In the rapidly evolving landscape of software development, the intersection of artificial intelligence, data validation, and database management has opened up unprecedented possibilities. This blog post explores an innovative approach to SQL-code generation and SQL code explanation using the Latest PydanticAI Framework and Google’s Gemini-1.5 model, demonstrating how cutting-edge AI technologies can streamline and enhance database query development.
For developers, data scientists, and data analysts, this exploration offers a glimpse into the future of intelligent code generation from natural language processing, where complex database queries can be created with ease and accuracy.
Learning Objectives
- Understand the fundamentals of Pydantic and PydanticAI.
- Learn how to implement an AI-powered SQL code generation system.
- Explore the capabilities of Gemini-1.5-Flash in natural language for SQL translation.
- Gain insight into building intelligent AI agents for database interactions.
This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Table of contents
What is PydanticAI?
PydanticAI is a powerful Python library that revolutionizes data validation and type checking. It provides a declarative approach to defining data models, making it easy to create and validate complex data structures.
Important features of Pydantic include:
Customization
- Validates a wide range of data types, including primitive types and complex nested structures.
- Supports nearly any Python object for validation and serialization
Flexibility
Allows control over data validation strictness:
- Coerce data to the expected type
- Enforce strict type-checking when needed
Serialization
- Support seamless conversion between Pydantic object, dictionary, and JSON.
- Enables self-documenting APIs and compatibility with tools that use JSON schema.
Performance
- Core validation logic is written in Rust for exceptional speed and efficiency.
- Ideal for high-throughput applications like scalable REST APIs.
Ecosystem
- Widely used in popular Python libraries such as FastAPI, Langchain, LlamaIndex, and many more.
- Modern Agentic LLM can not be implemented without Pydantic.
Examples of PydanticAI in Action
PydanticAI simplifies data validation and type-checking in Python, making it a powerful tool for creating robust data models. Let’s explore some practical examples that showcase its capabilities.
Basic Data Validation
from pydantic import BaseModel
class User(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
# Valid data
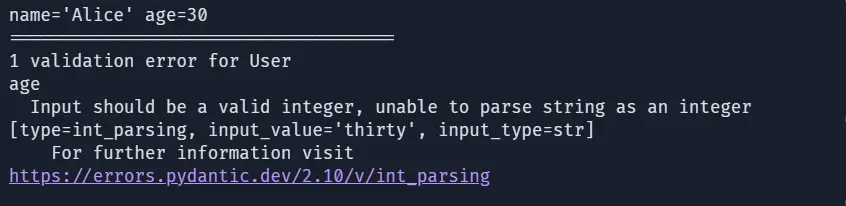
user = User(name="Alice", age=30)
print(user)
print("=====================================")
# Invalid data (age is a string)
try:
user = User(name="Alice", age="thirty")
except Exception as e:
print(e)The above code defines a User model using Pydantic’s BaseModel, enforcing name as a string and age as an integer. It validates correct data but raises a validation error when invalid data(a string for age) is provided.
Output:
Auto Type Coercion
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Product(BaseModel):
price: float
quantity: int
# Data with mismatched types
product = Product(price="19.99", quantity="5")
print(product)
print(type(product.price))
print(type(product.quantity))Here, the Product model with price as float and quantity as an integer. Pydantic automatically coerces string inputs (“19.99” and “5”) into the correct types (float and int), demonstrating its type conversion feature.
Output:

Nested Model
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Address(BaseModel):
street: str
city: str
class User(BaseModel):
name: str
address: Address
# Valid data
user = User(name="Bob", address={"street": "123 Main St", "city": "Wonderland"})
print(user)
# Access nested attributes
print(user.address.city)Here, We define a nested User model containing an Address model. Pydantic allows nested validation and auto-converts dictionaries into models. Valid data initializes a User object, and you can access nested attributes like ‘user.address.city’ directly.
Output:

Validation with Custom Rule
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field, field_validator
class User(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int = Field(..., gt=0, description="Age must be greater than zero")
@field_validator("name")
def name_must_be_non_empty(cls, value):
if not value.strip():
raise ValueError("Name cannot be empty")
return value
# Valid data
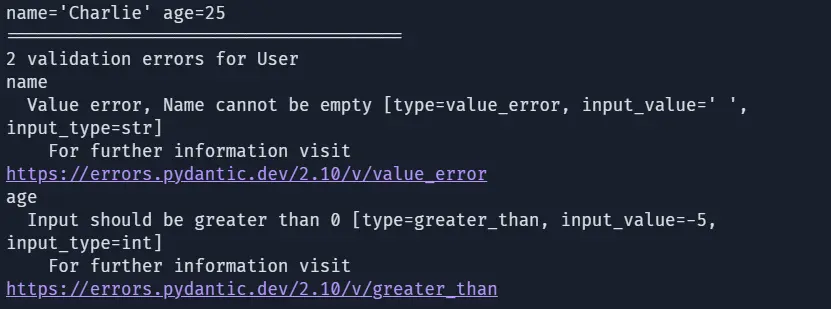
user = User(name="Charlie", age=25)
print(user)
# invalid data
try:
user = User(name=" ", age=-5)
except Exception as e:
print(e)Here, We define a User model with a validation rule, age must be greater than 0, and the name cannot be empty (validated via the name_must_be_non_empty method). Valid data creates a User instance, while invalid data (empty name or negative age) raises detailed validation errors, demonstrating Pydantic’s validation capabilities.
Output:
These are some of the core examples of Pydantic I hope they help you to understand the basic principle of Data Validation.
What is an AI Agent?
AI agents are intelligent systems designed to autonomously perform tasks, make decisions, and interact with their environment to achieve specific objectives. These agents are not new but recent rapid development in generative AI and combining it with agents makes Agentic software development on new era. Now, agents can process inputs, execute actions, and adapt dynamically. Their behavior mimics human-like problem-solving, enabling them to function in various domains with minimal human intervention.
What is Agentic Workflow?
An agentic workflow refers to the structures, goal-driven sequence of tasks managed and executed by one or multiple AI agents. Unline rigid traditional workflow, agentic workflow exhibits adaptability, autonomy, and context-awareness. AI agents within these workflows can independently make decisions, delegate subtasks, and learn from feedback, leading to efficient and optimized outcomes.
Modern Usage of AI Agents and Agentic Workflows
The integration of AI agents and agentic workflows has revolutionized industries by automating complex tasks, enhancing decision-making, and driving efficiency. These intelligent systems adapt dynamically, enabling smarter solutions across diverse domains.
Business Automation
AI agents automate repetitive tasks like customer support through chatbots, email management, and sales pipeline optimization. They enhance productivity by freeing up human resources from higher-value tasks.
Software Development
AI-powered agents accelerate software lifecycles by generating, testing, and debugging code, thereby reducing development time and human error.
Healthcare
AI agents assist in medical diagnosis, patient monitoring, and treatment personalization, improving healthcare delivery and operational efficiency.
Finance
Agentic workflows in financial systems automate fraud detection, risk assessments, and investment analysis, enabling faster and more reliable decision-making.
E-Commerce
Intelligence agencies enhance personalization in shopping experiences, optimizing product recommendations and customer service.
The rise of AI agents and agentic workflows signifies a shift toward highly autonomous systems capable of managing complex processes. Their adaptability and learning capabilities make them indispensable for modern industries, driving innovation, scalability, and efficiency across domains. As AI continues to evolve, AI agents will further integrate into our daily workflows, transforming how tasks are managed and executed.
What is the PydanticAI Framework?
PydanticAI is a Python Agent framework developed by the creator of Pydantic, FastAPI to streamline the construction of production-grade applications utilizing Generative AI, It emphasizes type safety, model-agnostic design, and seamless integration with large language models (LLMs).
Key features PydanticAI includes:
- Model-Agnostic Support: PydanticAI is compatible with various models, including OpenAI, Antropic, Gemini, Groq, Mistral, and Ollama, with a straightforward interface to incorporate additional models.
- Type-safety: Leveraging Python’s type systems and Pydantic’s validations, PydanticAI ensures robust and scalable agent development.
- Dependency Injection System: It introduces a novel, ty-safe dependency injection mechanism, enhancing testing and evaluation-driven development.
- Structured Response Validation: Utilizing Pydantic’s validation capabilities, ensures accurate and reliable structure responses.
- Logfire Integration: Offers integration with Pydantic Logfire for enhanced debugging and monitoring of LLm-powered applications.
Here is a minimal example of PydanticAI:
import os
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.models.gemini import GeminiModel
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
gemini_api_key = os.getenv("<GOOGLE_API_KEY>")
model = GeminiModel(
"gemini-1.5-flash",
api_key=gemini_api_key,
)
agent = Agent(
model=model,
system_prompt="Be concise, reply with one sentence.",
)
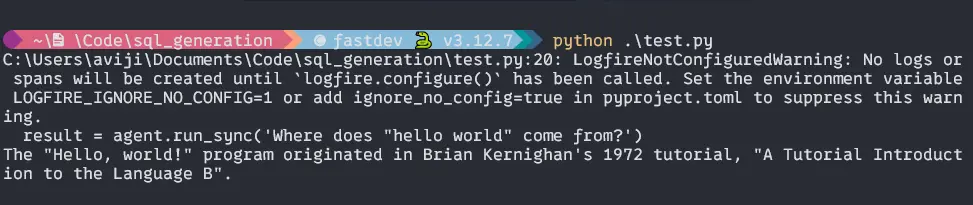
result = agent.run_sync('Where does "hello world" come from?')
print(result.data)Output:
Now it is time to do some real stuff. We will build a Postgres SQL Query Generation using the PydanticAI Agent Framework.
Getting Started with Your Project
Lay the foundation for your project with a step-by-step guide to setting up the essential tools and environment.
Setting Environment
We will create a conda environment for the project.
#create an env
$ conda create --name sql_gen python=3.12
# activate the env
$ conda activate sql_genNow, create a project folder
# create a folder
$ mkdir sql_code_gen
# change into the folder
$ cd sql_code_genInstall Postgres and Load Database
To install the Postgres, psql-command-tools, and pgadmin-4, Just go to EDB download your installer for your systems, and install all the tools in one go.
Now download the dvdrental database from here and to load it to Postgres follow these steps
Step1: Open your terminal
psql -U postgres
# It will ask for a password put it Step2: Create a database
# In the postgres=#
CREATE DATABASE dvdrental;Step3: Command for Terminal
Now, exit the psql command and then type in the terminal
pg_restore -U postgres -d dvdrental D:/sampledb/postgres/dvdrental.tarStep4: Connecing to psql
Now, Connect to the psql and check if your database is loaded or not.
psql -U postgres
# Connect with dvdrental
\c dvdrental
# let's see the tables
\dtOutput:
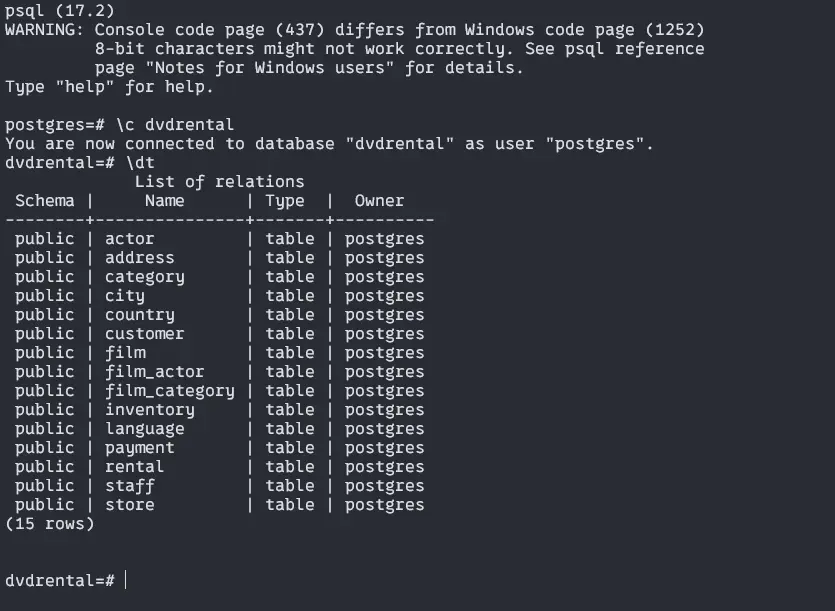
If you see the above tables then you are ok. We are all set to start our main project.
Now Install the necessary Python libraries into the sql_gen conda env.
conda activate sql_gen
# install libraries
pip install pydantic asyncpg asyncio pydantic-ai
pip install python-dotenv fastapi google-generativeai
pip install devtools annotated-types type-extensionsProject Structure
Our project has 4 files namely main, models, service, and schema.
sql_query_gen/
|
|--main.py
|--models.py
|--schema.py
|--service.py
|--.env
|--__init__.py
|--.gitignoreStep-by-Step Guide to Implementing Your Project
Dive into the detailed steps and practical techniques to bring your project from concept to reality with this comprehensive implementation guide.
Pydantic Models
We will start by creating data models in the models.py file
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Annotated
import asyncpg
from annotated_types import MinLen
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
@dataclass
class Deps:
conn: asyncpg.Connection
class Success(BaseModel):
sql_query: Annotated[str, MinLen(1)]
explanation: str = Field("", description="Explanation of the SQL query, as markdown")
class InvalidRequest(BaseModel):
error_message: strIn the above code,
- The Deps class manages database connection dependencies. @dataclass automatically generates special methods like __init__ and __repr__. Conn is typed as `asyncpg.Connection` and represents an active PostgreSQL connection. This design follows dependency injection patterns, making the code more testable and maintainable.
- The Success Class represents a successful SQL-query generation, sql_query must be a non-empty string (MinLen(1)) and use Annotated to add validation constraints. The explanation is an Optional field with a default empty string.
- The InvalidRequest class is the Error Response Model, representing failed SQL-query generation attempts.
This code established the foundation for Database connectivity management, input validation, Structured response handling, and Error handling.
Service module
Now, we will implement the PydanticAI services for SQL generation in the service module.
Import library and Configuration
import os
from typing import Union
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import asyncpg
from typing_extensions import TypeAlias
from pydantic_ai import Agent, ModelRetry, RunContext
from pydantic_ai.models.gemini import GeminiModel
from schema import DB_SCHEMA
from models import Deps, Success, InvalidRequestTo configure, create a .env file in the project root and put your Gemini API key there
# .env
GEMINI_API_KEY="asgfhkdhjy457gthjhajbsd"Then in the service.py file:
load_dotenv()
gemini_api_key = os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY")It will load the Google API key from the `.env` file.
Creating model and Agent
Response: TypeAlias = Union[Success, InvalidRequest]
model = GeminiModel(
"gemini-1.5-flash",
api_key=gemini_api_key,
)
agent = Agent(
model,
result_type=Response, # type: ignore
deps_type=Deps,
)- First Define a Response type that can be either Success or InvalidRequest
- Initializes the Gemini 1.5 Flash model with API key
- Create a PydanticAI agent with the specified response and dependency types
System Prompt Definition
Now we will define the system prompt for our SQL query generation.
@agent.system_prompt
async def system_prompt() -> str:
return f"""\
Given the following PostgreSQL table of records, your job is to
write a SQL query that suits the user's request.
Database schema:
{DB_SCHEMA}
Example
request: Find all films with a rental rate greater than $4.00 and a rating of 'PG'
response: SELECT title, rental_rate
FROM film
WHERE rental_rate > 4.00 AND rating = 'PG';
Example
request: Find the film(s) with the longest length
response: SELECT title, length
FROM film
WHERE length = (SELECT MAX(length) FROM film);
Example
request: Find the average rental duration for films in each category
response: SELECT c.name, AVG(f.rental_duration) AS average_rental_duration
FROM category c
JOIN film_category fc ON c.category_id = fc.category_id
JOIN film f ON fc.film_id = f.film_id
GROUP BY c.name
ORDER BY average_rental_duration DESC;
"""Here, we define the base context for the AI model and provide example queries to guide the model’s responses. We also include the database schema information in the model so that the model can analyze the schema and generate a better response.
Response Validation
To make the response from the AI model error-free and up to the projects requirements, we just validate the responses.
@agent.result_validator
async def validate_result(ctx: RunContext[Deps], result: Response) -> Response:
if isinstance(result, InvalidRequest):
return result
# gemini often adds extraneos backlashes to SQL
result.sql_query = result.sql_query.replace("\\", " ")
if not result.sql_query.upper().startswith("SELECT"):
raise ModelRetry("Please create a SELECT query")
try:
await ctx.deps.conn.execute(f"EXPLAIN {result.sql_query}")
except asyncpg.exceptions.PostgresError as e:
raise ModelRetry(f"Invalid SQL: {e}") from e
else:
return resultHere, we will validate and process the generated SQL queries
Key validation steps:
- Returns immediately if the result is an InvalidRequeste, clean up the extra backslashes
- Ensure the query is a SELECT statement
- Validates SQL syntax using PostgreSQL EXPLAIN
- Raise ModelRetry for invalid queries
Database Schema
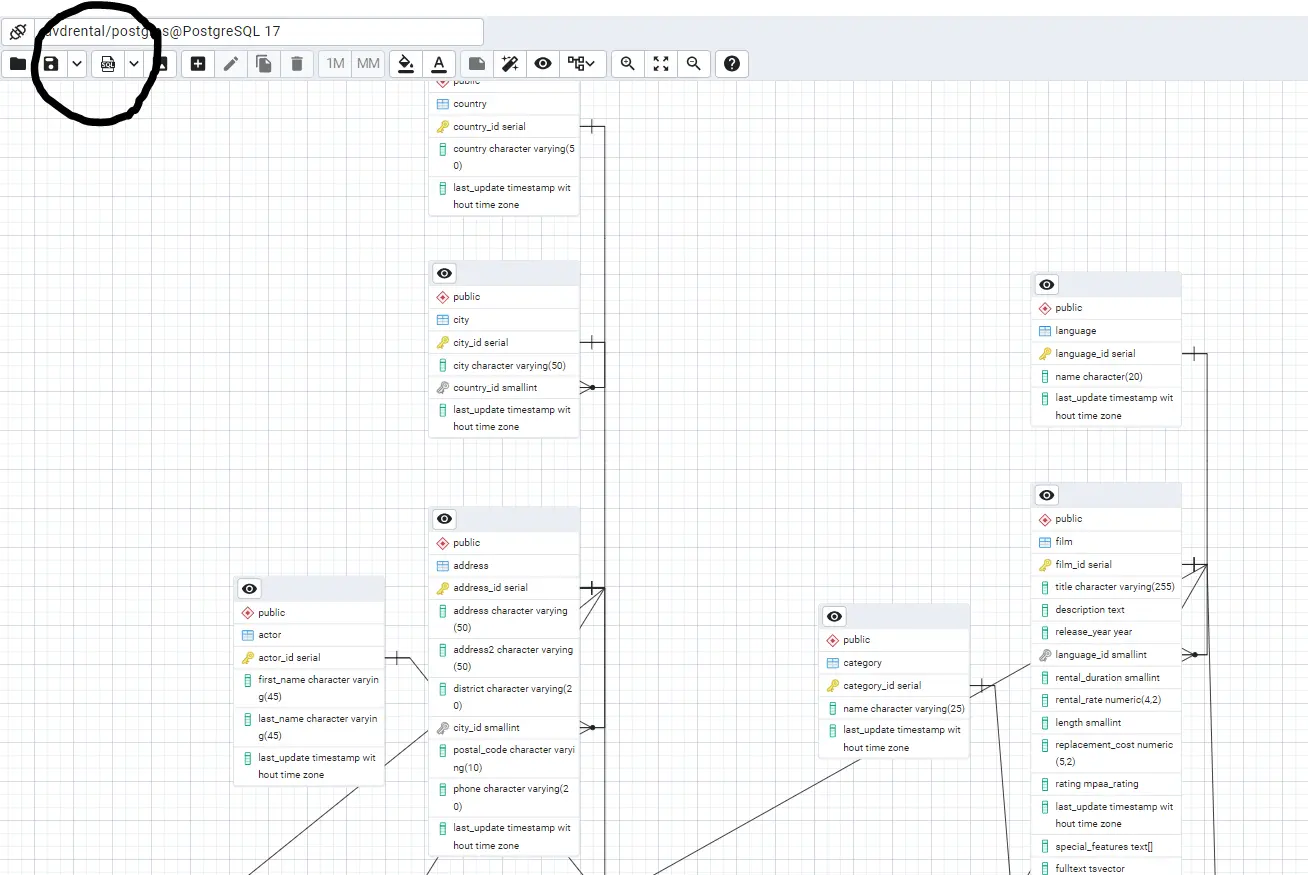
To get your database schema, Open the pgadmin4 you have installed during Postgres setup, Go to the `dvdrental` database, right-click on it, and click `ERD for Database`.
You will get the below ERD diagram, now generate SQL from the ERD (see the round black marking on the image).
Copy the Schema to the Schema.py module:
# schema.py
DB_SCHEMA = """
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.actor
(
actor_id serial NOT NULL,
first_name character varying(45) COLLATE pg_catalog."default" NOT NULL,
last_name character varying(45) COLLATE pg_catalog."default" NOT NULL,
last_update timestamp without time zone NOT NULL DEFAULT now(),
CONSTRAINT actor_pkey PRIMARY KEY (actor_id)
);
.
.
.
.
.
.
"""The above code block is Heavily truncated, to get full code please visit the Project Repo.
Now, that all necessary modules have been completed, time to implement the main method and test.
Implementing Main
We will do the Main function definition and prompt handling.
import asyncio
import os
import sys
from typing import Union
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import asyncpg
from devtools import debug
from typing_extensions import TypeAlias
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.models.gemini import GeminiModel
from models import Deps, Success, InvalidRequest
load_dotenv()
gemini_api_key = os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY")
Response: TypeAlias = Union[Success, InvalidRequest]
model = GeminiModel(
"gemini-1.5-flash",
api_key=gemini_api_key,
)
agent = Agent(
model,
result_type=Response, # type: ignore
deps_type=Deps,
)
async def main():
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
prompt = "Please create a SELECT query"
else:
prompt = sys.argv[1]
# connection to database
conn = await asyncpg.connect(
user="postgres",
password="avizyt",
host="localhost",
port=5432,
database="dvdrental",
)
try:
deps = Deps(conn)
result = await agent.run(prompt, deps=deps)
result = debug(result.data)
print("=========Your Query=========")
print(debug(result.sql_query))
print("=========Explanation=========")
print(debug(result.explanation))
finally:
await conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())Here, first, define an asynchronous main function, and check the command-line argument for client query. If no args are provided, use the default prompt.
Then we set the Postgres connection parameters to connect with dvdrental database service.
In the try block, create a Deps instance with a database connection, run the AI agents with the prompt, Processes the results using the debug function (pip install devtools). Then prints the formatted output including the Generated SQL query and explanation of the query. after that, we finally closed the database connection.
Now run the main module like below:
# in the terminal
python main.py " Get the total number of rentals for each customer"Output:
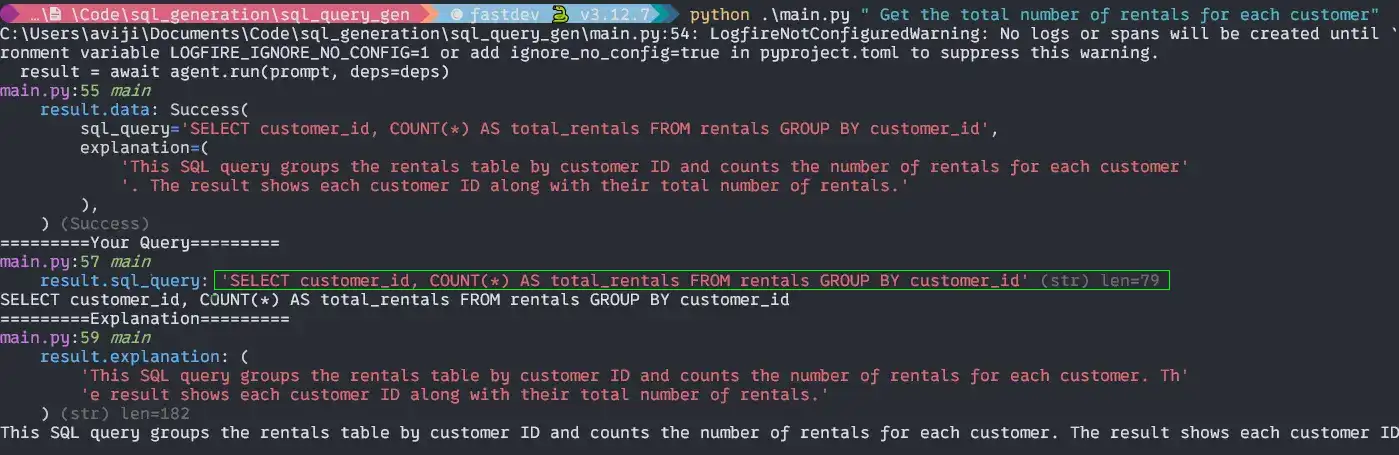
After testing the SQL query in the pgadmin4:
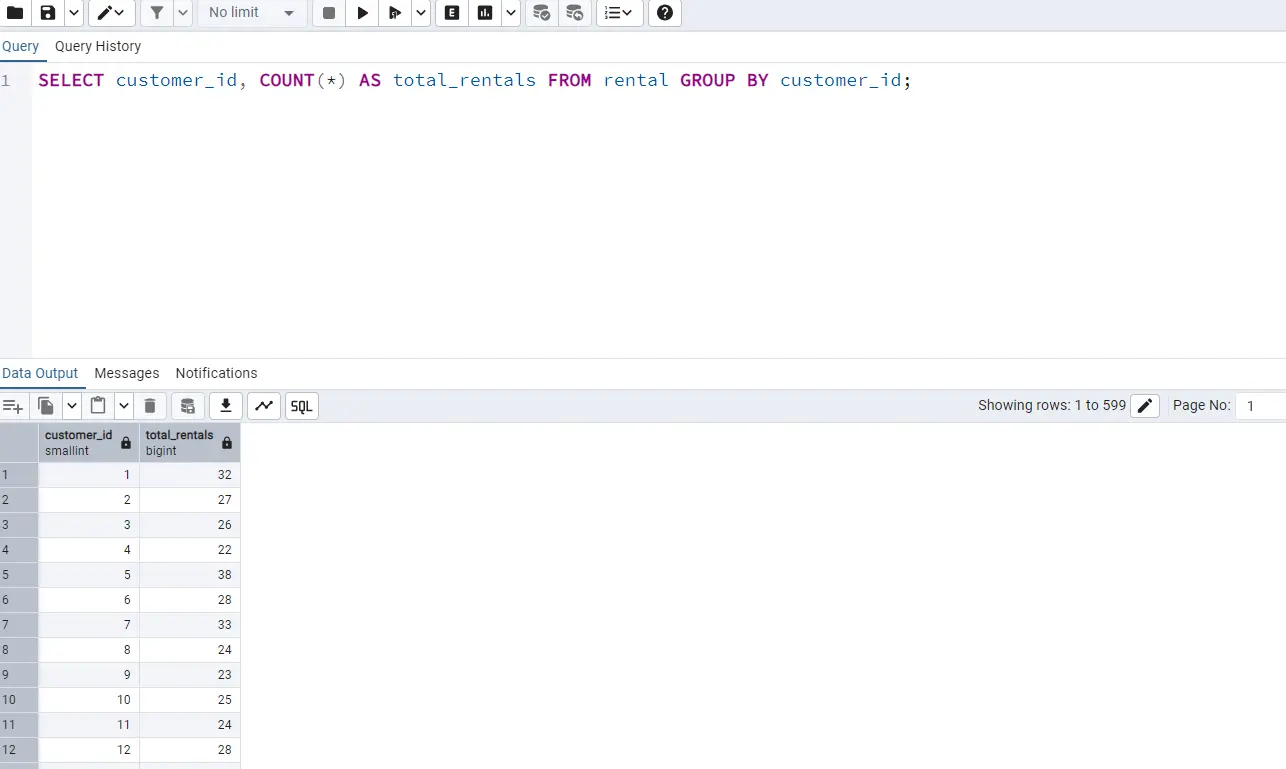
Wow! It is working like we want. Test more queries like this and enjoy the learning.
Conclusion
This project represents a significant step forward in making database interactions more intuitive and accessible. By combining the power of AI with robust software engineering principles, we’ve created a tool that not only generates SQL queries but does so in a way that is secure, educational, and practical for real-world use.
The success of this implementation demonstrates the potential for AI to enhance rather than replace traditional database operations, providing a valuable tool for both learning and productivity.
Project Repo – All the code used in this project is available here.
Key Takeaways
- PydanticAI enables intelligent, context-aware code generation.
- Gemini-1.5-Flash provides advanced natural language understanding for technical tasks.
- AI agents can transform how we interact with databases and generate code.
- Robust validation is crucial in AI-generated code systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. PydanticAI offers type-safe, validated code generation with built-in error checking and contextual understanding.
A. Gemini model provides advanced natural language processing, translating complex human queries into precise SQL statements.
A. Absolutely! The architecture can be adapted for code generation, data transformation, and intelligent automation across various domains.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.





