Deep within the bustling streets of Shenzhen’s Huaqiangbei electronics area, an underground market for high-end Nvidia AI chips has emerged. This hidden world operates discreetly as vendors navigate export restrictions and intense demand for these cutting-edge processors. In this article, we delve into the intriguing details of China’s clandestine trade in Nvidia chips, revealing the challenges buyers and sellers face in a politically charged landscape.
Also Read: NVIDIA Towards Being The First Trillion Dollar AI Chip Company
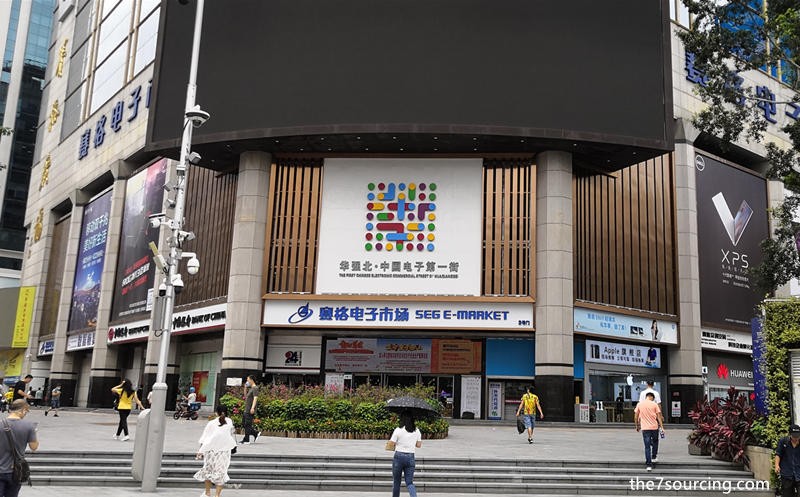
The Secret of SEG Plaza: Unveiling China’s Underground Chip Market
Located within the iconic SEG Plaza skyscraper, the first ten floors house a treasure trove of electronic shops. Vendors quietly offer access to Nvidia A100 artificial intelligence chips, a highly sought-after product. While not openly advertised, discreet inquiries can lead interested buyers to this elusive market.

Exorbitant Prices: The High Stakes of Acquiring Nvidia AI Chips
Securing these high-end Nvidia AI chips comes with a hefty price tag. In conversations with anonymous vendors, Reuters revealed that the chips are priced at $20,000 each—a significant increase from the standard cost. The scarcity of these chips, coupled with export restrictions, has created a niche market where inflated prices have become the norm.
The Underworld of Nvidia Chip Trading: Navigating Export Restrictions
It is not illegal to buy or sell high-end U.S. chips in China. However, export restrictions imposed by the U.S. government have forced these transactions underground. Vendors, wary of drawing attention from both American and Chinese authorities, operate discreetly to fulfill the demand for Nvidia A100 chips, resulting in an unregulated market.
Political Tensions and Export Controls: The Impact on Nvidia’s Chips
In September, President Joe Biden’s administration prohibited the export of Nvidia’s most advanced chips, including the A100 and recently developed H100, to mainland China and Hong Kong. These restrictions aim to curtail China’s AI and supercomputing development amid escalating political and trade tensions. A range of semiconductor-related export controls has followed suit.
Also Read: NVIDIA Builds AI SuperComputer DGX GH200
Surging Demand for AI Chips: Fueling the Underground Market
With the global rise of artificial intelligence, fueled by the success of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, the demand for high-end chips has skyrocketed. Nvidia’s microprocessors, known for their exceptional performance in machine learning tasks, have become highly coveted. As a result, the underground market in China thrives due to the insatiable appetite for these powerful AI chips.
Also Read: China’s Billion-Dollar Bet: Baidu’s $145M AI Fund Signals a New Era of AI Self-Reliance
Chasing Scarce Resources: How Vendors Source the Nvidia A100 Chips
Vendors seeking Nvidia A100 chips resort to unconventional means to acquire them. They often purchase excess stock that enters the market after Nvidia supplies large quantities to major U.S. companies. Additionally, they import the chips through locally incorporated companies in India, Taiwan, and Singapore. However, vendors can only secure small quantities due to limited availability, making large-scale projects challenging.
Limited Quantities, Powerful Impact: Enhancing AI Models with Nvidia Chips
Though the quantities obtained by vendors may be insufficient for building advanced AI models from scratch, even a handful of Nvidia A100 chips can revolutionize complex machine-learning tasks and improve existing AI models. While research firm TrendForce estimates that over 30,000 A100 cards are required for a model like OpenAI’s GPT, these limited acquisitions still have a significant impact.
Future Enforcement and Market Evolution: Uncertain Prospects
Charlie Chai, an analyst at 86Research, suggests that the United States may not be concerned about small-scale chip transactions. However, stricter enforcement might follow if China poses a more significant threat due to technological advancements. Chai also predicts that as Chinese AI startups, driving current chip purchases, eventually withdraw from the market, the premiums commanded by Chinese vendors for A100 and H100 chips may decline.
Also Read: Alibaba and Huawei’s Announce Debut of Their Chatbots: The Rise of Generative AI Chatbots in China
Our Say
China’s underground market for Nvidia AI chips offers a glimpse into the complex world of technology trade amidst political tensions. The demand for these cutting-edge processors, coupled with export restrictions, has given rise to a secretive and inflated marketplace. As the AI landscape continues to evolve, the fate of this underground market remains uncertain, highlighting the delicate balance between technology, regulations, and international relations.





