Introduction
Ever wondered, “what algorithm google uses to maximize its target ads revenue?”. What about the e-commerce websites which advocates you through options such as ‘people who bought this also bought this’. Or “How does Facebook automatically suggest us to tag friends in pictures”?
The answer is Recommendation Engines. With the growing amount of information on world wide web and with significant rise number of users, it becomes increasingly important for companies to search, map and provide them with the relevant chunk of information according to their preferences and tastes.
Companies nowadays are building smart and intelligent recommendation engines by studying the past behavior of their users. Hence providing them recommendations and choices of their interest in terms of “Relevant Job postings”, “Movies of Interest”, “Suggested Videos”, “Facebook friends that you may know” and “People who bought this also bought this” etc.
What are Recommendation Engines ?
Often termed as Recommender Systems, they are simple algorithms which aim to provide the most relevant and accurate items to the user by filtering useful stuff from of a huge pool of information base. Recommendation engines discovers data patterns in the data set by learning consumers choices and produces the outcomes that co-relates to their needs and interests.
Types of Recommendation Engine:
In this article, we will explain two types of recommendation algorithms that are also used by most of the tech giants like Google and Facebook in their advanced recommender system modules.
As a typical business problem,
Consider a scenario of an e-commerce website which sells thousands of smartphones. With growing number of customers every day, the task in hand is to showcase the best choices of smartphones to the users according to their tastes and preferences.
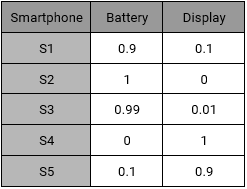
To understand how recommendation engine works, let’s slice the data into a sample set of five smartphones with two major features “Battery and Display”. The five smartphones have following properties:
- S1 has good battery life but poor display
- S2 has an amazing battery performance but very rough display
- S3’s battery is one of the best but display lacks quality
- S4 & S5 are good in terms of display but poor in terms of battery performance.
Using these characteristics, we can create an Item – Feature Matrix. Value in the cell represents the rating of the smartphone feature out of 1.
Item – Feature Matrix
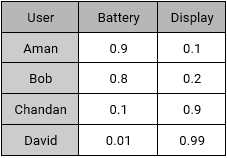
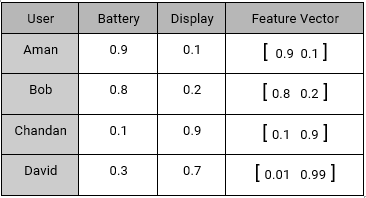
Our sample set also consist of four active users with their preferences.
- Aman: He prefers battery over display as an ideal smartphone feature.
- Bob: He likes a long lasting battery.
- Chandan: For Chandan, display should be decent, battery should be normal.
- David: For David, Display is extremely important but not the battery.
Using their interests, we can create a User – Feature Matrix as follows:
We have two matrices: Item – Feature and User – Feature. We can create the recommendation of smartphones for our users using following algorithms:
Content Based Recommendations
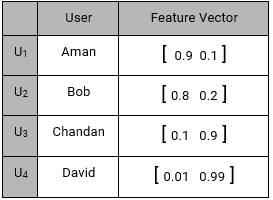
Content based systems, recommends item based on a similarity comparison between the content of the items and a user’s profile. The feature of items are mapped with feature of users in order to obtain user – item similarity. The top matched pairs are given as recommendations, as demonstrated below: Representing every user by a feature vector:
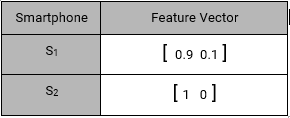
Also, every item representation as a feature vector:
and so on…
Content Based Item – User Mapping Recommendations are given by the equation:
MAX ( U(j)T . I(i) )
i,j -> n,m
For User U1 (Aman), Smartphone recommendation is:
MAX( U1TS1, U1TS2, U1TS3, U1TS4, U1TS5)
MAX([0.9 0.1]T [0.9 0.1], [0.9 0.1]T [1 0], [0.9 0.1]T [0.99 0.01], [0.9 0.1]T [0.1 0.9], [0.9 0.1]T [0.01 0.99])
MAX(0.82 , 0.9 , 0.89 , 0.18 , 0.10)
= S2(0.9), S3(0.89) & S1(0.82)
Smartphones S2, S3 and S1 has the highest recommendation scores, Hence S2, S3 and S1 are recommended to Aman.
Collaborative Filtering
Content-based recommendation lacks in detecting inter dependencies or complex behaviors. For example: People might like smartphones with Good Display, only if it has retina display and wouldn’t otherwise.
Collaborative Filtering algorithm considers “User Behaviour” for recommending items. They exploit behaviour of other users and items in terms of transaction history, ratings, selection and purchase information. Other users behaviour and preferences over the items are used to recommend items to the new users. In this case, features of the items are not known.
We have a similar User – Feature Matrix as content based:
User – Feature Matrix
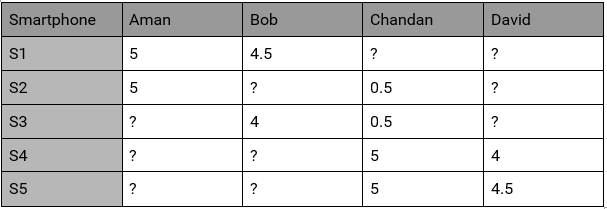
This time we don’t know features of the items but we have user behaviour. i.e. How the Users brought/rated the existing items.
User- Behaviour Matrix
where values of the behaviour matrix can be described as:
Bi,j = {r , if Uj has given “r” rating to a Si
?, if no rating is given
This user behavior matrix can be used to derive unknown features of the most liked items. Lets try to derive features of S1 using this behavior matrix.
S1 is rated 5 by U1
S1 is rated 4.5 by U2
S1 rating by U3 & U4 are not known
Using this information Feature Vector of S1 can be assumed as:
S1 : [x1 x2]
and the equations are:
U1TS1 = 5
U2TS1 = 4.5
[0.9 0.1]T [x1 x2] = 5
[0.8 0.2]T [x1 x2] = 4.5
0.9 * x1 + 0.1 * x2 = 5
0.8 * x1 + 0.1 * x2 = 4.5
solving these equations, gives x1 = 5.5 and x2 = 0.5
S1 = [5.5 0.5]
Similarly,
S2 = [5.5 0]
S3 = [5 0]
S4 = [0.5 5.5]
S5 = [2.7 5.25]
Now all the feature vectors are known. Hence the recommendations will be mappings of User Feature Vectors and Item Feature Vectors. Thus for Aman, based on his preferences and behaviours, recommendation will be:
MAX(U1TS1, U1TS2, U1TS3, U1TS4, U1TS5)
MAX([0.9 0.1]T [5.5 0.5] , [0.9 0.1]T [5.5 0], [0.9 0.1]T [5 0], [0.9 0.1]T
[0.5 5.5],[0.9 0.1]T [2.7 5.25])
MAX(5, 4.99, 4.95, 1, 2.9)
> S1, S2 and S3
which comes out the be S1, S2 and S3 again. Since S1 and S2 are already rated by Aman, So we will recommend him a new smartphone S3.
In the above example where we assumed that there are two primary features of S1 as governed by the users who rated it. In real case, we end up with more number of features than this. For example, if we had data for all the N number of users who rated S1, then feature vector look like:
S1: [ x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 … ]
End notes
In this article, we learnt about two types of Recommendation Engines: Content based recommendations and Collaborative Recommendations. There exists more advanced techniques like ALS : Alternating Least Square Recommendations and Hybrid Recommendation Engines. The Recommendation Engines have become an important need with the growing information space. Did you find this article useful ? Have you also worked on recommender systems? Share your opinions / views in the comments section below.






EXCELLENT BLOG!!!
Hi Kunal, In the collaborative filtering method, I understood till [x1 , x2] for S1. I lost you after that. How did you calculate the feature vector for S2 - S5?? Regards,
You can see that every row in this matrix has atleast two cells filled. Hence, you can always create two equations which can be solved simultaneously to find S2 - S5. I hope this makes it clear. Tavish
How did you come up with the score in User – Feature Matrix and Item– Feature Matrix ?
Generally these matrix comes from User ratings which are collected over time.