Machine learning is changing how we use technology and data every day. This guide will explain the basics of machine learning, different types of algorithms, and how it’s used in fields like healthcare, banking, and retail. We’ll also clear up the confusion around terms like artificial intelligence and deep learning. Let’s break it down in a simple way that anyone can understand, Here are a few example –
Overview
- Get introduced to the basics of machine learning with some examples
- Statistics, Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning, and Data Mining are a few technical terms associated with machine learning.
- Learn about the different types of machine learning algorithms
Coming to the point, given the amount of confusion on the topic, we thought to create an awesome introductory series of articles on machine learning. The idea is to eliminate all the jargon that might have intimidated you in the past and create something that a 5-year-old can read (or perhaps a high school graduate)!
Table of contents
So what exactly is machine learning? My small experiment…
Just to make sure I don’t over-estimate (or under-estimate) the capability of the target audience, I got hold of 10 people who were completely new to analytics. None of them had heard about machine learning before (yes, there are people like that!). Here is what they said:
- I don’t know, may be learning from machines?
- Making machines learn something a.k.a. programming machine software
- Learning with help of computers
- Learning through online courses (!!!)
That was fun! Perfect group to explain machine learning to. Here is how I started explaining to these people:
Machine Learning refers to the techniques involved in dealing with vast data in the most intelligent fashion (by developing algorithms) to derive actionable insights.
By this time, they were looking at me as if I have spoken a few things in front of people from Mars! So, I stopped and then asked them a question in return, which they could relate to more:
KJ: What do you think happens when you search for something on Google?
Group: Google shows up the most relevant web pages related to that search.
KJ: That’s good! but what really happens so that Google can show these relevant pages to you?
This time it looked like they were thinking a bit more. Then some one from the group spoke
Group member: Google looks at the past clicks from the people to understand which pages are more relevant for those searches and then serves those results on top of search.
This was a far better attempt. I also had to control my urge to preach that how Google does this is far more smarter way than this simple concept. But, I thought I had a good hook to explain machine learning here. So, I continued:
KJ: OK, that sounds like a good approach. But, how many searches and what all kind of searches would Google handle regularly?
Group: Must be a real big number – may be a trillion searches every year
KJ: So, how do you think Google can serve so many requests with such accuracy? Do you think there are people sitting in Google offices and continuously deciding which search result is relevant and which is not?
Group member: Haven’t really thought about it, but no, that sounds humanly impossible to do.
KJ: You are right. This is where machine learning comes into play. Machine learning is a set of techniques, which help in dealing with vast data in the most intelligent fashion (by developing algorithms or set of logical rules) to derive actionable insights (delivering search for users in this case).
A logical nod from the group, looks like mission accomplished…yay! But wait…
Now the common question – How is machine learning different from X?
The minute you start reading about machine learning, you see various rockets bombarding you with high velocity. These are jargons used loosely in the industry. Here are some of them: Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning, Data Mining and Statistics.
For your clear understanding, I have explained these terms below in the simple manner. You will also understand the importance of these terms in context of machine learning:
X = Artificial Intelligence(AI):
It refers to the procedure of programming a computer (machine) to take rational. Ah! what is rational? Rational is the basis of taking a decision.
I mentioned ‘rational’ instead of intelligence (as expected) because we human beings tend to take decisions which are high on being rational and feasible rather than being explicitly intelligent. This is because all intelligent decisions needn’t be rational and feasible (my hypothesis). Hence, the central motive behind using AI is to achieve the computer (machine) behave in a dandy fashion in lieu of human guidance instead of being doltish!
AI may include programs to check whether certain parameters within a program are behaving normally. For example, the machine may raise an alarm if a parameter say ‘X’ crosses a certain threshold which might in turn affect the outcome of the related process.
Use of Artificial Intelligence in Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI where the machine is trained to learn from it’s past experience. The past experience is developed through the data collected. Then it combines with algorithms such as Naïve Bayes, Support Vector Machine(SVM) to deliver the final results.
X = Statistics:
At this high level stage, I assume you would know about statistics. If you don’t, here’s a quick definition, Statistics is that branch of mathematics which utilizes data, either of the entire population or a sample drawn from the population to carry out the analysis and present inferences. Some statistical techniques used are regression,variance, standard deviation, conditional probability and many others. To know about this topic, read How to understand population distributions using statistics?
Use of Statistics in Machine Learning
Let’s understand this. Suppose, I need to separate the mails in my inbox into two categories: ‘spam’ and ‘important’. For identifying the spam mails, I can use a machine learning algorithm known as Naïve Bayes which will check the frequency of the past spam mails to identify the new email as spam. Naïve Bayes uses the statistical technique Baye’s theorem( commonly known as conditional probability). Hence, we can say machine learning algorithms uses statistical concepts to execute machine learning.
Additional Information: The main difference between machine learning and statistical models come from the schools where they originated. While machine learning originated from the department of computer science and statistical modelling came down from department of mathematics. Also any statistical modelling assumes a number of distributions while machine learning algorithms are generally agnostic of the distribution of all attributes.
X = Deep Learning:
Deep Learning is associated with a machine learning algorithm (Artificial Neural Network, ANN) which uses the concept of human brain to facilitate the modeling of arbitrary functions. ANN requires a vast amount of data and this algorithm is highly flexible when it comes to model multiple outputs simultaneously. ANN is more complex topic and we may do justice to it in an altogether separate article.
X = Data Mining:
During my initial days as an analyst, I always used to muddle the two terms: Machine Learning and Data Mining. But, later I learnt, Data Mining deals with searching specific information. And Machine Learning solely concentrates on performing a given task. Let me cite the example which helped me to remember the difference; Teaching someone how to dance is Machine Learning. And using someone to find best dance centers in the city is Data Mining. Easy!
Also Read: Introduction to Online Machine Learning
But, How exactly do we teach machines?
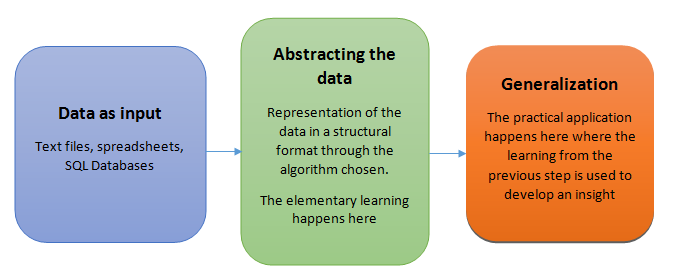
Teaching the machines involve a structural process where every stage builds a better version of the machine. For simplification purpose, the process of teaching machines can broken down into 3 parts:
I shall be covering each of these 3 steps in detail in my subsequent write-ups. As of now, you should understand, these 3 steps ensures the holistic learning of the machine to perform the given task with equal importance. Success of machine depends on two factors:
1. How well the generalization of abstraction data take place.
2. How well the machine is able to put it’s learning into practical usage for predicting the future course of action.
Also Read: Learn about Scikit-Learn – Machine Learning tool in Python
What are the steps used in Machine Learning?
There are 5 basic steps used to perform a machine learning task:
- Collecting data: Be it the raw data from excel, access, text files etc., this step (gathering past data) forms the foundation of the future learning. The better the variety, density and volume of relevant data, better the learning prospects for the machine becomes.
- Preparing the data: Any analytical process thrives on the quality of the data used. One needs to spend time determining the quality of data and then taking steps for fixing issues such as missing data and treatment of outliers. Exploratory analysis is perhaps one method to study the nuances of the data in details thereby burgeoning the nutritional content of the data.
- Training a model: This step involves choosing the appropriate algorithm and representation of data in the form of the model. The cleaned data is split into two parts: training and test sets (the proportion depends on the prerequisites). You use the first part (training data) to develop the model, while you use the second part (test data) as a reference.
- Evaluating the model: To test the accuracy, the second part of the data (holdout / test data) is used. This step determines the precision in the choice of the algorithm based on the outcome. A better test to check the accuracy of a model involves examining its performance on data that the model did not use during its build.
- Improving the performance: This step might involve choosing a different model altogether or introducing more variables to augment the efficiency. That’s why significant amount of time needs to be spent in data collection and preparation.
Any model can use these five steps to structure the technique. When we discuss the algorithms, you will find how these five steps appear in every model!
Also Read: Getting Smart with Machine Learning – Ada Boost and Gradient Boost
Supervised Learning / Predictive models:
Predictive models, as the name suggests, predict future outcomes based on historical data. Typically, these models receive clear instructions from the beginning about what to learn and how to learn it. These class of learning algorithms are termed as Supervised Learning.
For example: Supervised Learning is used when a marketing company is trying to find out which customers are likely to churn. We can also use it to predict the likelihood of occurrence of perils like earthquakes, tornadoes etc. with an aim to determine the Total Insurance Value. Some examples of algorithms used are: Nearest neighbour, Naïve Bayes, Decision Trees, Regression etc.
Unsupervised learning / Descriptive models:
It is used to train descriptive models where no target is set and no single feature is important than the other. The case of unsupervised learning can be: When a retailer wishes to find out what are the combination of products, customers tends to buy more frequently. In the pharmaceutical industry, unsupervised learning may help predict which diseases are likely to occur alongside diabetes. Example of algorithm used here is: K- means Clustering Algorithm
Reinforcement learning (RL):
It is an example of machine learning where the machine trains itself to make specific decisions based on business requirements, aiming to maximize efficiency (performance). The idea behind reinforcement learning involves the machine or software agent continually training itself based on the environment it encounters and applying its enriched knowledge to solve business problems. This continual learning process ensures less involvement of human expertise which in turn saves a lot of time!
An example of algorithm used in RL is Markov Decision Process.
Important Note: There is a subtle difference between Supervised Learning and Reinforcement Learning (RL). RL essentially involves learning by interacting with an environment. An RL agent learns from its past experience, rather from its continual trial and error learning process as against supervised learning where an external supervisor provides examples.
A good example to understand the difference is self driving cars. Self driving cars use Reinforcement learning to make decisions continuously – which route to take? what speed to drive on? are some of the questions which are decided after interacting with the environment. A simple manifestation for supervised learning would be to predict fare from a cab going from one place to another.
What are the applications of Machine Learning?
It is very interesting to know the applications of machine learning. Google and Facebook uses ML extensively to push their respective ads to the relevant users. Here are a few applications that you should know:
- Banking & Financial services: Machine learning can predict customers likely to default on loans or credit card bills. This capability helps banks identify customers eligible for loans and credit cards.
- Healthcare: It is to diagnose deadly diseases (e.g., cancer) based on patients’ symptoms and by comparing them with past data from similar patients.
- Retail: It is used to identify products which sell more frequently (fast moving) and the slow moving products which help the retailers to decide what kind of products to introduce or remove from the shelf. Also, Machine learning algorithms can identify which two, three, or more products sell together. This approach helps design customer loyalty initiatives, which in turn enables retailers to develop and maintain loyal customers.
These examples are just the tip of the iceberg. Machine learning has extensive applications practically in every domain. You can check out a few Kaggle problems to get further flavor. The examples included above are easy to understand and at least give a taste of the omnipotence of machine learning.
Conclusion
In this article, we started by developing a basic understanding of what machine learning is. We also looked at how it gets confused with several other terms. We also covered the process to teach a machine, the essential steps used in machine learning, the algorithms used in machine learning followed by the applications of machine learning.
I hope this article helps you get acquainted with the basics of machine learning. We would love to hear about it from you. Did you find it useful? What aspects of machine learning confuse you the most? Feel free to post your thoughts through comments below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Data preparation is the most important step in machine learning. A good model is only as good as the data it is trained on.
The best ML algorithm depends on your problem and data.. The best machine learning algorithm for you will depend on the specific problem you are trying to solve and the data you have available.
There are many different ways to deploy a machine learning model. One common approach is to use a cloud-based service such as Google Cloud Platform or Amazon Web Services. These services provide easy-to-use tools for deploying and managing machine learning models.
Yes, but ML is the most popular approach to AI. Other areas of AI include knowledge representation and reasoning, planning and search, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics.






Thanks Kunal. Nice Article... Good explanations.. Simple examples which really ease out every level of audience!
Very nice & great explanation for a novice...
HII
Nice article. Thanks for posting this article. But I am not convince with the explanation of Machine Learning Vs Data Mining. As per the definition posted in the article it seems like Data Mining = BI Reporting (Business Intelligence Reporting) . As per my experience I feel, Data Mining is a set of algorithm or statistical/mathematical technique , which is used in Machine Learning.
I fully agree with your comment The 5 steps used in ML are also applicable to Data Mining, same for the business applications. Reinforcement Learning is maybe what really distinguishes ML from Data Mining.