This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Introduction
Medical Imaging plays an important role in modern medicine. It allows us to visualize and examine the human body in depth which manifests structures inside our body in great detail. Nowadays, medical devices are constantly becoming more advanced in terms of — cost, precision, and safety — to improve the medical experience of the end-users.
After the recent boost in the field of AI, effective solutions came to light to solve countless intricate problems in multiple sectors using both machine learning and deep learning algorithms.
One such area that has gained continuous momentum in the aspect of research and development is the healthcare domain.
Few reasons why AI in healthcare is flourishing day by day are as follows:-
- The amount of data generated from medical devices is extensive- In an era where data is produced faster than its consumed, processing such a volume of data by humans alone induces a lot of physician burnout.
- Furnish high accuracy and precision- AI can enhance efficiency, reduce human errors, and achieve goals with the minimal human operation.
- Extremely cost-effective- developing and maintaining AI solutions are less expensive when compared to bringing in doctors from across the globe to screen a patient’s health conditions.
The flow of AI in medical imaging
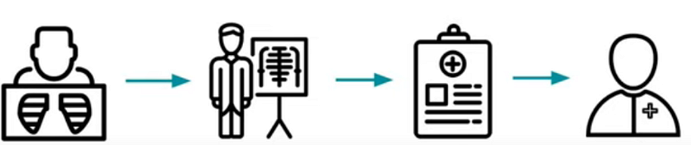
Fig:- Real-world flow of medical imaging- 1) Imaging tools, 2) radiologist to provide insights about images, 3) Picture archiving and communication system(PACS) to store image and patient data, 4) Diagnostic Clinician to examine patients and render a diagnosis. AI can be incorporated in any of the steps in the flow.
Now let us dive into each segment present in the flow in order to understand the process better. Firstly, imaging tools are used to generate image data using advanced imaging techniques.
Imaging tools
Diagnostic imaging tools help narrow the causes of an injury or illness and ensure that the diagnosis is accurate. These techniques include X-Rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
These imaging tools let your doctor “see” inside your body to get a “picture” of your bones, organs, muscles, tendons, nerves, and cartilage. Such that the doctor can determine if there are any abnormalities present.
Imaging tools are broadly classified into two categories: 2-Dimensional and 3-Dimensional imaging tools.
- 2D imaging: an imaging technique where pictures are taken from a single angle. Example:- X-Ray, Ultra Sound Scan, and Microscopy.
- 3D imaging: an imaging technique where pictures are taken from different angles to create a volume of images. Example:- Computed Tomography (CT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
The three most commonly used imaging tools include x-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) which are differentiated in the table below.
The generated data from the imaging tools are viewed by Radiologists, who are the primary readers of the image. They analyze the image and write a small note based on their observations, which is understood by a commoner without any medical knowledge. Radiologists create a specific file format called DICOM combining all the data present upon which the data is moved to a storage unit called PACS using specific file formats.
Picture Archiving and Communication System(PACS)
PACS Systems are a medical imaging technology that provides economical storage, retrieval, management, distribution, and presentation of medical images. Electronic images and reports are transmitted digitally via PACS systems. This eliminates the need to manually file, retrieve, or transport film jackets. It allows a healthcare organization (such as a hospital) to capture, store, view, and share all types of images both internally and externally.
Source: Wikipedia
Equivalent to pdfs and docs on our system folder, PACS stores files either in DICOM or NIFITI format. Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine(DICOM) is the standard for the communication and management of medical imaging information and related data. DICOM files consist of both patient information along with image information and modality.
The final step in the flow is a Diagnostic Clinician who takes the report provided by the radiologist from the storage system along with a few other parameters like, patient’s current condition/symptoms, other labs result, and prior medical knowledge to provide the diagnosis.
Different Machine Learning Techniques Used
1. Classification:– Classification is a technique where we categorize data into a given number of classes. The main goal of a classification problem here is to identify whether a disease or anomaly is present in the image.
Use case- Identifying the presence of Pneumonia from lung X-Rays.
2.Segmentation:- Segmentation in Image Processing is being used in the medical industry for efficient and faster diagnosis, detecting diseases by identifying specific pixels in an image that contains a structure or finding.
Use case- Identify tumors and calculate the size of the abnormality.
Source: Chimaera GmbH gallery
3. Localization:- Localization is used to narrow down the area of the image that may contain the abnormality.
Use case- Helps to draw attention to mass in breasts to identify the presence of Breast cancer.
The final step after building a machine learning model is to get medical approval from a certified regulatory body such as — FDA. FDA is a federal agency that is responsible for protecting public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and biological products. Only upon approval from the regulatory body allows us to use the model/solution to treat patients in the real-world. Which generally is a very time taking process with a lot of standards that need to be met.
AI in the healthcare industry can be used in various scenarios from disease detection to prioritization of records in PACS to fasten the retrieval process. However, any solution that is provided using algorithms irrespective of its high performance can only contribute to the betterment of the results but not to replace Radiologists/Doctors as the scope of the model is limited to a specific problem statement and will fail to take into account a holistic view of a patient’s condition.
The media shown in this article are not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.







