
Introduction
SQL(Structured Query Language) commands are instructions. It is used to interact with the database, and it is also used to perform specific tasks, functions, and data queries. SQL can perform Several tasks like creating a table, adding data to tables, dropping the table, modifying the table, set permission for users. Here, I explain different SQL commands and respective syntax so that this quick read can be your refresher.
I begin with a broad classification of SQL commands.. 🚀
Types of SQL Commands
Depending on which operation the SQL code will be doing, there are five different types of SQL commands, as shown below.
1. DDL: Data Definition Language
2. DML: Data Manipulation Language
3. DCL: Data Control Language
4. TCL: Transaction Control Language
5. DQL: Data Query Language
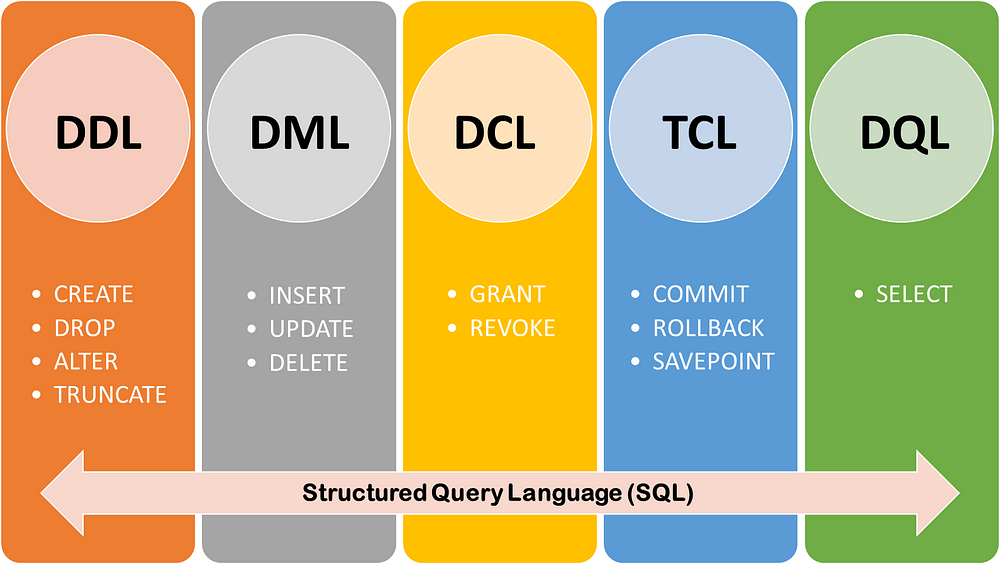
I explain these types and the SQL commands used in the subsequent sections below.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL changes the format of the table, such as creating a table, deleting a table, and altering a table.
All the command of DDL is auto-committed which means it permanently save all the changes in the database. Below are the DDL commands and their syntax.
CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE Creates a new table in the database. It allows you to specify the name of the table and the name of each column in the table.
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_1 datatype,
column_2 datatype,
column_3 datatype);
ALTER
ALTER TABLE Let’s you alter the table as per your requirement.
For example, you can add, remove and rename the columns as shown below.
-- Add a column ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name datatype;
-- Remove a column ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;
-- Rename a column ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE COLUMN old_name new_name;
Moreover, ALTER lets you change the table name itself with the below syntax.
ALTER TABLE old_table_name RENAME TO new_table_name;
DROP
It is used to delete both the structure and record stored in the table.
DROP TABLE table_name;
TRUNCATE
It is used to delete all the rows from the table and free the space containing the table.
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;
Data Manipulation Language
DML commands are used to Customize the database, and it is responsible for all forms of changes in the database.
The command of DML is not auto-committed, which means it can’t permanently save all the changes in the database. They can be rollback. Below are the DML commands and their syntax.
INSERT
INSERT Statements are used to add a new row to a table.
INSERT INTO table_name (column_1, column_2, column_3) VALUES (value_1, value_2, value_3);
UPDATE
UPDATE statements allow you to edit rows in a table.
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = value WHERE condition;
DELETE
DELETE statements are used to remove rows from a table.
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE some_column = some_value;
Data Control Language
DCL commands grants and takes back authority from any database user. It works as shown below.
GRANT
GRANT command is for giving users access to a database.
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON My_TABLE TO FIRST_USER, SECOND_USER;
REVOKE
It is used to take back permissions from the user.
REVOKE SELECT, UPDATE ON My_TABLE TO FIRST_USER, SECOND_USER;
Transaction Control Language
Transaction Control Language — as its name suggests — is used to control the actions done by other non-auto-committed commands such as INSERT, DELETE and UPDATE.
As I mentioned, DML commands are not auto-committed so TCL commands can be used with the DML. Below are the commonly used TCL statements.
COMMIT
This is used for saving every transaction to the database.
DELETE FROM VENDOR WHERE AGE = 29; COMMIT;
ROLLBACK
This command aims to undo the transactions that are not saved to the database.
DELETE FROM VENDOR WHERE AGE = 29; ROLLBACK;
SAVEPOINT
This is used for returning a transaction to a specific point without affecting the whole transaction.
SAVEPOINT SAVEPOINT_NAME;
Data Query Language
DQL is used to fetch the data from the database. SELECT is the only and essential command widely and commonly used by all data analysts and scientists.
SELECT
The prime purpose of this statement is to get data from a database. Every query will begin with SELECT, followed by the names of columns you want to get from the table.
A particular column from the table can be selected with,
SELECT column_name FROM table_name;
And all the columns can be determined by using * as shown below,
SELECT * FROM table_name;
Conclusion
This article has taught you about the various SQL commands and simple SQL queries with examples. Some of the main concepts learnt in this article are as follows:
Data Definition Language(DDL) helps you define the database structure or schema.
Data Manipulation Language (DML) allows you to modify the database instance by inserting, changing, and deleting its data.
DCL (Data Control Language) includes commands like GRANT and REVOKE, which help give “rights & permissions.”
Transaction control language or TCL commands deal with the transaction within the database.
Data Query Language (DQL) is used to fetch the data from the database.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.





