This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Introduction
A Database is a collection of inter-related data, and a Database Management System is a set of programs that helps users create and maintain this data. DBMS is a computer-based data record-keeping system. DBMS provides enhanced security for storing and retrieving data and has various techniques to reduce Redundancy and Duplication of Data. But, ever wondered why DBMS? Didn’t we have alternate solutions for storing data? What makes Database a go-to option for every developer to store their data?
In this article, We will have a walkthrough of the traditional File systems, their failures, and how DBMS helps overcome them. We will also learn about Data Abstraction, schemas, instances, and different DBMS types.
File Systems
A file system is a software application that keeps files on a computer device organized and updated. It controls how data is stored and retrieved in blocks of files. Traditionally, database applications were built directly with the help of file systems. Data is stored in a file, which is located in the directory. A directory can have many other files or be a part of another directory. File System follows a hierarchical approach to storing data.

The file system stores the data about the data, i.e., the Metadata. Metadata includes the name of the file, length of the file, location of the file, etc. The file system allocates memory for the files in variable block sizes. Sometimes, the file size is too large compared to the required space. This gives rise to an unused block of space called the slack space. The file system is committed to maintaining the changes to the data/files by regularly updating the metadata and the file directories. The file system provides multiple ways to handle unauthorized data access. It includes passwords stored in the metadata or permissions in the form of permission bits and access control lists.
Drawbacks of File Systems
1. Data Redundancy: duplication of data in different files.
2. Data access difficulty: A new program every time to carry out new tasks.
3. Data Isolation: Multiple files and file format makes data isolation difficult.
4. Integrity problem: Managing and updating new constraints is difficult.
5. Atomicity: Failure in the middle of an operation may lead to an inconsistent state with partial updates only.
6. Security problems: Difficult to restrict user access to all the data.
Solution- DataBase Management System
A database is a collection of data used to efficiently and optimally search, insert, and delete data. A database management system is a software application to manage the database. DBMS examples include Oracle SQL, MySQL, and MongoDB, which provide a platform to create, modify and delete databases and help store and retrieve data. The main purpose of introducing DBMS was to overcome the failures of the File systems.
Data Abstraction:
Data abstraction is hiding the user from unnecessary or irrelevant data. It offers a distinct perspective and aids in achieving data independence, which enhances data security.
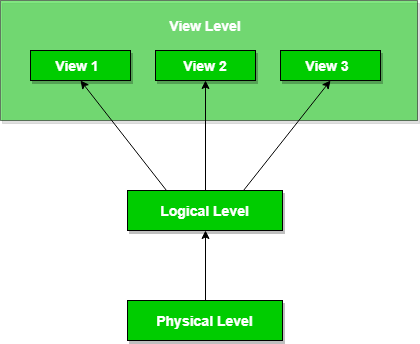
The 3 levels of Abstraction are:
1. Physical Level(lowest level): It describes how a record is stored
2. Logical Level(conceptual level): It describes the data and the relationship between them.
3. View Level(highest level): Application programmers hide datatype details as well as other important data from some users for security purposes.
Source: GeeksForGeeks
Schema and Instances:
Schema is the logical structure of the database, while Instance is the actual content of the database at a particular point in time.

Types of DBMS

- Centralized Database: A database located, kept, and maintained in a single location is referred to as a centralized database (often abbreviated CDB). Most frequently, this location is a mainframe computer, server CPU, or other central computer or database system.
- Relational Database: To organize data in tables, rows, and columns, we use a relational database (RDB). By connecting tables, an RDB may create links, or relationships, between information, making it simple to comprehend and acquire insights into how different data points are related. e.g., MySQL, Oracle SQL
- Distributed Database: A distributed database comprises two or more files spread across various places, whether the same network connects them. The database is split up into different physical places for storage and processing, and numerous database nodes are involved.
- NoSQL: Unlike relational databases, NoSQL databases store data in an unstructured format. As a result, we categorize them as “non-SQL” or “Non-Relational Database” and divide them into different flexible data model categories. Pure document databases, key-value stores, wide-column databases, and graph databases are some examples of NoSQL database types. For instance, MongoDB is a document database while Neo4J is a graph-based NoSQL database.
Features of DBMS

Source: educba
- Data Integrity: Data integrity is all about the accuracy and consistency of the data in the database. Given that DBMS contains numerous databases, it is crucial. These databases all contain information that is accessible to several individuals. As a result, it is crucial to guarantee that the data is accurate and consistent across all databases for all users.
- Data Security: A database’s key notion is data security. Under no circumstances should unauthorized users be permitted access to the database, which violates the integrity constraints. A DBMS gives businesses a better foundation for data privacy, enabling them to offer increased data security.
- Reduced Data Inconsistencies: When distinct versions of the same data appear in different locations, data inconsistency exists between files. The database guarantees data consistency and eliminates data duplication. Additionally, there is no data inconsistency because all users promptly reflect database updates.
- Faster Data Access: The DBMS assists users in providing quick responses to queries, resulting in accurate and quick data access. Validity, precision, and the time required to read the data are all ultimately improved by higher quality. Although it offers a framework to simplify improving data quality, it does not ensure the quality of the data.
- Simplicity: DBMS provides a clear, straightforward, logical view that helps us understand data better. Many activities, including deletion, insertion, and creation, are simple while using DBMS.
- Recovery and Backup: DBMS handles recovery and backup automatically. In addition, it repairs databases after crashes or system failures to prevent them from returning to their original state.
Conclusion
Traditionally, File systems were used for storing and maintaining data in an environment. The drawbacks of the File systems made it difficult for developers and users to continue with file systems. Hence, an efficient storing and retrieving technique – Database Management System was introduced to counter the drawbacks of the File systems. DBMS provides improvised data integrity, security, faster access, and the recovery and backup feature. It also reduces data inconsistencies and redundancies through various techniques. Hence, DBMS was replaced with the traditional file systems.
In this article,
- We learned about the traditional data storing technique, i.e., the file system
- We saw its drawbacks
- We learned about DBMS and types of DBMS
- We finally saw the features of DBMS, which helped us overcome the drawbacks of File systems.
Thank you for reading the article. If you like my article, feel free to connect with me on Linkedin.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.