This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Introduction
If you want to know – How to use MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS for prediction, then –Keep Reading & Keep Learning.
Although there aren’t any industry standards on ascertaining the expense of losing a salaried employee, a few studies, (for instance SHMR) foresee that each time a business replaces a salaried employee, it costs about 5 to 8 months’ compensation all expenses considered. For a supervisor making $50,000 per year, that is $30,000 to $40,000 in enrolling and hiring costs.
Yet, others foresee that the expense is considerably more – than losing a salaried worker can cost as much as 2x their yearly compensation, particularly for a top/middle level manager. Huge costs incorporate the expense of recruiting, onboarding, and long loss of efficiency.
By reading this article, one can understand two different perspectives: –
Individual perspective – How an organization calculates attrition rate using machine learning algorithms, and it can also estimate the chances of there being an opportunity to apply in an organization or not.
Company Perspective: An organization also gets to know if they should start recruiting or not. If an attrition rate is high, then, an organization also gets to know the time for making amendments in the current employee retention policies.
Analyzing the factors and requisites that can influence the IBM employees attrition rate and finally classifying — on an average what percentage of employees position has not been filled yet.
What is Orange?
Orange is a visual programming software package used for this domain. It has uses widely ranging from machine learning, data mining, and data analysis, etc. Orange tools (called widgets) are within the realm of simple data visualization & pre-processing empirical evaluation of learning algorithms and predictive modeling. Visual programming is implemented via a combination in which workflows are designed by linking user-designed widgets.
At the same time, proficient users can use Orange as a Python library to manipulate data and alter widget.
Attrition Rate
An attrition rate is utilized to quantify employees lost over a period who aren’t yet replaced. The rate appears to be a percentage contrasted with the total workforce. HR(s) often use an attrition rate to determine the number of vacant positions.
Firstly, the .CSV File was uploaded (containing IBM employees data), then all the target column(s) were selected, i.e., Attrition & then the RANK widget was chosen from the Data Column, as ranking helps in giving a gist of what is required the most in a data. Then the first 20 Data Heads have been selected according to the different ranks.
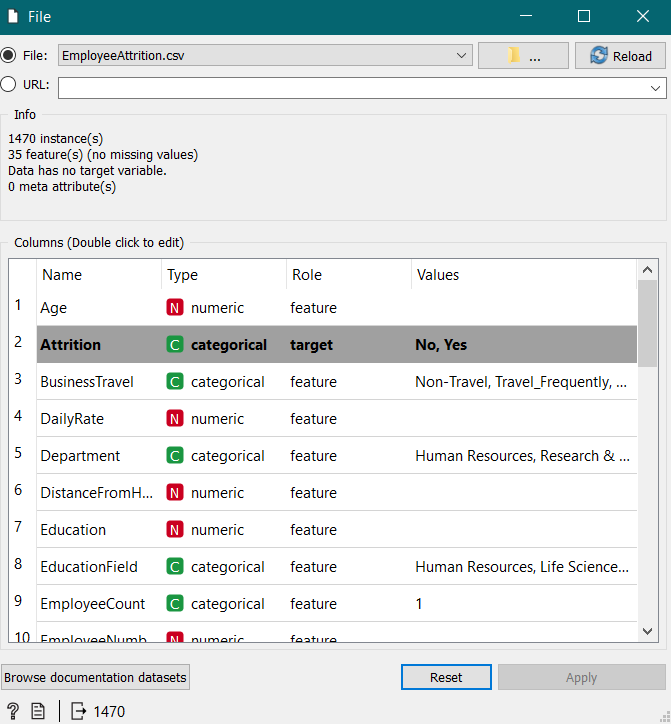
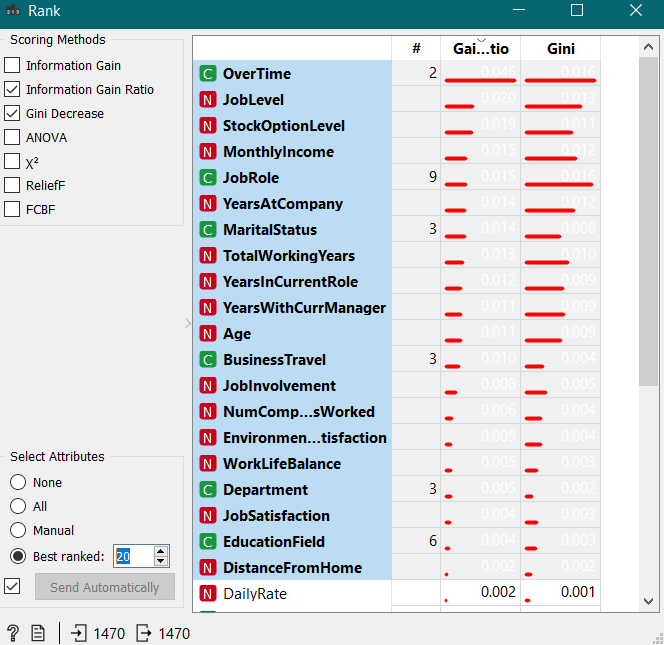
Viewing the data according to the RANK and then SELECTING the Data from the FILE.
The Data has been checked using Data Table — to know whether the Data has any missing values or not, according to the Data Table — the Data has no missing values.

It shows that Data has NO MISSING VALUES.
The prediction was made by orange using different models and then evaluated by using Test & Score.

In the previous article, it was mentioned that the RANDOM FOREST was the BEST MODEL. So, this time three different models have been used — RANDOM FOREST, SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM) & ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK (ANN), and then the comparison was made to understand which model will be more efficient and effective for a better prediction.
– Random Forest model was used in the prediction because: –
Random Forest is a tree-based learning algorithm with the power to form accurate decisions as it has many decision trees together. As its name says — it’s a forest of trees. Hence, Random Forest takes more training time than a single decision tree. Each branch and leaf within the decision tree works on the random features to predict the output. Then this algorithm combines all the predictions of individual decision trees to generate the final prediction, and it can also deal with the missing values.
– Support Vector Machine (SVM) model was used in the prediction because: –
SVM has a regularization feature. So, it has good generalization capabilities, which prevent it from over-fitting, and it can also be used to solve both categorical and numerical problems. A small change to the Data does not significantly affect the SVM. So, the SVM model is stable.
– Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model was used in the prediction because: –
ANN is like our brain; millions and billions of cells – called neurons, which processes information in the form of electric signals. Similarly, in ANN, the network structure has an input layer, a hidden layer, and the output layer. It is also called Multi-Layer Perceptron as it has multiple layers. The hidden layer is known as a “distillation layer” that distills some critical patterns from the data/information and passes it onto the next layer. It then makes the network quicker and more productive by distinguishing the data from the data sources, leaving out the excess data.
- It captures a non-linear relationship between the inputs.
- It helps in converting the information/data into more useful insight.
After Test & Score (it helps analyze and translate qualitative data(characters) into quantitative data(numbers)), Confusion Metrics was used to see all the True Positives, False Negative values, misclassified data & correct data. And lastly, the Distribution visualization was used to understand the data.
Conclusion
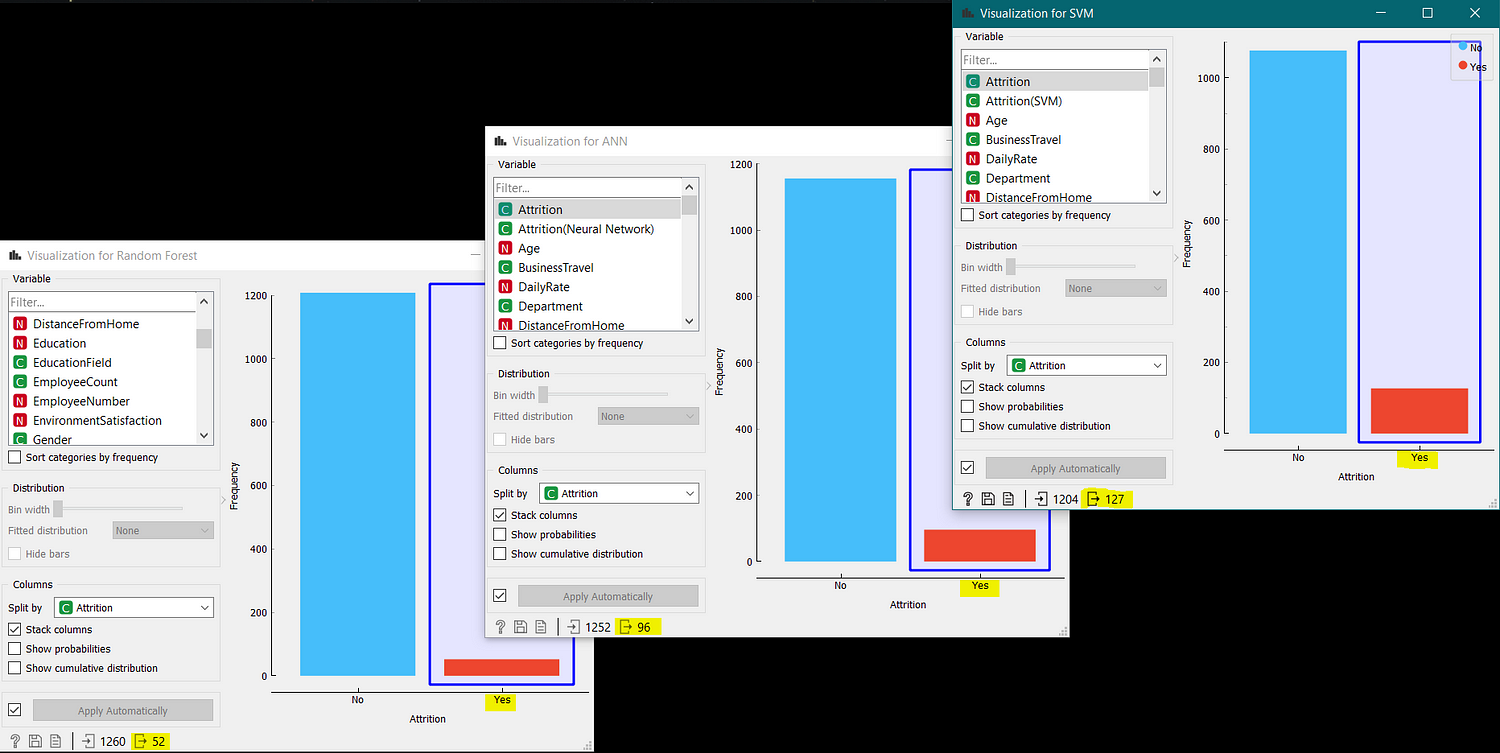
The final results were turned out to be different as all the three models have some different values. So, there is a need to take an average of all the results.
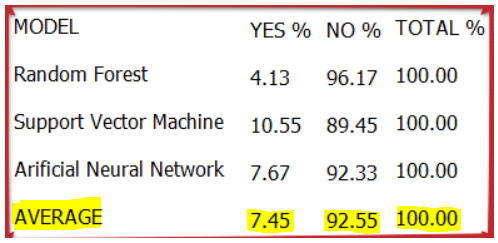
An average has taken to know the Attrition rate.
By doing this, it can be said that in ATTRITION, only 7.45% of the population (Total Population is 1236) comes under the YES category, and the rest, i.e., 92.55% of the population, comes under the NO category.
And, it can also be said that Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is a better model than Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Random Forest because it has a higher AUC (Area Under Curve) as:
- AUC is scale-invariant — i.e., — it measures how well the predictions are ranked.
- AUC is also a classification threshold invariant — i.e., — it measures how well the quality of the model’s prediction is.
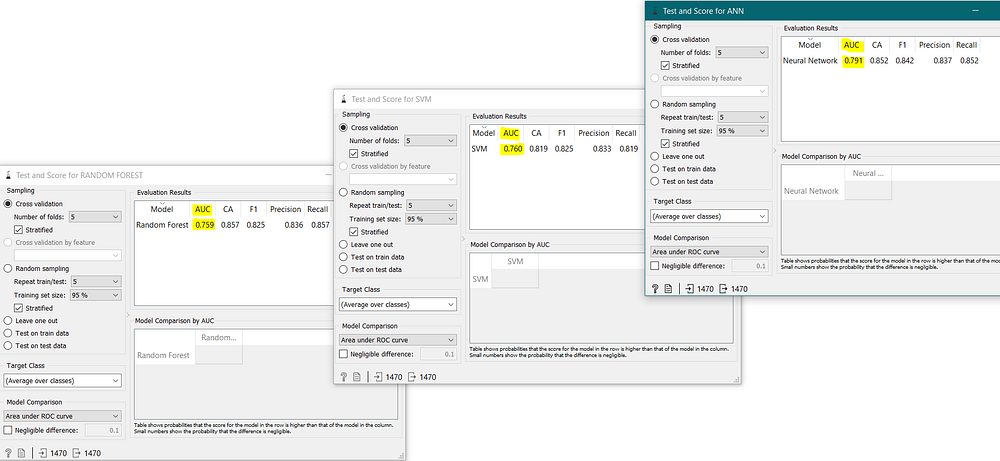
In this case, it can be seen that — Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is a better model as it has a HIGHER AUC (Area Under Curve).
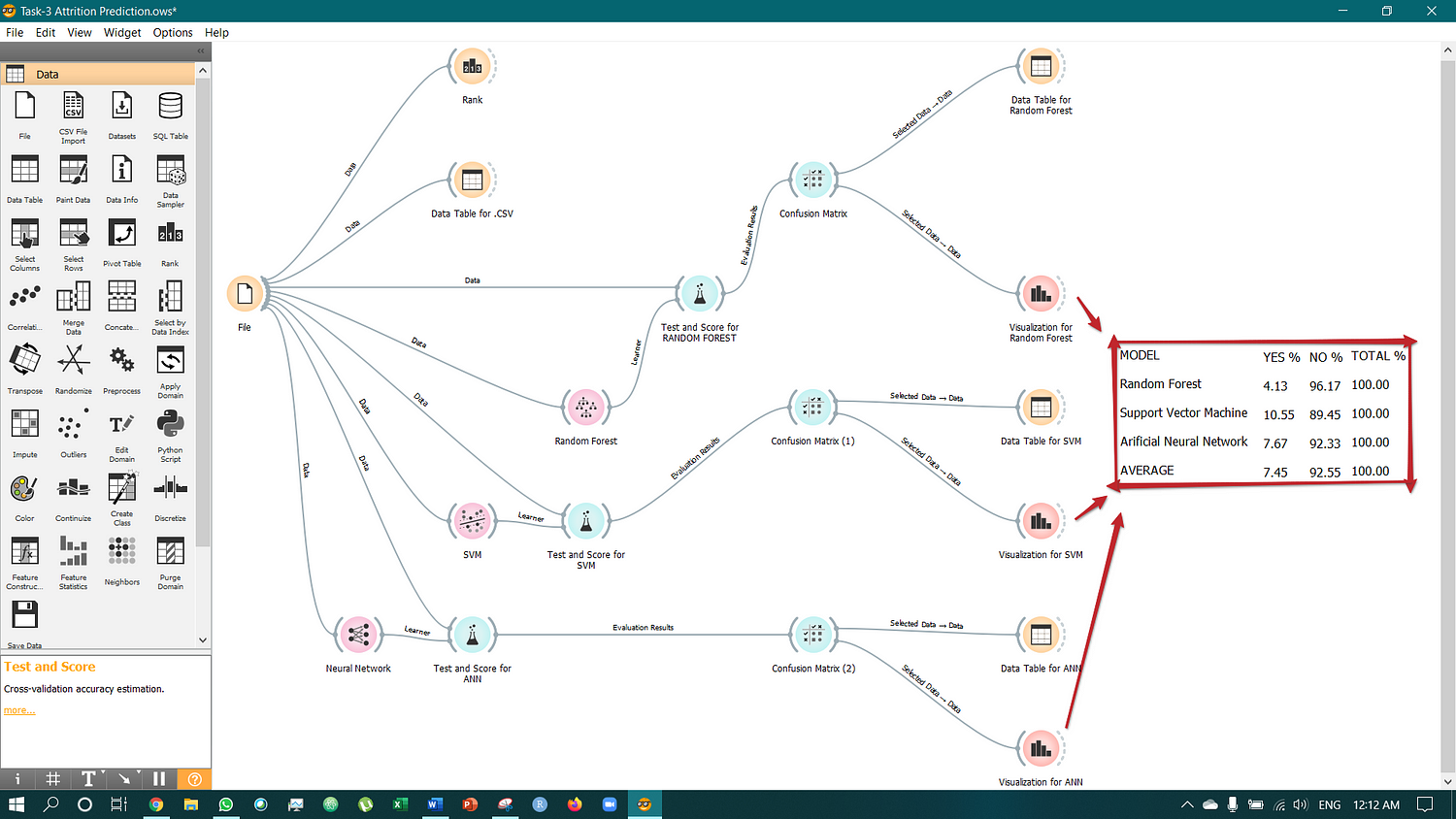
This is the full MODEL VIEW.
This dataset (.CSV file) is taken from Kaggle.
Contacts
In case you have any questions or any suggestions on what my next article should be about, please leave a comment below or E-mail me at [email protected]
If you want to keep updated with my latest articles and projects, follow me on Medium.
Connect with me via:



Very well written, hope to see a lot more articles soon!
Good work done👍 with excellent appropriate content..
Great work!