In previous articles on Hadoop, our focus have been on MapReduce routines. MapReduce are the basic functional unit of a Hadoop system. Following are the links of few articles published on Hadoop till date :
1. What is Hadoop? – Simplified!
3. Tricking your elephant to do data manipulations (using MapReduce)
However with time we have progressed beyond MapReduce to handle big data with Hadoop. MapReduce, however exceptionally powerful becomes complex and time consuming when doing complete analysis on distributed network. Today, we have many more system which can work in conjunction with MapReduce or simply on HDFS to complete such complex functionalities. Our focus of this article will be to give an introduction to these systems or have an overview of Hadoop ecosystem beyond simple MapReduce.
Two types of MapReduce architectures
MapReduce Version 1: In most of the articles we were primarily referring to the first type of MapReduce architecture which is known as MapReduce Version 1. This architecture has been discussed in our previous article on Hadoop ( https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2014/05/hadoop-simplified/ ).
MapReduce Version 2 : Version 2 uses YARN cluster management system. Instead of Job Tracker and Task tracker now we have something known as Resource Manager, Application Master and Node Manager. This architecture is no longer dependent on converting every query to Map Reduce type. Following is a schematic of how YARN enables a few other tools to be operated on Hadoop. This diagram will be later shown with more details in the next section, where we will expand the section Others (data processing).
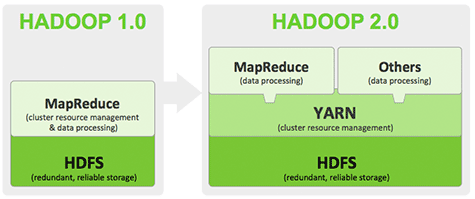 Extended Hadoop Ecosystem
Extended Hadoop Ecosystem
Many tools which are mostly open source integrate into these two MapReduce architectures. These are not strictly core Hadoop systems but come under Hadoop Ecosystem. These tools help us to do any of the following :
- Data Analysis : Any analysis become extremely complicated if we directly use MapReduce. For instance, social network mining if done using MapReduce directly might end up becoming unnecessarily complicated. These analysis can be much simplified if we use these additional tools.
- Hadoop Workflow management : For corporates using Hadoop, it is very important to manage Hadoop workflow. Today we have many tools which can do this job for us.
- Data Transfer from one platform to other : Given that today we collect data from various sources, it has become very common to transfer data between platforms. We today have tools to do this job as well.
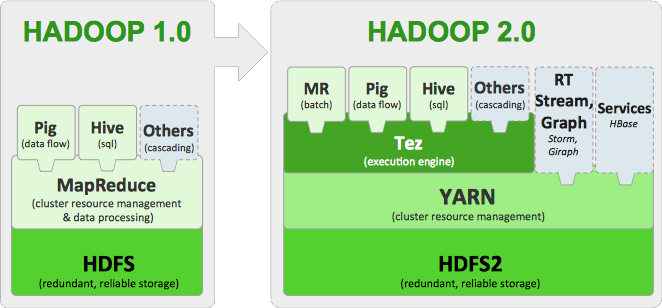
Following is a detailed schematic of the Hadoop ecosystem :
Hadoop Ecosysted Tools – Brief introduction
APACHE PIG : PIG is an alternate way to writing detailed MapReduce functions. Just imagine this as an interpreter which will convert a simple programming language called PIG LATIN to MapReduce function. This interpreter operates on the client machine, where it does all the translation. Once this translation is completed, MapReduce functions are executed in the same way as directly written MapReduce functions work.
APACHE HIVE : The functionality of HIVE is very similar to that of PIG. The only difference being the client side language. HIVE uses a similar query language to SQL known as HiveQL. It also operates on the client processor and acts like an interpreter. However, it is very handy when it comes to niche analysis like sentiment analysis using Hadoop with a few built in functionality.
 CLOUDERA IMPALA : Impala is very similar to HIVE. However, for a few functionality it is extremely fast when compared to HIVE. But this is a project still in progress and hence is not used to the extent HIVE is used in the industry.
CLOUDERA IMPALA : Impala is very similar to HIVE. However, for a few functionality it is extremely fast when compared to HIVE. But this is a project still in progress and hence is not used to the extent HIVE is used in the industry.
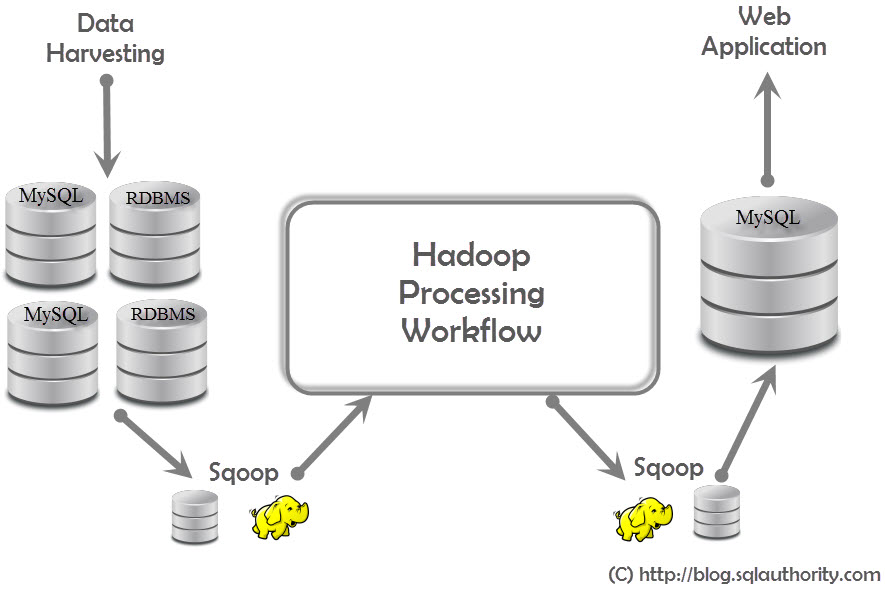
APACHE SQOOP : Sqoop is a tool which comes in very handy when you want to shift data from RDBMS to HDFS or vice versa. This functionality of Sqoop is done using Map-only functions.Following is a general schematic how servers are connected together in a real life scenario :
![]()
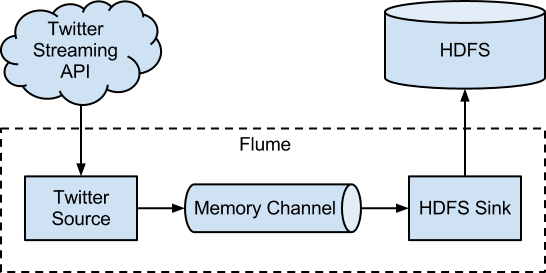
 FLUME : Flume is in general used for high velocity data. Such as streaming data from social network or logs from server. The high velocity data can be processed on Hadoop server to create real time triggers. Following is a simple schematic of Flume network :
FLUME : Flume is in general used for high velocity data. Such as streaming data from social network or logs from server. The high velocity data can be processed on Hadoop server to create real time triggers. Following is a simple schematic of Flume network :
 OOZIE :Oozie comes in handy to manage processing workflow. It is basically meant to handle, execute and cordinate between individual job in a Hadoop cluster. Such tool becomes very essential when Hadoop is installed in a corporate environment where getting a top view of the entire job being processed in parts becomes very essential.
OOZIE :Oozie comes in handy to manage processing workflow. It is basically meant to handle, execute and cordinate between individual job in a Hadoop cluster. Such tool becomes very essential when Hadoop is installed in a corporate environment where getting a top view of the entire job being processed in parts becomes very essential.
HBASE : HBASE also uses HDFS and is capable of storing massive amounts of data. It can also handle high velocity data ranging to hundreds of thousands of inserts per second.
End Notes
Hopefully after reading this article, you might have got a good understanding of the Hadoop Ecosystem. As the data becomes bigger, necessity of Hadoop is bound to get stronger. In future articles we will focus on how does these components of Hadoop ecosystem actually work in detail.
Did you find the article useful? Share with us any practical application of Hadoop ecosystem you encountered in your work . Do let us know your thoughts about this article in the box below.
If you like what you just read & want to continue your analytics learning, subscribe to our emails, follow us on twitter or like our facebook page.









I can not view the images in this article. Could you please check if the images have been removed?
This should now be fixed. Do let me know, if you are still facing this challenge. Kunal