Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have become an integral part of AI models, enabling them to access vast amounts of relevant data and deliver more informed and context-aware responses. However, their capabilities have largely been confined to digital text, overlooking valuable information in multimodal formats like scanned documents, images, and handwritten notes. Mistral OCR breaks this limitation by seamlessly integrating complex documents into intelligent retrieval systems, expanding the reach of usable knowledge. This advancement enhances AI interactions, making information more accessible, comprehensive, and applicable across diverse real-world scenarios. In this article, we will explore the features and applications of Mistral OCR and understand its impact on RAG systems.
Table of Contents
Understanding RAG and Its Limitations
RAG models operate by retrieving relevant documents and using them to generate responses. While they excel at handling large text repositories, they struggle with non-text data. This is due to:
- Inability to interpret images, equations, and tables: Many critical documents contain structured data in the form of tables and equations that traditional RAG models cannot comprehend.
- Loss of context in OCR-extracted text: Even when text is extracted from scanned documents, its meaning often gets distorted if the structure and layout are ignored.
- Challenges in processing multimodal content: Combining visual and textual elements in a meaningful way is beyond the capacity of most conventional RAG systems.
- Limited applicability across industries: Sectors such as research, law, and finance rely on complex documents that require more than just text-based understanding.
Without an effective way to extract and structure information from diverse formats, RAG remains incomplete. That’s where Mistral OCR changes the game.
What is Mistral OCR and What Makes It Different?
Mistral OCR is an advanced Optical Character Recognition (OCR) API built to do more than just extract text. Unlike traditional OCR tools, it recognizes the structure and context of a document, ensuring that the information it retrieves is both accurate and meaningful. Its blend of precision and performance makes it the perfect choice for handling large volumes of documents with ease. Here’s what makes it stand out:
- Deep Document Understanding: It recognizes and extracts not just text but also tables, charts, equations, and interleaved images, maintaining document integrity.
- High-Speed Processing: With the capability to process up to 2000 pages per minute on a single node, Mistral OCR is built for high-throughput environments.
- Doc-as-Prompt Functionality: This feature allows users to treat entire documents as prompts, enabling precise and structured information extraction.
- Structured Output Formats: The extracted content can be formatted as JSON, making it easier to integrate into workflows and AI applications.
- Secure and Flexible Deployment: For organizations with strict privacy policies, Mistral OCR offers self-hosting options, ensuring data security and compliance.
These capabilities make Mistral OCR a powerful tool for transforming unstructured documents into AI-ready knowledge sources.
How Mistral OCR Enhances RAG
Integrating Mistral OCR with RAG unlocks a new dimension of knowledge retrieval. Here’s how it improves the system:
- Expanding RAG to Multimodal Data: By processing scanned documents, images, and PDFs, Mistral OCR allows RAG models to work beyond just text-based information.
- Preserving Document Structure for Better Context: Mistral OCR maintains the relationships between text, images, and structured elements, ensuring the meaning of the extracted text is not lost.
- Accelerating Knowledge Retrieval: The ability to process vast document repositories at high speeds ensures that AI-driven search and analysis remain efficient and up to date.
- Empowering Industries with AI-Ready Data: Whether it’s legal filings, scientific research, or customer support documentation, Mistral OCR helps make knowledge-rich documents more accessible to AI systems.
- Enabling Seamless Integration with AI Pipelines: Structured outputs allow RAG systems to seamlessly integrate extracted information into various AI applications.
Hands-on with Mistral OCR: A Step-by-Step Guide
Mistral OCR is a powerful tool for extracting structured information from images and scanned documents. In this section, we will walk through a Python script that leverages Mistral OCR to process an image and return structured data.
Pre-requisite: Accessing the API
Before we start with the steps to test the mistral ocr, let’s first see how we can generate the required API keys.
1. Mistral API Key
To access the Mistral API key, visit Mistral API and sign up for a mistral account. If you already have an account, simply log in.
After logging in, click on “Create new key” to generate a new key.
2. OpenAI API Key
To access the OpenAI API key, visit OpenAI and login to your account. Sign up for one if you don’t already have an OpenAI account.
After logging in, click on “Create new secret key” to generate a new key.
3. Gemini API Key
To access the Gemini API key, visit the Google AI Studio website and log in to your Google account. Sign up if you don’t already have an account.
After logging in, navigate to the API keys section and click on “Create API Key” to create a new key.
Now that we’re all set, let’s begin the implementation.
Step 1: Importing Dependencies
The script imports essential libraries, including:
- Enum and BaseModel from “pydantic”
- Path for handling file paths.
- base64 for encoding image files.
- “pycountry” to map language codes to their full names.
- Mistral SDK to interact with the OCR API.
from enum import Enum
from pathlib import Path
from pydantic import BaseModel
import base64
import pycountry
from mistralai import MistralStep 2: Setting Up the Mistral OCR Client
The script initializes the Mistral OCR client with an API key:
api_key = "API_KEY"
client = Mistral(api_key=api_key)
languages = {lang.alpha_2: lang.name for lang in pycountry.languages if hasattr(lang, 'alpha_2')}Ensure you replace “API_KEY” with your actual API key.
Step 3: Defining Language Handling
To ensure the extracted text is tagged with proper language information, the script uses “pycountry” to create a dictionary mapping language codes (e.g., en for English) to full names.
languages = {lang.alpha_2: lang.name for lang in pycountry.languages if hasattr(lang, 'alpha_2')}
class LanguageMeta(Enum.__class__):
def __new__(metacls, cls, bases, classdict):
for code, name in languages.items():
classdict[name.upper().replace(' ', '_')] = name
return super().__new__(metacls, cls, bases, classdict)
class Language(Enum, metaclass=LanguageMeta):
passAn Enum class (Language) dynamically generates language labels for structured output.
Step 4: Defining the Structured Output Model
A StructuredOCR class is created using “pydantic”. This defines how the extracted OCR data will be formatted, including:
- file_name: The processed image filename.
- topics: Detected topics from the image.
- languages: Identified languages.
- ocr_contents: Extracted text in a structured format.
class StructuredOCR(BaseModel):
file_name: str
topics: list[str]
languages: list[Language]
ocr_contents: dict
print(StructuredOCR.schema_json())Step 5: Processing an Image with OCR
The structured_ocr() function handles the core OCR process:
- Image Encoding: The image is read and encoded as a base64 string to send to the API.
- OCR Processing: The image is passed to Mistral OCR, and the extracted text is retrieved in Markdown format.
- Structuring the OCR Output: A follow-up request converts the extracted text into a structured JSON format.
def structured_ocr(image_path: str) -> StructuredOCR:
image_file = Path(image_path)
assert image_file.is_file(), "The provided image path does not exist."
# Read and encode the image file
encoded_image = base64.b64encode(image_file.read_bytes()).decode()
base64_data_url = f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{encoded_image}"
# Process the image using OCR
image_response = client.ocr.process(document=ImageURLChunk(image_url=base64_data_url), model="mistral-ocr-latest")
image_ocr_markdown = image_response.pages[0].markdown
# Parse the OCR result into a structured JSON response
chat_response = client.chat.parse(
model="pixtral-12b-latest",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
ImageURLChunk(image_url=base64_data_url),
TextChunk(text=(
"This is the image's OCR in markdown:\n"
f"<BEGIN_IMAGE_OCR>\n{image_ocr_markdown}\n<END_IMAGE_OCR>.\n"
"Convert this into a structured JSON response with the OCR contents in a sensible dictionnary."
))
],
},
],
response_format=StructuredOCR,
temperature=0
)
return chat_response.choices[0].message.parsed
image_path = "receipt.png"
structured_response = structured_ocr(image_path)
response_dict = json.loads(structured_response.json())
json_string = json.dumps(response_dict, indent=4)
print(json_string)Input image

Step 6: Running the OCR and Viewing Results
The script calls the structured_ocr() function with an image (receipt.png), retrieves the structured OCR output, and formats it as a JSON string.
image_path = "receipt.png"
structured_response = structured_ocr(image_path)
response_dict = json.loads(structured_response.json())
json_string = json.dumps(response_dict, indent=4)
print(json_string)This prints the extracted information in a readable format, making it easy to integrate into applications.
Visit here to view the complete version of the code.
Mistral Vs Gemini 2.0 Flash Vs GPT 4o
Now that we’ve seen how Mistral OCR works, let’s compare its performance to that of Gemini 2.0 Flash and GPT-4o. To ensure a consistent and fair comparison, we’ll be using the same image that was tested on Mistral OCR in the hands-on section. The goal is to evaluate how Mistral, Gemini 2.0, and GPT-4o performs on the exact same input. Below is the output generated by each model.
Output using mistral-ocr:
Here’s the response we got during the hands-on.

Output using gemini-2.0-flash:
from google import genai
from PIL import Image
# Initialize the GenAI client with your API key
client = genai.Client(api_key="AIzaSyCxpgd6KbNOwqNhMmDxskSY3alcY2NUiM0")
# Open the image file
image_path = "/content/download.png"
image = Image.open(image_path)
# Define the prompt for the model
prompt = "Please extract and provide the text content from the image."
# Generate content using the Gemini model
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
contents=[image, prompt]
)
# Print the extracted text
print(response.text)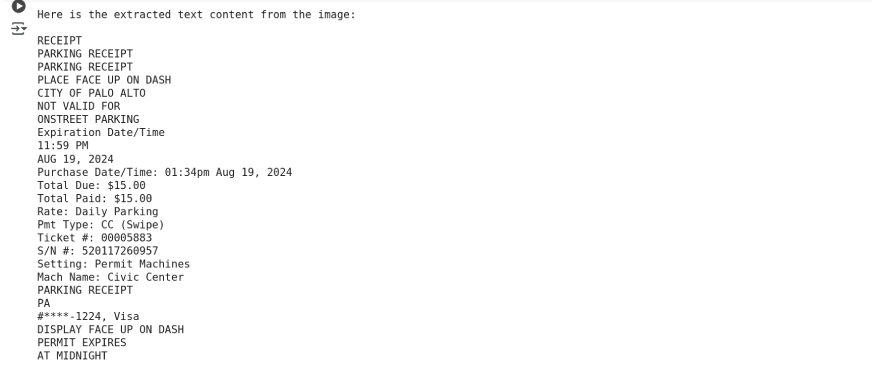
Output using gpt-4o:
When I tested GPT-4o, it was unable to access local files. Therefore, I provided the URL of a similar image for GPT to evaluate its text extraction capabilities.
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(api_key="api_key")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "What's in this image?"},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "https://preview.redd.it/11gu042ydlub1.jpg?width=640&crop=smart&auto=webp&s=8cbb551c29e76ecc31210a79a0ef6c179b7609a3",
}
},
],
}
],
max_tokens=300,
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)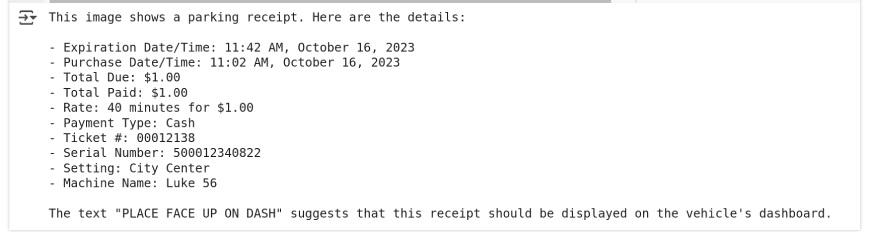
Comparative Analysis
| Criteria | Mistral OCR | GPT-4o | Gemini 2.0 Flash |
| API Price | 1000 pages / $ (and approximately double the pages per dollar with batch inference). | $5.00 per 1 million input tokens | $0.10 (text / image / video) |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy | Heavy |
Mistral OCR Performance Benchmarks
Now, let’s have a look at how Mistral OCR performs across various benchmarks.
1. Standard Benchmarks
Mistral OCR has set a new standard in document analysis, consistently outperforming other leading OCR models in rigorous benchmark evaluations. Its advanced capabilities extend beyond simple text extraction, accurately identifying and retrieving embedded images alongside textual content – something many competing models struggle to achieve.
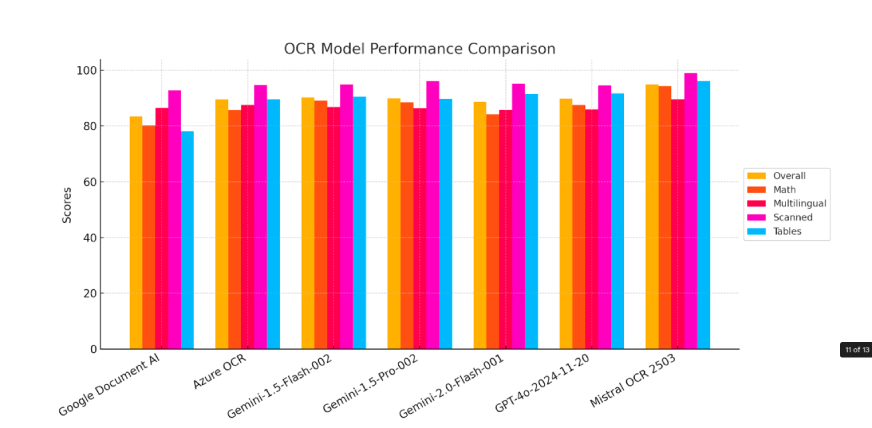
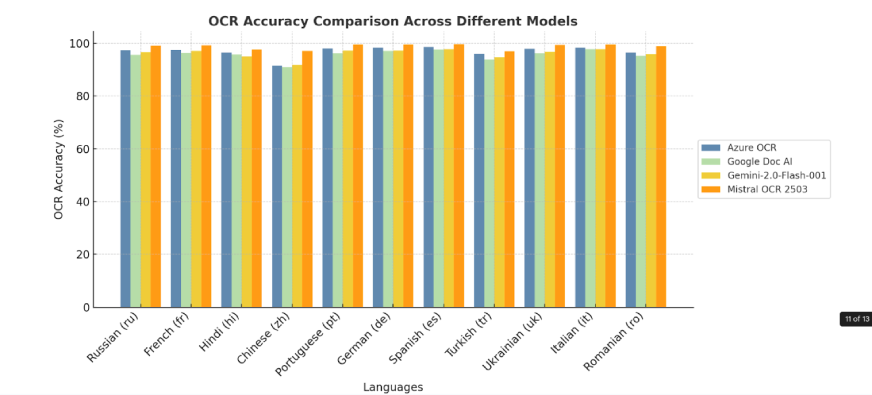
2. Benchmark by Language
Mistral OCR sets the bar high with its capacity to identify, decipher, and translate thousands of languages, scripts, and fonts from all over the globe. With Mistral OCR effortlessly processing varied linguistic structures, nothing is left behind in translation, and it becomes an incredibly useful tool for bridging language gaps.
Future Applications of Mistral OCR
Mistral OCR has the potential to revolutionize various industries by making complex documents more accessible and actionable. Here are some key applications:
- Digitizing Scientific Research: Research organizations may employ Mistral OCR to translate scientific articles, journals, and technical reports into AI-compatible forms. This expedites the sharing of knowledge, facilitates smoother collaboration, and improves AI-aided literature reviews.
- Preserving Historical and Cultural Heritage: Historical manuscripts, artworks, and cultural artifacts from museums, libraries, and archives can be made more accessible to researchers and the public while also being digitally preserved in the long term.
- Streamlining Customer Service: Companies can convert user guides, product manuals, and FAQs into organized, searchable knowledge bases, lowering response times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Making Literature Across Design, Education, and Legal Sectors AI-ready: From engineering blueprints to legal agreements and educational content, Mistral OCR makes sure that key industry documents are indexed and readily accessible for AI-driven insights and automation.
Conclusion
For too long, valuable knowledge hidden in complex documents—whether scientific diagrams, handwritten manuscripts, or structured reports—has remained out of AI’s reach. Mistral OCR changes that, turning RAG systems from simple text retrievers into powerful tools that truly understand and navigate information in all its forms. This isn’t just a step forward in technology—it’s a breakthrough in how we access and share knowledge. By opening the door to documents that were once difficult to process, Mistral OCR is helping AI bridge the gap between information and understanding, making knowledge more accessible than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Mistral OCR can process a wide range of documents, including PDFs, scanned images, handwritten notes, legal contracts, research papers, and financial reports. It accurately extracts and structures text, tables, and embedded images.
A. Mistral OCR is designed for high-speed processing, capable of handling up to 2000 pages per minute on a single node, making it ideal for enterprises and research institutions dealing with large datasets.
A. “Doc-as-Prompt” allows users to treat entire documents as prompts, enabling precise information extraction and structured responses from the extracted content. This feature enhances AI-driven document processing workflows.
A. Yes, Mistral OCR supports thousands of languages, making it an excellent tool for multilingual document processing. It also features fuzzy matching to recognize and correct minor errors in scanned text.
A. Mistral OCR provides structured outputs in JSON format, making it easy to integrate into AI pipelines and enterprise applications.
A. While Mistral OCR is highly advanced, its performance may vary depending on the quality of scanned documents. Extremely low-resolution images or distorted text may affect accuracy.
A. Yes, Mistral OCR offers self-hosting options for organizations with strict privacy requirements. It ensures data security and compliance with industry standards.





