This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Introduction
In this article, we are going to introduce you to Docker tutorial and will further learn the basic commands as well from installing docker, Pulling images from the hub to running Linux machines in docker.

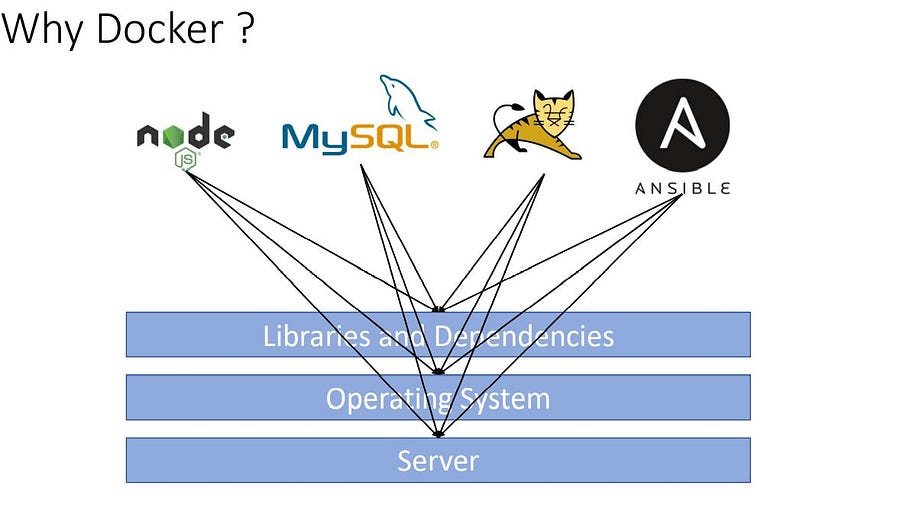
Let’s first understand the challenges we face while deploying an application or server and then how docker solved this problem
When we run and deploy any application or a machine learning model or application or a database or some third parties package they need some libraries and dependencies, Working on multiple applications requires different versions of dependencies can lead to a dependencies conflict.
Using separate machines or packaging all the dependencies with their application could solve this problem.
What is Docker?
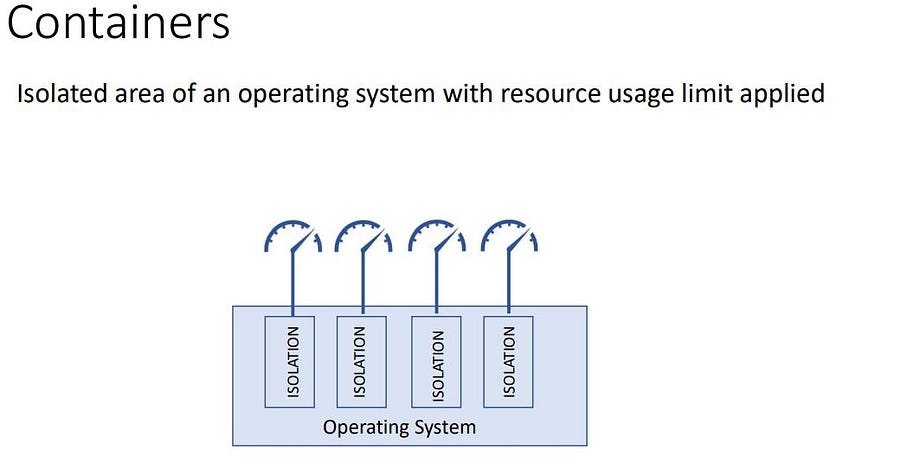
Docker is a containerization and manager tool, Docker means Develop, Ship, and Run anywhere no matter what operating system we are using and the environment. Docker is a kind of isolated space where an application runs by using system resources.
Note: In this article, I have used the word Capsule for the word Container. Containers are often called Capsules.
Features of Docker
Docker is a full package solution for an app migration. It comes with the following features:
- Containers are light and flexible compared to running an application on virtual machines. It doesn’t depend on the version of the Operating System
- It can be easily deployed to the cloud server or local servers with ease.
- easily scalable. Supports Scaling with ease.
Docker Components
Docker is made up of 3 components, these components are responsible for their own tasks from building, and running to creating capsules.
- Docker Engine ( Used for building and creating docker containers).
- Docker Hub ( This is a place where you can host your docker images).
- Docker Compose ( It defines applications )
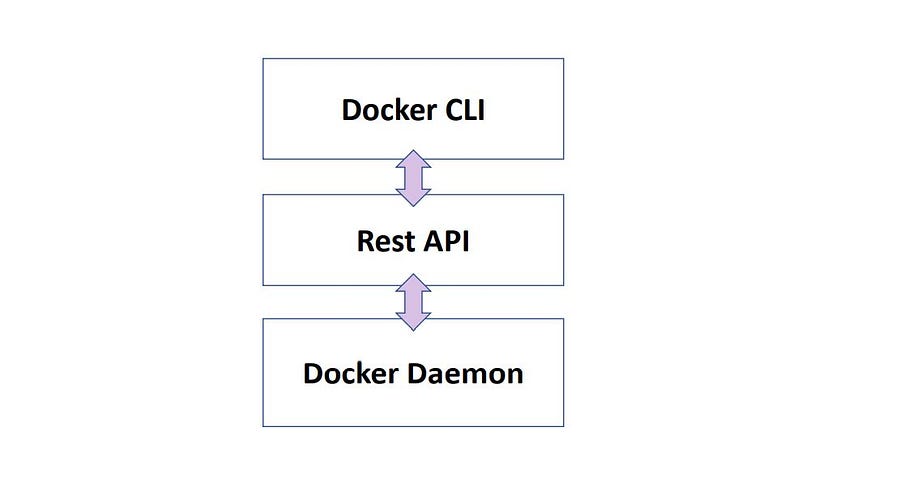
Docker Architecture
Docker Architecture consists of the Units that the docker is made up of these units are responsible for their own pre-defined tasks.
- Docker CLI ( Command Line Interface)
- Rest API ( connects docker daemon)
- Docker Daemon ( Responsible for Objects, Images, Containers, Engines, etc.)
After 2015, Docker redesigned itself according to standardization and ensured support for the Runtime Specification and Image Specification.
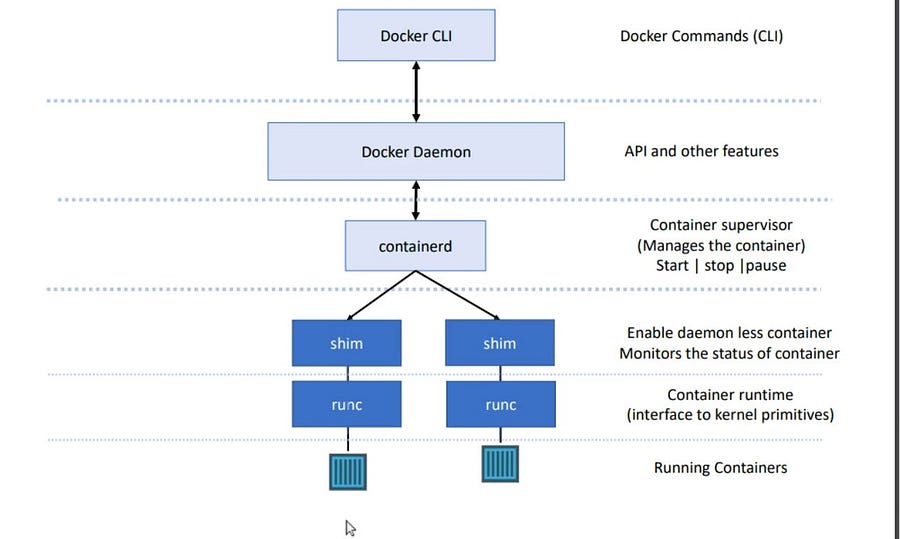
- Runtime Specification defines the lifecycle of the capsule technology.
- Earlier Docker Daemon was responsible for all the processes in docker but after the Standardization
runc(Container Runtime) is responsible for spinning the Image. In Container orchestration tools like Kubernetes, we only need to install a container runtime to spin a container on its pod. shimrunc + shimmakes docker daemon less.Shimmonitors the running capsules.
Docker Setup
The complexity of docker installation depends on the operating system. Use this link for installing docker in your system.
For this article, I’ll be using docker on my Linux machine.
After installing verify if docker is installed by typing the code
$ docker --version
Managing Docker as a Service
Getting the Status of Docker-Engine if it’s up or not.
$ systemctl status docker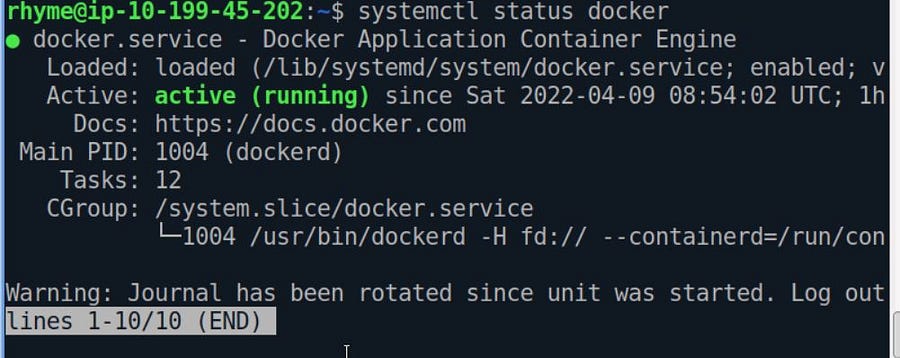
As you see our docker engine is up and active. It can be easily stopped by the command
# stops the docker engine
$ systemctl stop docker
#Starts the docker engine
$ systemctl start dockerStarting the docker in debug mode if the docker service is facing errors.
$ sudo dockerd --debugDocker CLI & Deploy Your first Container
A docker image contains all the dependencies, source files, and tools needed to run an application. A Docker image is a source file that creates a capsule.
A capsule is a running instance created by a docker image.
Docker Hello-world
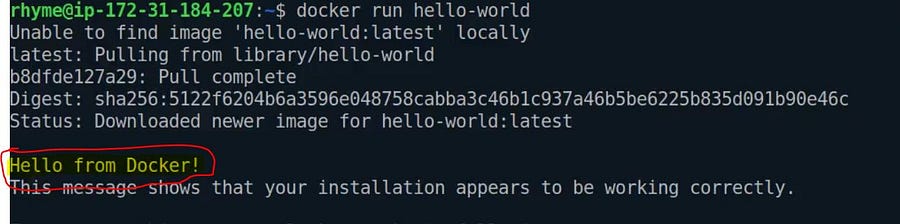
Docker hello-world is an image file that makes a docker capsule and that prints hello world.
docker run hello-world
It will first check the hello-world image file in its local registry. If not found, it pulls the image file from the docker hub ( default public registry) and runs the capsule.
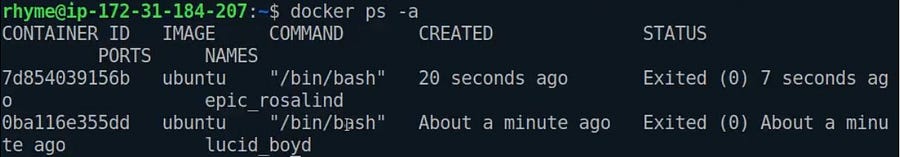
Printing All the Containers
List only already running capsules
docker psList down all the docker-capsules
docker ps -a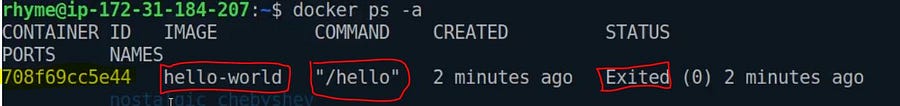
The highlighted part with the yellow colour is the Capsule ID/Container ID, and whenever we want to select a specific capsule, we use its Container ID.
Note: We don’t need to write the whole container-ID, if the container-ID is unique we can only provide its first few starting characters.
docker rm 70This command will remove the Capsules whose container ID starts with 70.
List Down All the Images
This lists all the docker images available in our local registry.
docker images

Deleting an Image
If you want to delete an image from our local repository, we need to execute the following commands.
docker image rm ID_OF_CONTAINER
#---OR----
docker image rm Image_Name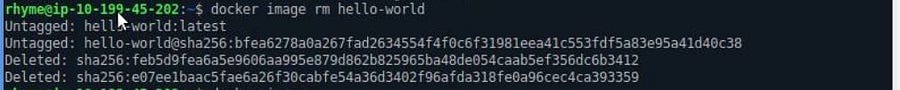
Pulling Image from Docker Hub
Any Image file available on the docker hub or from other sources can be pulled in the local docker registry using the pull command.
The command docker pull only download the image file; it won’t make any capsule using the image file unless we ask docker to do that.

Docker Inspect
The Docker inspect is a powerful command that lets us examine a container’s information, exposed ports, and network properties.
Inspect command can be used to inspect an image file or a capsule.
#Inspecting docker image
docker image inspect IMAGE_ID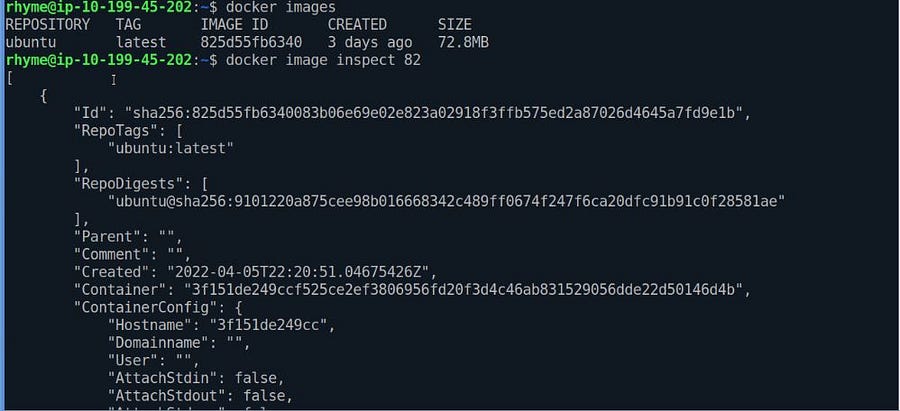
# Docker Container Inspect
docker container inspect ID_OF_CONTAINER
# --- OR----
docker inspect ID_OF_CONTAINER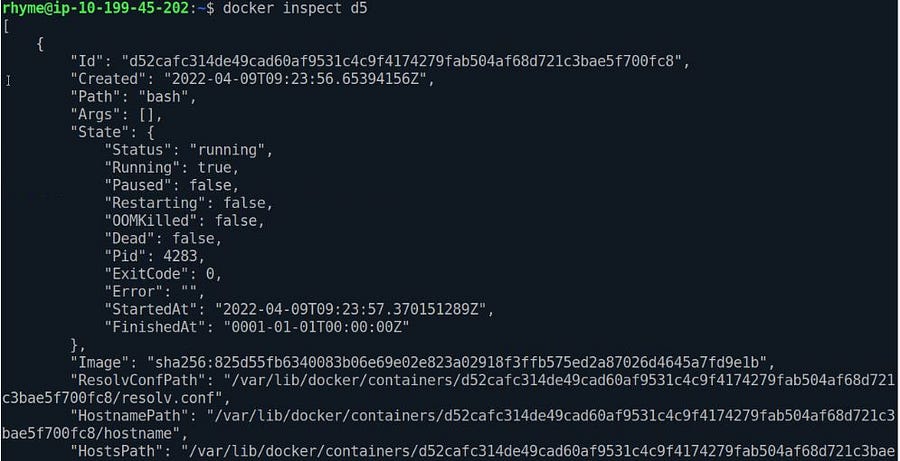
Running Ubuntu in Docker
To run a Linux as a docker capsule, we first need to pull the ubuntu image file.
docker pull ubuntu
docker images
Now we have an ubuntu image file in our local registry. It’s time to spin the capsule using the image file.
docker run -it ubuntu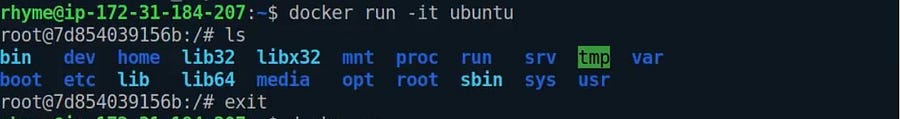
- Here
-itsignifies that we want our capsule to run in interactive mode. It will wait for our response. - We can run the Linux commands now to check if our Linux capsule is up or not.
- Ubuntu uses the command “/bin/bash” to enter the capsule. We can use the terminal of ubuntu in our spinning ubuntu capsule using the command “bin/bash”.
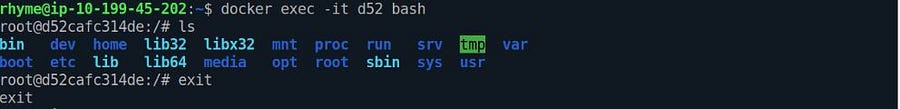
docker execThis command runs a new command in already spinning capsules.
Stopping the Running Capsules
We need its id to stop a Running capsule and run this command.
ˆdocker stop ID_OF_CONTAINER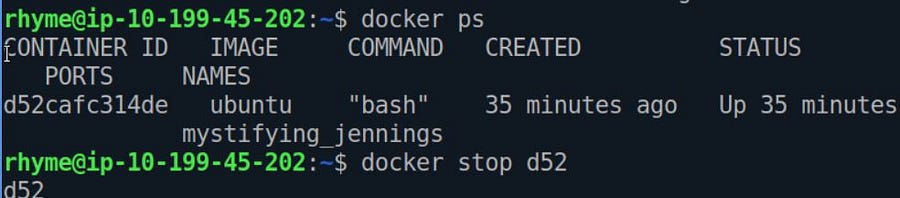
Conclusion
In this article, we learned some basics codes of docker to manage docker services and performed some Linux-based docker commands.
- We discussed commands for managing capsules, docker-images, and the docker engine pulling Images from the hub to the local repository.
- We don’t need to install the docker to run its capsule, and we only need docker runtime to run a deployment.
- You can create Docker images from the project files
- Linux natively supports docker.
Docker became daemon-less since a capsule no longer needs docker daemon to run. Docker provides storage layers where the capsules keep their files, and even if the tablet crashes, it won’t delete the stored files.
Feel Free to Connect with me on LinkedIn.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.





