:

ChatGPT provided valuable suggestions directly in the Canvas window. By clicking the Apply button, the changes were incorporated seamlessly. This feature makes editing and maintaining formatting much easier, even when transferring content to Google Docs.
Enhanced Feedback Mechanism
One standout feature is ChatGPT’s ability to provide contextual comments on user-provided text. This is particularly valuable for writers seeking detailed feedback or students wanting to polish academic essays.
Example
For the same article, I wanted to check if it covered everything a student needs to learn about Generative AI. I asked Canvas:
Think like a student planning to make a career in GenAI. Is this article really benfificial. Add feedback accordingly.
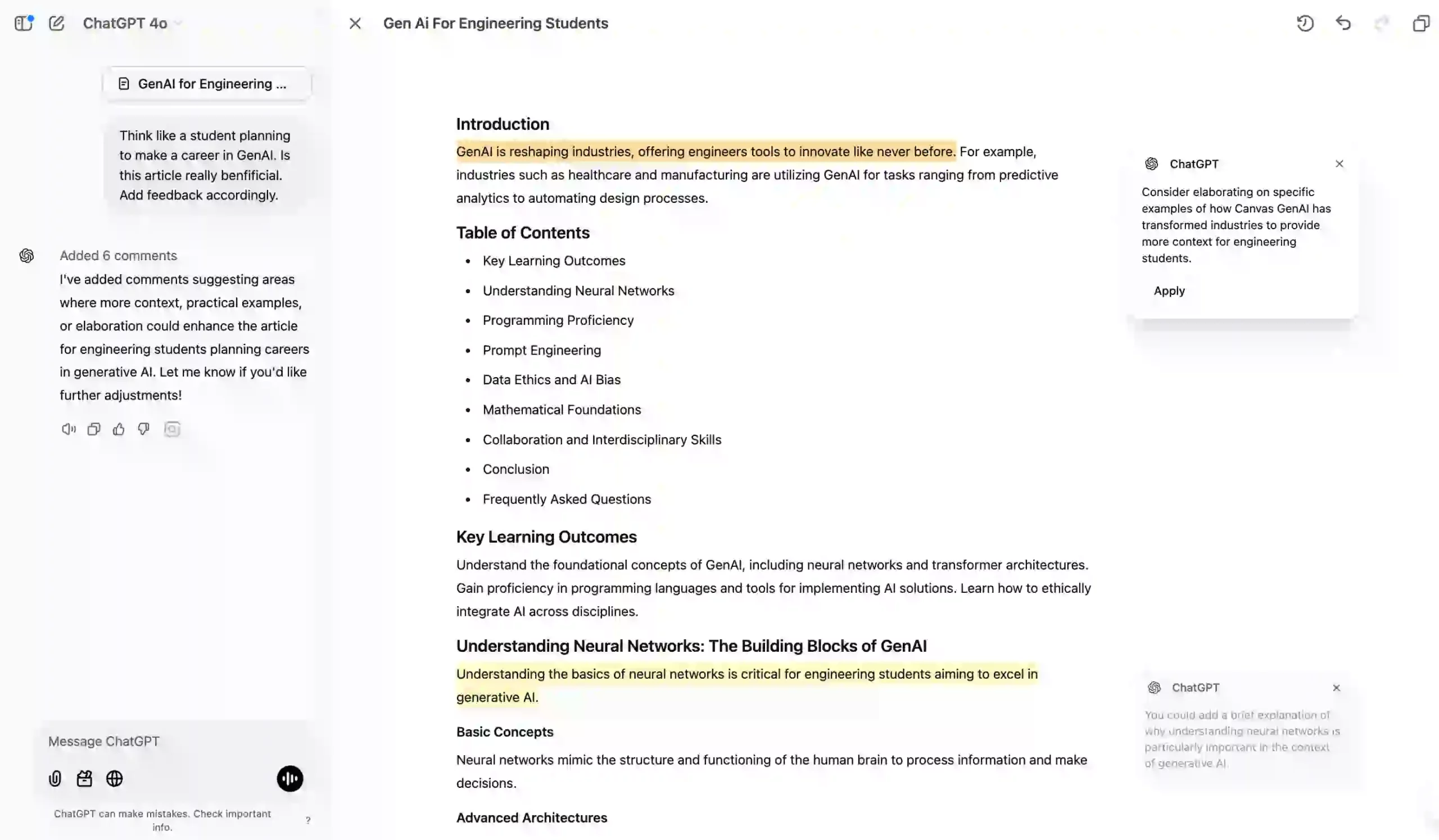
Canvas provided valuable suggestions that could help students enhance their learning experience.
Coding with Canvas
For programmers, Canvas offers real-time debugging and code execution within the editor. This includes syntax highlighting, error detection, and visual outputs for data science tasks.
Example
I tested a code snippet with bugs and gave it to Canvas with this prompt:
Why is my code not working?
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Create data
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
# Create a figure with publication-quality aesthetics
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4), dpi=300) # Set figure size and resolution
plt.plot(x, y, label="Sine Wave", color='b', linewidth=2)
# Adding labels and title
plt.xlabel("X-axis label", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Y-axis label", fontsize=14)
plt.lable("Sine Wave Example", fontsize=16)
# Adding grid and legend
plt.grid(True, which='both', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
# Saving the figure as a high-resolution PNG
plt.savefig("sine_wave_figure.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()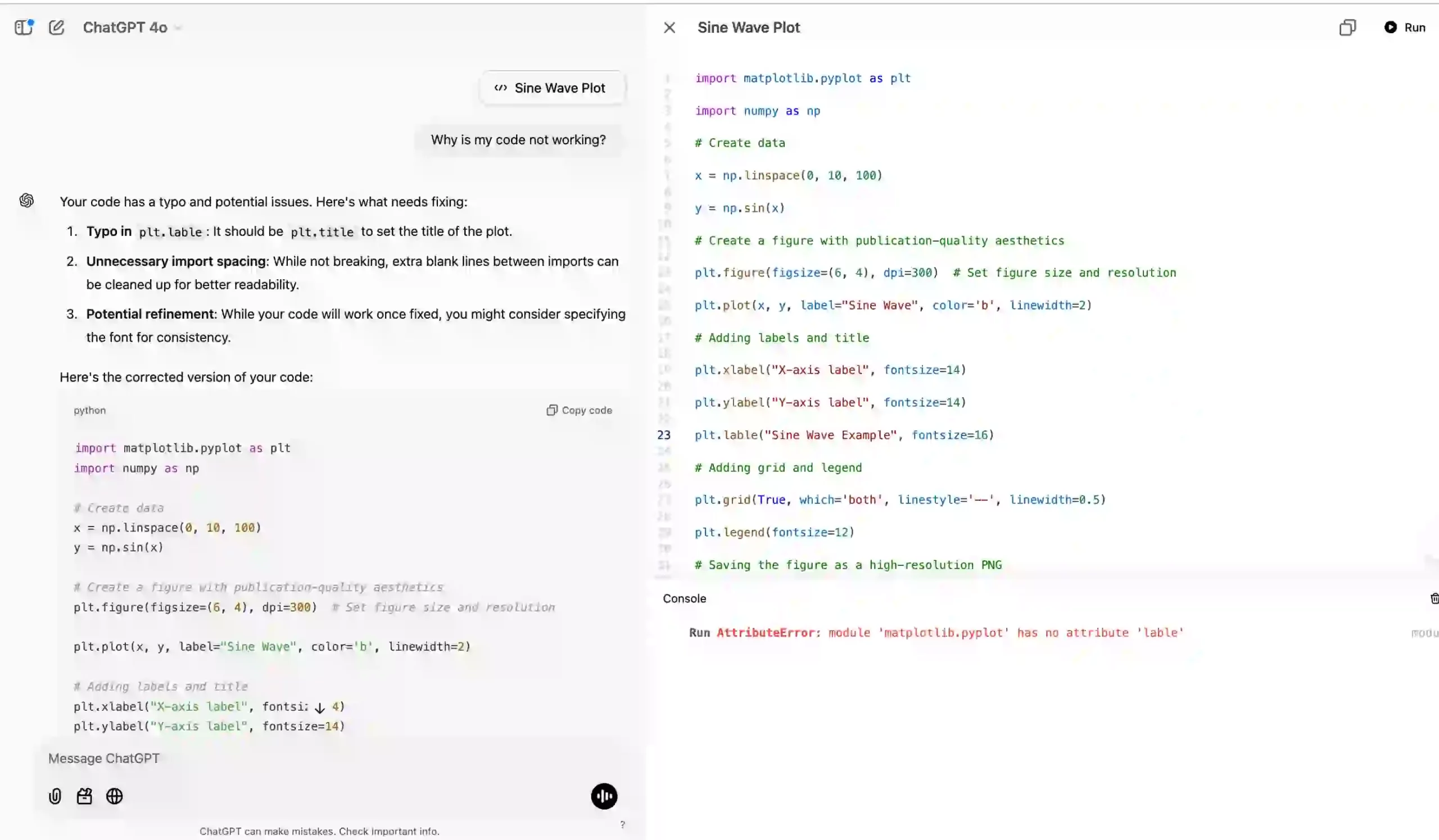
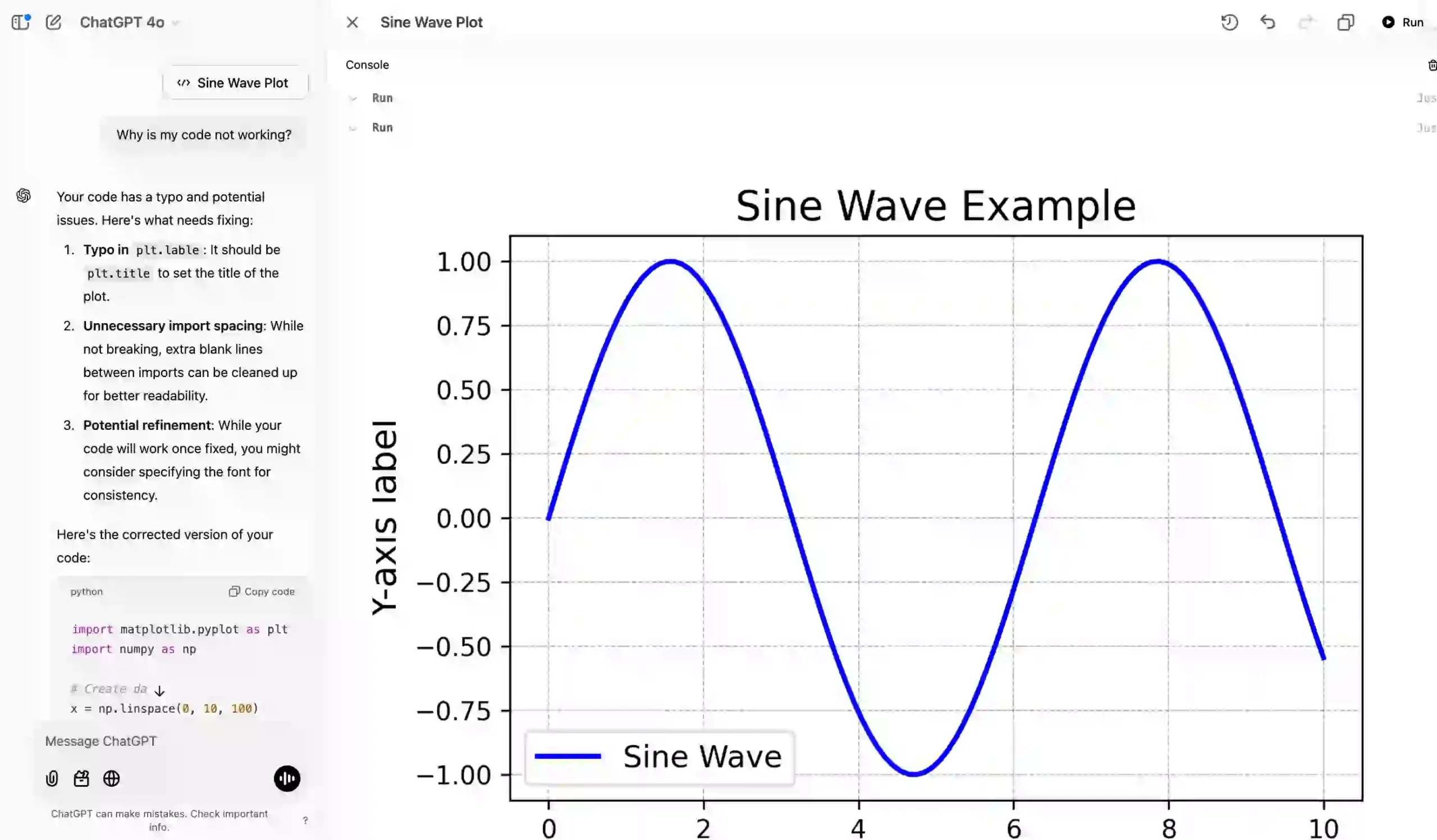
Canvas identified the bugs and allowed me to fix and run the code on the right-side window. This feature is going to be really helpful for the coders.
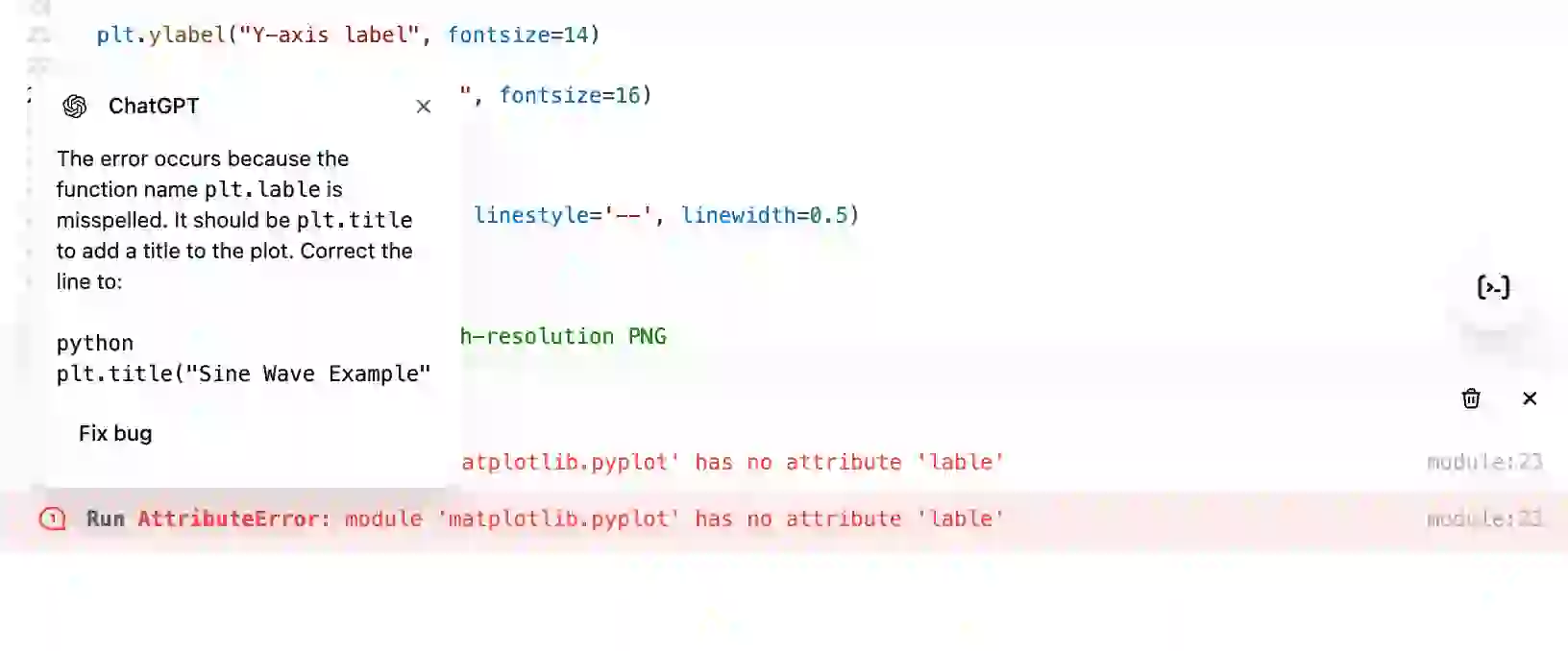
The fix bug option on Canvas window rewrites the entire code line-by-line to ensure there are no errors.
Canvas Edited Code:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Create data
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
# Create a figure with publication-quality aesthetics
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4), dpi=300) # Set figure size and resolution
plt.plot(x, y, label="Sine Wave", color='b', linewidth=2)
# Adding labels and title
plt.xlabel("X-axis label", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Y-axis label", fontsize=14)
plt.title("Sine Wave Example", fontsize=16)
# Adding grid and legend
plt.grid(True, which='both', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
# Saving the figure as a high-resolution PNG
plt.savefig("sine_wave_figure.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()Output:
Custom GPTs with Canvas
The integration of Canvas with custom GPTs opens up a new scope of possibilities. As part of this initiative, Canvas will become a default tool for new custom GPTs, while existing GPTs can enable it through their configuration settings.
Previous OpenAI Launches
What’s Next?
Canvas is a fun and interactive way to work with AI. It makes working on projects feel natural and productive, whether you’re a writer polishing an article, a coder debugging scripts, or an educator designing lessons. OpenAI has made it simple and accessible, encouraging users to dive in and see what they can achieve.
As OpenAI continues to improve Canvas, it’s clear this is just the beginning. The tool promises to grow into an even more essential part of working with AI, making our interactions smoother and more effective.
So why wait?
Explore Canvas, share your experiences with me in the comment section below!





