This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon
Introduction
This article is part of an ongoing blog series on Natural Language Processing (NLP). In the previous article, we completed our discussion on Topic Modelling Techniques. Now, in this article, we will be discussing an important application of NLP in Information Retrieval.
So, In this article, we will discuss the basic concepts of Information Retrieval along with some of the models that are used in Information Retrieval.
NOTE: In this article, we will discuss only the basics related to Information Retrieval. If you want to learn more about Information Retrieval, you can learn on your own otherwise you can ping me for making a blog series also on Information Retrieval in the Future.
This is part-20 of the blog series on the Step by Step Guide to Natural Language Processing.
Table of Contents
1. What are Information Retrieval (IR) Systems?
2. Basics of IR Systems
3. Classical Problem in IR Systems
4. What are IR Models?
5. What are the types of IR Models?
6. What are Boolean Models?
7. Advantages and Disadvantages of Boolean Models
8. What are Vector Space Models?
9. How to Evaluate IR Systems?
Information Retrieval Systems

Image Source: Google Images
Firstly we will discuss what exactly is Information Retrieval?
Information retrieval is defined as the process of accessing and retrieving the most appropriate information from text based on a particular query given by the user, with the help of context-based indexing or metadata.
Google Search is the most famous example of information retrieval.
Now let’s discuss what are Information Retrieval Systems?
An information retrieval system searches a collection of natural language documents with the goal of retrieving exactly the set of documents that matches a user’s question. They have their origin in library systems.
These systems assist users in finding the information they require but it does not attempt to deduce or generate answers. It tells about the existence and location of documents that might consist of the required information that is given to the user. The documents that satisfy the user’s requirement are called relevant documents. If we have a perfect IR system, then it will retrieve only relevant documents.
Basics of IR Systems
Image Source: Google Images
From the above diagram, it is clear that a user who needs information will have to formulate a request in the form of a query in natural language. After that, the IR system will return output by retrieving the relevant output, in the form of documents, about the required information.
The step by step procedure of these systems are as follows:
- Indexing the collection of documents.
- Transforming the query in the same way as the document content is represented.
- Comparing the description of each document with that of the query.
- Listing the results in order of relevancy.
Retrieval Systems consist of mainly two processes:
- Indexing
- Matching
Indexing
It is the process of selecting terms to represent a text.
Indexing involves:
- Tokenization of string
- Removing frequent words
- Stemming
Two common Indexing Techniques:
- Boolean Model
- Vector space model
Matching
It is the process of finding a measure of similarity between two text representations.
The relevance of a document is computed based on the following parameters:
1. TF: It stands for Term Frequency which is simply the number of times a given term appears in that document.
TF (i, j) = (count of ith term in jth document)/(total terms in jth document)
2. IDF: It stands for Inverse Document Frequency which is a measure of the general importance of the term.
IDF (i) = (total no. of documents)/(no. of documents containing ith term)
3. TF-IDF Score (i, j) = TF * IDF
Classical Problem in IR Systems
The main aim behind IR research is to develop a model for retrieving information from the repositories of documents. Ad-hoc retrieval problem is the classical problem in IR systems.
Now, let’s discuss what exactly is ad-hoc retrieval?
In ad-hoc retrieval, the user must have to enter a query in natural language that describes the required information. Then the IR system will return the output as the required documents that are related to the desired information.
For Example, suppose we are searching for something on the Internet and it gives some exact pages that are relevant as per our requirement but there can be some non-relevant pages too. This is due to the ad-hoc retrieval problem.
Aspects of Ad-hoc Retrieval
The aspects of ad-hoc retrieval that are addressed in IR research are as follows:
- How users with the help of relevant feedback can improve the original formulation of a query?
- How to implement database merging, i.e., how results from different text databases can be merged into one result set?
- How to handle partly corrupted data? Which models are appropriate for the same?
Information Retrieval Models
Information retrieval models predict and explain what a user will find in relevance to the given query. These are basically a pattern that defines the above-mentioned aspects of retrieval procedure that we discussed in ad-hoc retrieval and consists of the following:
- A model for documents.
- A model for queries.
- A matching function that compares queries to documents.
Mathematically, a retrieval model consists of the following components:
- D: Representation for documents.
- R: Representation for queries.
- F: The modeling framework for D, Q along with the relationship between them.
- R (q, di): A ranking or similarity function that orders the documents with respect to the query.
Types of IR Model
The following are three models that are classified for the Information model (IR) model:
Classical IR Models
These are the simplest and easy-to-implement IR models. These are based on mathematical knowledge that was easily recognized and understood as well.
Following are the examples of classical IR models:
- Boolean models,
- Vector models,
- Probabilistic models.
Non-Classical IR Models
These are completely opposite to the classical IR models. These are based on principles other than similarity, probability, Boolean operations.
Following are the examples of Non-classical IR models:
- Information logic models,
- Situation theory models,
- Interaction models.
Alternative IR Models
It is the enhancement of the classical IR model that makes use of some specific techniques from some other fields.
Following are the examples of Alternative IR models:
- Cluster models,
- Fuzzy models,
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) models.
Boolean Model
Boolean Model is the oldest model for Information Retrieval (IR). These models are based on set theory and Boolean algebra, where
- Documents: Sets of terms
- Queries: Boolean expressions on terms
As a response to the query, the set of documents that satisfied the Boolean expression are retrieved.
The boolean model can be defined as:
D: It represents a set of words, i.e, the indexing terms present in a document. Here, each term is either present (1) or absent (0) in the document.
Q: It represents a Boolean expression, where terms are the index terms and operators are logical products such as:
- AND,
- Logical sum − OR,
- Logical difference − NOT.
F: It represents a Boolean algebra over sets of terms as well as over sets of documents.
If we talk about the relevance feedback, then in the Boolean IR model the Relevance prediction can be defined as follows:
R: A document is predicted as relevant to the query expression if and only if it satisfies the query expression as −
((𝑡𝑒𝑥𝑡 ˅ 𝑖𝑛𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛) ˄ 𝑟𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑒𝑣𝑎𝑙 ˄ ˜ 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑜𝑟𝑦)
We can explain this model by a query term as an unambiguous definition of a set of documents.
For Example, suppose we have the query term “analytics”, which defines the set of documents that are indexed with the term “analytics”.
Now, think on what is the result after we combining terms with the Boolean ‘AND’ Operator?
After doing the ‘AND’ operation, it will define a document set that is smaller than or equal to the document sets of any of the single terms.
For Example, now we have the query with terms “Vidhya” and “analytics” that will produce the set of documents that are indexed with both the terms. In simple words, the document set with the intersection of both the sets described here.
Now, also think on what is the result after combining terms with the Boolean ‘OR’ operator?
After doing the ‘OR’ operation, it will define a document set that is bigger than or equal to the document sets of any of the single terms.
For Example, now we have the query with terms “Vidhya” or “analytics” that will produce the set of documents that are indexed with either the term “Vidhya” or “analytics”. In simple words, the document set with the union of both sets described here.
Advantages of the Boolean Model
Following are the advantages of the Boolean model:
1. It is the simplest model based on sets.
2. It is easy to understand and implement.
3. It only retrieves exact matches.
4. It gives the user, a sense of control over the system.
Disadvantages of the Boolean Model
Following are the disadvantages of the Boolean model:
1. The model’s similarity function is Boolean. Hence, there would be no partial matches. This can be annoying for the users.
2. In this model, the Boolean operator usage has much more influence than a critical word.
3. The query language is expressive, but it is complicated too.
4. There is no ranking for retrieved documents by the model.
Vector Space Model
As we have seen that there are some limitations in the Boolean model, so we have come up with a new model which is based on Luhn’s similarity criterion, which states that “the more two representations agreed in given elements and their distribution, the higher would be the probability of their representing similar information”.
To understand more about the vector Space model, you have to understand the following points:
1. In this model, the index representations (documents) and the queries are represented by vectors in a T dimensional Euclidean space.
2. T represents the number of distinct terms used in the documents.
3. Each axis corresponds to one term.
4. Ranked list of documents ordered by similarity to the query where the similarity between a query and a document is computed using a metric on the respective vectors.
5. The similarity measure of a document vector to a query vector is usually the cosine of the angle between them.
Image Source: Google Images
Evaluation of IR Systems
The two common effective measures for evaluating IR systems are as follows:
- Precision
- Recall
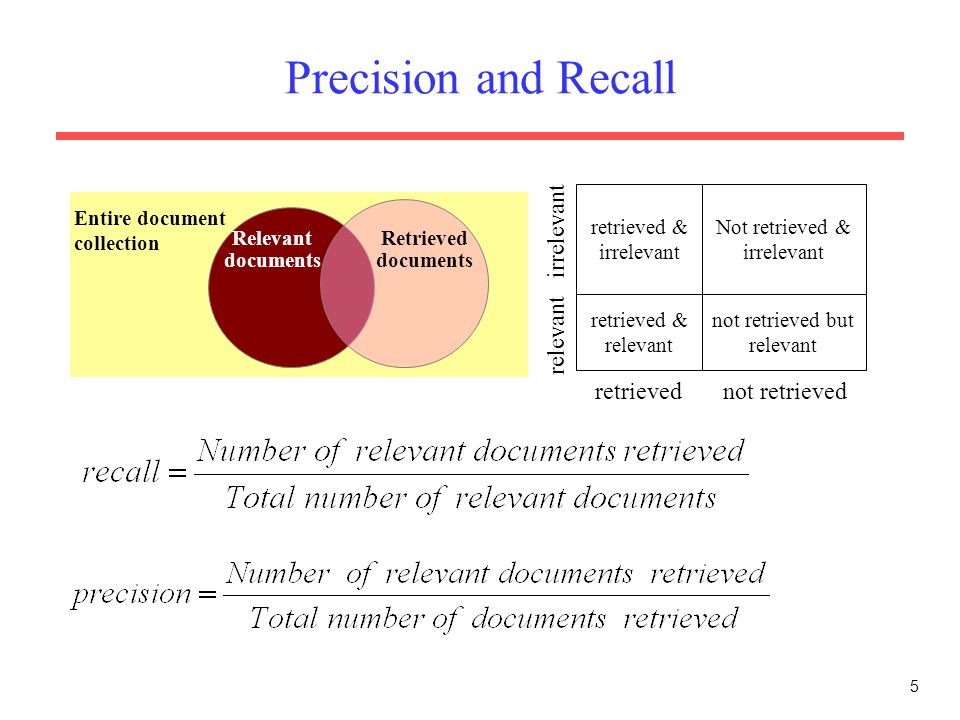
Image Source: Google Images
Precision: Precision is the Proportion of retrieved documents that are relevant.
Recall: The recall is the Proportion of relevant documents that are retrieved.
Ideally both precision and recall should be 1. In practice, these are inversely related.
This ends our Part-20 of the Blog Series on Natural Language Processing!
Other Blog Posts by Me
You can also check my previous blog posts.
Previous Data Science Blog posts.
Here is my Linkedin profile in case you want to connect with me. I’ll be happy to be connected with you.
For any queries, you can mail me on [email protected]
End Notes
Thanks for reading!
I hope that you have enjoyed the article. If you like it, share it with your friends also. Something not mentioned or want to share your thoughts? Feel free to comment below And I’ll get back to you. 😉




Very informative, really it is much helpful for understanding the basics of deep learning and machine learning.