This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Introduction
Hello friends, In this article, we will discuss End to End NLP pipeline in an easy way. If we have to build any NLP-based software using Machine Learning or Deep Learning then we can use this pipeline. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is one of the fastest-growing fields in the world. Natural language processing (NLP) is a field of artificial intelligence in which computers analyze, understand, and derive meaningful information from human language in a smart and useful way. The set of ordered stages one should go through from a labeled dataset to creating a classifier that can be applied to new samples is called the NLP pipeline.
NLP Pipeline
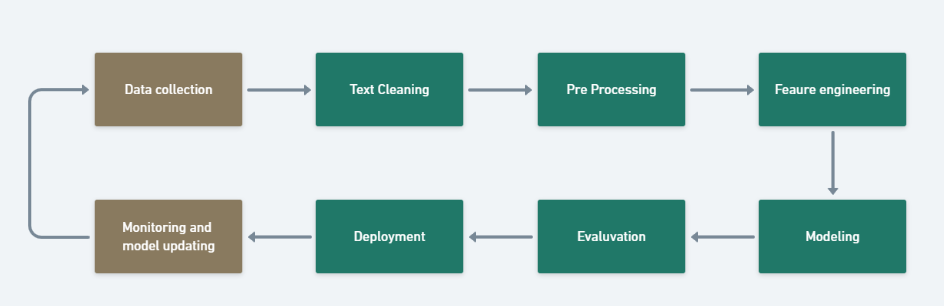
NLP Pipeline is a set of steps followed to build an end to end NLP software.
Before we started we have to remember this things pipeline is not universal, Deep Learning Pipelines are slightly different, and Pipeline is non-linear.
1. Data Acquisition
In the data acquisition step, these three possible situations happen.
1. Data Available Already
A. Data available on local Machine – If data is available on the local machine then we can directly go to the next step i.e. Data Preprocessing.
B. Data available in Database – If data is available in the database then we have to communicate to the data engineering team. Then Data Engineering team gives data from the database. data engineers create a data warehouse.
C. Less Data Available – If data is available but it is not enough. Then we can do data Augmentation. Data augmentation is to making fake data using existing data. here we use Synonyms, Bigram flip, Back translate, or adding additional noise.
2. Data is not available in our company but is available outside. Then we can use this approach.
A. Public Dataset – If a public dataset is available for our problem statement.
B. Web Scrapping – Scrapping competitor data using beautiful soup or other libraries
C. API – Using different APIs. eg. Rapid API
3. Data Not Available – Here we have to survey to collect data. and then manually give a label to the data.
2. Text Preprocessing
So Our data collection step is done but we can not use this data for model building. we have to do text preprocessing.
This text preprocessing I have already explained in my previous blog. Click here.
Steps –
1. Text Cleaning – In-text cleaning we do HTML tag removing, emoji handling, Spelling checker, etc.
2. Basic Preprocessing — In basic preprocessing we do tokenization(word or sent tokenization, stop word removal, removing digit, lower casing.
3. Advance Preprocessing — In this step we do POS tagging, Parsing, and Coreference resolution.
3. Featured Engineering
Feature Engineering means converting text data to numerical data. but why it is required to convert text data to numerical data?. because our machine learning model doesn’t understand text data then we have to do feature engineering. This step is also called Feature extraction from text. I have already written a complete guide on Feature extraction techniques used in NLP. Click here.
In this step, we use multiple techniques to convert text to numerical vectors.
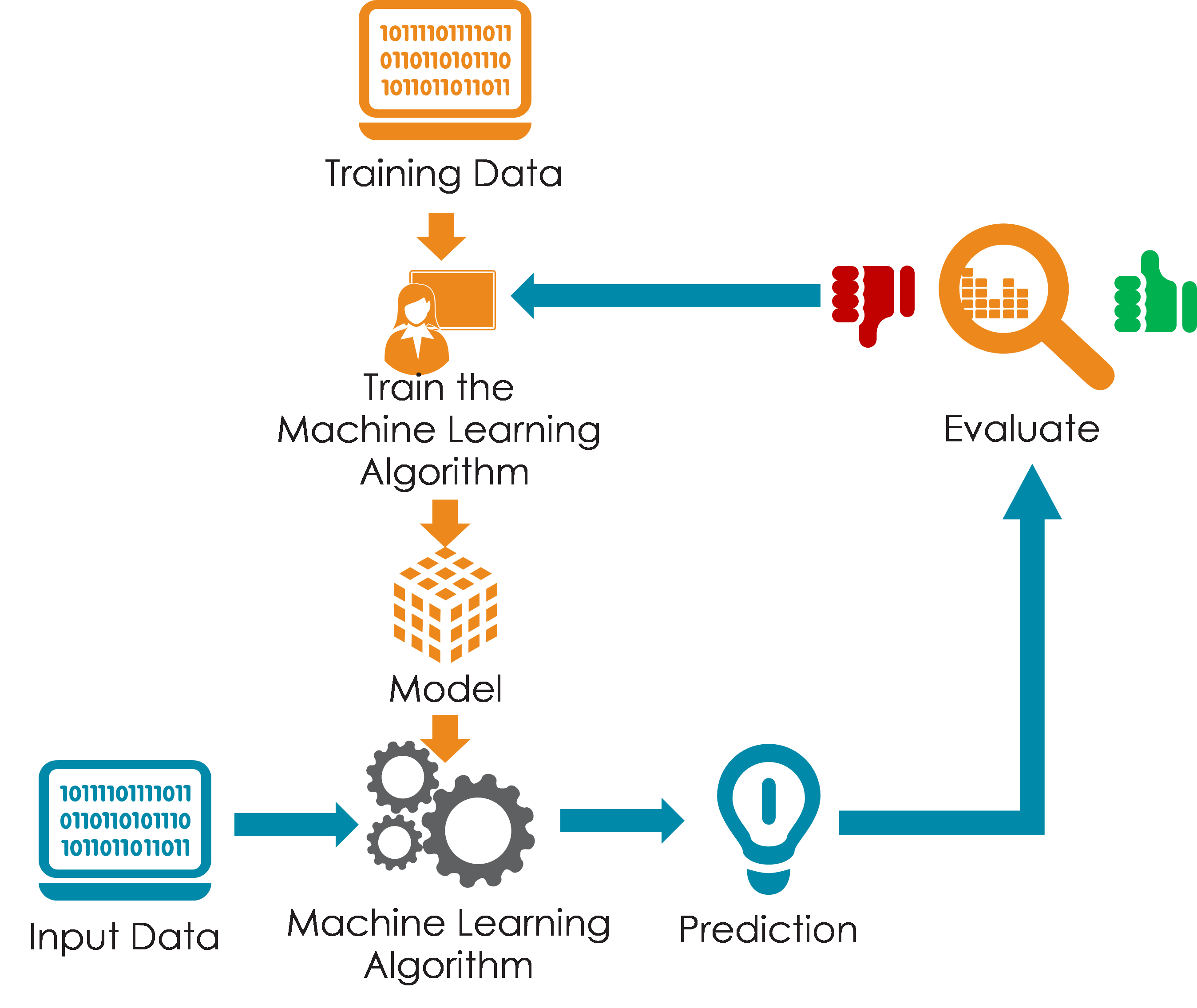
4. Modelling/Model Building
In the modeling step, we try to make a model based on data. here also we can use multiple approaches to build the model based on the problem statement.
Approaches to building model –
1. Heuristic Approach
2. Machine Learning Approach
3. Deep Learning Approach
4. Cloud API
Here comes one question, Which approach do we have to use? Right? then this is based on two things,
1. Amount of data
2. Nature of the problem.
If we have very less data then we can not use ML or DL approach then we have to use the heuristic approach. but if we have a good amount of data then we can use a machine learning approach and if we have a large amount of data then we can use a deep learning approach.
second, based on the nature of the problem, we have to check which approach gives the best solution because if the nature of the problem changes all things get changed.
5. Model Evaluation
In the model evaluation, we can use two metrics Intrinsic evaluation and Extrinsic evaluation.
Intrinsic evaluation – In this evaluation, we use multiple metrics to check our model such as Accuracy, Recall, Confusion Metrics, Perplexity, etc.
Extrinsic evaluation — This evaluation is done after deployment. This is the business-centric approach.
6. Deployment
In the deployment step, we have to deploy our model on the cloud for the users. and users can use this model. deployment has three stages deployment, monitoring, and retraining or model update.
Three stages of deployment –
1. Deployment – model deploying on the cloud for users.
2. Monitoring – In the monitoring phase, we have to watch the model continuously. Here we have to create a dashboard to show evaluation metrics.
3. Update- Retrain the model on new data and again deploy.