Introductory

Artificial Intelligence is purely math and scientific exercise but when it becomes computational, it starts to solve human problems.
Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence. ML is the study of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience. ML explores the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from data and make predictions on data. Based on more data, machine learning can change actions and responses which will make it more efficient, adaptable, and scalable.
Deep Learning is a technique for implementing machine learning algorithms. It uses Artificial Neural Networks for training data to achieve highly promising decision making. The neural network performs micro calculations with computational on many layers and can handle tasks like humans.
Types of Machine Learning

1. Supervised Learning: In a supervised learning model, the algorithm learns on a labeled dataset, to generate expected predictions for the response to new data.
Eg; For House price prediction, we first need data about houses such as; square foot, no. of rooms, the house has a garden or not, and so on features. We then need to know the prices of these houses ie; class labels. Now data coming from thousands of houses, their features, and prices, we can now train a supervised machine learning model to predict a new house’s price based on past experiences of the model.
Supervised Learning is of two types:
a) Classification: In Classification, a computer program is trained on a training dataset, and based on the training it categorizes the data in different class labels. This algorithm is used to predict the discrete values such as male|female, true|false, spam|not spam, etc.
Eg; Email spam detection, speech recognition, identification of cancer cells, etc.
Types of Classification Algorithms:
- Naive Bayes classifier
- Decision Trees
- Logistic Regression
- K-Nearest Neighbours
- Support vector machine
- Random forest classification
b) Regression: The task of the regression algorithm is to find the mapping function to map input variables(x) to the continuous output variable(y). Regression algorithms are used to predict continuous values such as price, salary, age, marks, etc.
Eg; Weather prediction, house price prediction, fake news detection, etc.
Types of Regression Algorithms:
- Simple linear Regression
- Multiple linear Regression
- polynomial Regression
- Decision Tree Regression
- Random forest Regression
- Ensemble Method
2. Unsupervised Learning: In an unsupervised learning model, the algorithm learns on an unlabeled dataset and tries to make sense by extracting features, co-occurrence, and underlying patterns on its own.
Eg; Anomaly detection, including fraud detection. Another example is Opening emergency hospitals to the maximum prone to accident areas. K-means clustering will group these locations of max prone areas into clusters and define a cluster center(ie;hospital) for each cluster(ie;accident prone areas).
Types of Unsupervised Learning:
- Clustering
- Anomaly detection
- Association
- Autoencoders
- Latent variable models
- Neural Networks
3. Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where the model learns to behave in an environment by performing some actions and analyzing the reactions. RL takes appropriate action in order to maximize the positive response in the particular situation. The reinforcement model decides what actions to take in order to perform a given task that’s why it is bound to learn from the experience itself.
Eg; Lets take an example of a baby when she is learning how to walk. In the first case, when the baby starts walking and makes it to the chocolate since the chocolate is the end goal for the baby and the response of a baby is positive as she is happy. In the second case, when the baby starts walking and while walking she gets hit by the chair and couldnot reach to the chocolate then she starts crying which is a negative response. It is to say that how we human learn from trail and error. Here, the baby is “agent” , chocolate is the “reward” and many hurdles in between. Now the agent tries several ways and finds out the best possible path to reach the reward.
Machine Learning Life cycle
Machine Learning helps to increase the performance and productivity of the task. It includes learning and self-correction when introduced with new data.
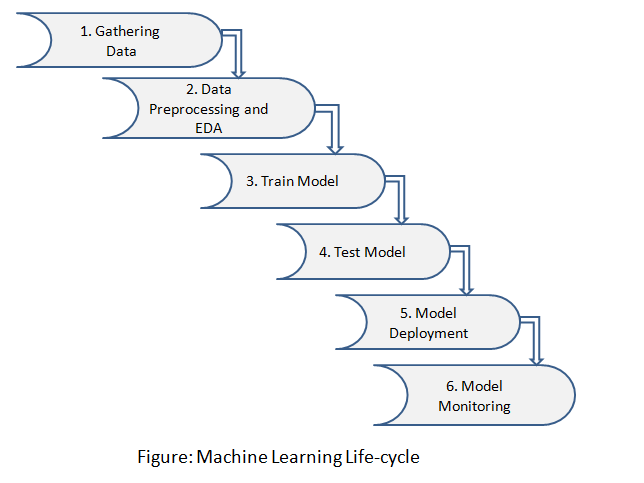
Machine Learning lifecycle involves six major steps:
Step 1: Gathering Data
Identify various data sources such as Kaggle and collect the required dataset
Step 2: Data Preprocessing and EDA
In this step, we do an analysis of the data for missing values, duplicate data, invalid data using different analytical techniques. And also preprocessing the data for feature extractions, feature analysis, and data visualization.
Step 3: Train Model
We use a dataset to train the model using various machine learning algorithms. Training a model is important so that it can understand the various patterns, rules, and features.
Step 4: Test Model
In this step, we check for the accuracy of our model by providing a test dataset to the trained model.
Step 5: Model Deployment
Model deployment means integrating a machine learning model into an existing production environment that takes input and returns output to make business decisions based on data. Various technologies that you can use to deploy your machine learning models are listed:
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- AWS SageMaker
- MLFlow
- Azure Machine Learning Service
Step 6: Model Monitoring
After deployment of the model here comes model monitoring which monitors your machine learning models for factors like errors, crashes, and latency and most importantly to ensure that your model is maintaining the desired performance. Model monitoring is very important because your models will degrade over time due to several factors such as unseen data, changes in the environment, and relationships between variables.
Some Real-World Applications of Machine Learning
- Automatic Language Translation in Google Translate
- Faster route selection in Google Map
- Driverless/Self-driving car
- Smartphone with face recognition
- Speech Recognition
- Ads Recommendation System
- Netflix Recommendation System
- Auto friend tagging suggestion in Facebook
- Stock market trading
- Fraud Detection
- Weather Prediction
- Medical Diagnosis
- Chatbot
- Machine Learning in Agriculture
Benefits of machine learning
- Work Automation
- Powerful predictive Ability
- Increased in sales in the e-commerce market
- ML benefits in the medical domain for enhancing medical diagnosis, drug development
- Machine Learning is used in robotic medical surgery
- ML in finance increases productivity enhances revenue and gives secure transactions
- Modeling the data to make useful decisions
Summary
Machine Learning can be used in almost all sectors of human life to make our work efficient, robust, and Uncomplicated. As we know everything comes with its own pros and cons, machine learning has also its disadvantages such as with the increase in machine learning many people may lose their current scenario job. But most importantly it is beneficial in the long run for humankind.
The media shown in this article are not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.






Nice article
The author has put in a lot of effort to keep it simple and informative. Really enjoyed 😊 it.
very nicely presented , thank you , may God bless you.. ...