Here is a typical situation during performance reviews:
“All the business leaders and stakeholders are present in a room. A performance report / MIS is projected. The colorful report contains a whole list of metrics starting from business inputs (like resources deployed, cost of marketing etc.) and the output (like Sales, applications, X-sell, up-sell).
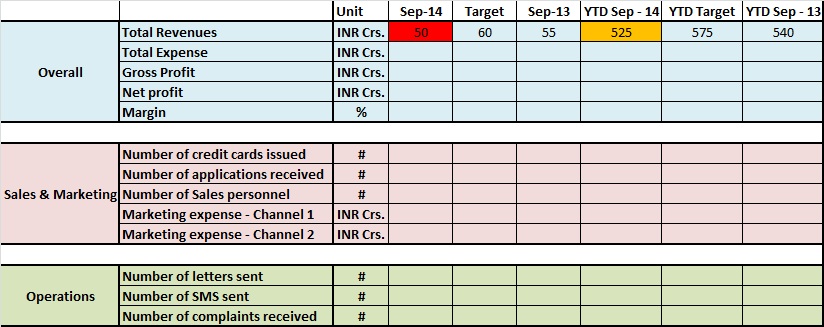
Following is a snapshot of one such report for a credit card lender:
While the report might be doing a good job of what is happening, there are some serious problems with this report. Can you spot some of them?
The biggest challenge in using this report is that it only answers what happened, it makes no attempt to answer why and how.
So when you use this report for performance reviews, there are only 2 possible outcomes:
- Business users answer why and how basis their knowledge and ability to put some story
- The performance review ends up being a summary of what happened with no actions or insights about what is working well and what is not.
Both these outcomes are far away from the objective of any performance review.
So, how do you make sure that your reporting has meaningful metrics which bring out insights and drive actions?
The remaining post assumes that you have good business understanding and context, if that is not the case, please do so first. Here are four rules which I have learnt over years which will help you create insightful and actionable reporting:
[stextbox id=”section”]1. Use absolute numbers only when comparing against targets or benchmarks. For all other metrics, ratios and percentage are more powerful and meaningful:[/stextbox]
The only purpose of keeping absolute numbers should be when you want to compare them against targets or benchmarks, or they are there for some contexts. Otherwise, keeping absolute numbers don’t add value in reporting / analysis.
For example, if you simply state that we sold 1400 Credit cards this month (lets say it is lower than plan), it only tells business that we did not achieve plan. Comparing against targets or performance last year / last month can provide a context (again only what happened), but you need to move to some ratios to understand why and how of it. Following are some of the questions you can ask and report through metrics:
- Has Sales per Sales person improved or deteriorated? If it has improved compared to expectation / benchmark, you know that the drop is because of lower number of Sales person deployed. Otherwise, it is driven by something else.
- Are there particular channels whose performance is lower than expected? Possible meaningful metrics to look at are (number of cards sold through a channel / expense of the channel) or (number of cards issued / number of cards applied)
- Looking at percentage of various cards (products) will give an idea whether this is driven by lower Sales of particular products.
[stextbox id=”section”]2. Segment till you can!:[/stextbox]
Some of the questions in previous point touch on this briefly. Averages can not drive action, you need to analyze and understand things at a segment level. Click here to understand how to create a segmentation.
In summary, each segment would differ differently and you can not take action until you report / analyze things at segment level. If you know that the drop in this question is driven only by a channel or product which has not performed well, it is easier to take actions on that basis.
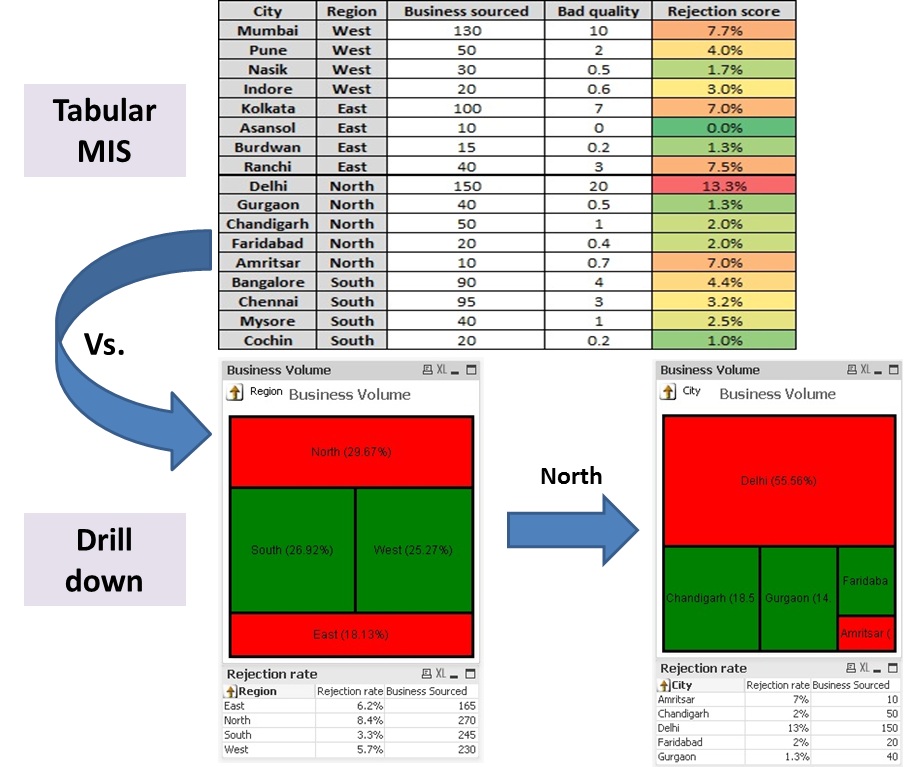
[stextbox id=”section”]3. Use visualizations and drill downs instead of just reporting numbers:[/stextbox]
Use of graphs, visualizations and drill downs can just take actions and insights to the next level. The main benefit of graphs over just numbers is that it gives you lot more context compared to just staring at numbers. A simple look at the graphs can answer various questions like:
- Has the drop occurred this month or we are recovering from a drop in past?
- When did the performance start to worsen?
Further, drill-downs can represent the segmentation effectively and pin point the areas of improvement. For example, the drill down in image below conveys same information in a better manner.
[stextbox id=”section”]4. Tie in metrics to the fundamental level of action:[/stextbox]
While you can start the reporting at high level, the actions can only happen when relevant metrics at right level are looked at. For example, looking at Approval ratio by Regions / Geographies will help you answer what, but looking at Approval ratio by Sales people can help trigger instant actions. You can provide better training to these Sales people or ask them to re-look at their target segment.
Similarly, until you analyze and report Keyword level performance, you can not optimize Search campaigns.
What do you think about these rules? Do you have any rules which make your reports more insightful and actionable? Please add them through comments.



Great article.
Good tips. Thank you for posting.
Hello to all, since I am truly keen of reading this web site's post to be updated daily. It consists of good stuff.