Introduction
Are you planning to become a data scientist but dont know where to start? Don’t worry, we have got you covered. This article will cover the entire data science curriculum for self study, along with list of resources and programs that can help you pace up the process.
This curriculum covers the basics of the tools, tricks, and knowledge you need to be a great data scientist. If you already know a little about science and statistics, you’re in a good place. If you’re new to this stuff, it might help to learn more about those things first. And if you’re pretty good at data already, this can be a quick refresher.
Remember, you won’t use all these skills in every project. Some projects need special tricks or tools not on this list. But if you get good at what’s in this curriculum, you’ll be ready for most data science jobs. And you’ll know how to learn new stuff when you need it.
Let’s begin!
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Why Follow Data Science Curriculum?
- Data Science Curriculum for Self Study
- Math Basics
- Programming Basics
- Data Basics
- Probability and Statistics Basics
- Data Visualization Basics
- Linear Regression Basics
- Machine Learning Basics
- Time Series Analysis Basics
- Productivity Tools Basics
- Data Science Project Planning Basics
- Domain Knowledge
- Big Data and Cloud Computing
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Deep Learning
- Data Ethics and Privacy
- Resource List
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Follow Data Science Curriculum?
Following a curriculum in data science is essential for structured and efficient learning. It provides you with a clear path for acquiring knowledge and skills, preventing you from feeling overwhelmed by the vastness of the field. A good curriculum ensures comprehensive coverage, guiding you through foundational concepts to advanced techniques. This step-by-step approach is a building block, establishing a solid foundation before delving into complex topics.
Moreover, a curriculum facilitates practical application. Many programs include hands-on projects and exercises, allowing you to translate theoretical knowledge into real-world skills. It tracks your progress systematically, helping you stay motivated and focused on your learning journey.
Beyond immediate benefits, following a curriculum pra epares you for the workforce. Completing a structured education in data science demonstrates commitment and proficiency to potential employers, enhancing your job prospects. Furthermore, this approach fosters adaptability, enabling you to tailor your pace based on your needs and delve deeper into challenging subjects.
In essence, a well-designed data science curriculum not only equips you with essential skills but also instills the ability to continue learning independently, a valuable trait in the ever-evolving field of data science.
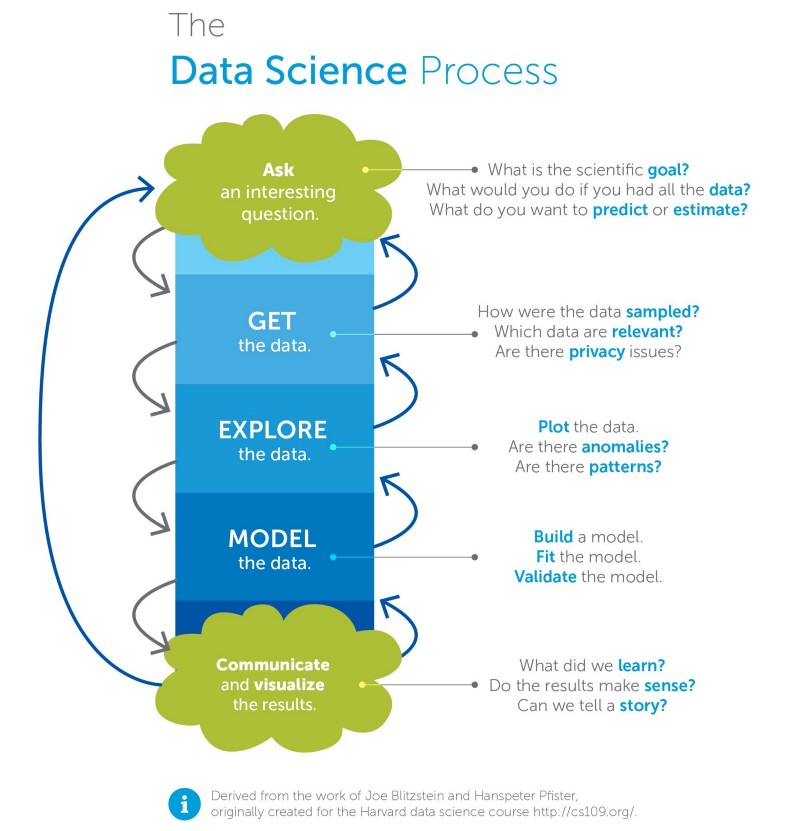
Data Science Curriculum for Self Study
Below is a condensed roadmap of key areas to explore when beginning your journey in data science:
Math Basics
- Multivariable Calculus: Understand functions of several variables, derivatives, gradients, step functions, sigmoid functions, cost functions, and more.
- Linear Algebra: Master vectors, matrices, matrix operations like transpose and inverse, determinants, dot products, eigenvalues, and eigenvectors.
- Optimization Methods: Learn about cost functions, likelihood functions, error functions, and algorithms like Gradient Descent (including variants like Stochastic Gradient Descent).
Programming Basics
- Choose Python or R as your primary language.
- For Python, become proficient in libraries like NumPy, pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch.
Data Basics
- Learn data manipulation in various formats (CSV, PDF, text).
- Acquire skills for data cleaning, imputation, scaling, importing, exporting, and web scraping.
- Explore data transformation and dimensionality reduction techniques, such as PCA and LDA.
Probability and Statistics Basics
- Gain insights into fundamental statistical concepts like mean, median, standard deviation, variance, correlation, and probability distributions.
- Understand hypothesis testing, p-values, Bayes’ Theorem, A/B testing, and Monte Carlo Simulation.
Data Visualization Basics
- Recognize the importance of data type and choose appropriate visualization techniques (scatter plots, histograms, etc.).
- Focus on components like data type, geometric choice, mapping, scaling, labels, and ethical considerations.
- Familiarize yourself with visualization tools like matplotlib, seaborn, and ggplot2.
Linear Regression Basics
- Learn the fundamentals of simple and multiple linear regression.
- Explore tools for linear regression analysis in Python (e.g., NumPy, scikit-learn) and R (caret package).
Machine Learning Basics
- Study supervised learning techniques for continuous and discrete variable prediction.
- Explore regression, classification, and ensemble methods (e.g., Random Forest).
- Delve into unsupervised learning, including clustering (e.g., K-means) and dimensionality reduction.
Time Series Analysis Basics
- Discover methods like Exponential Smoothing, ARIMA, and GARCH for time-dependent data analysis.
- Implement these techniques using Python and R.
Productivity Tools Basics
- Become proficient in essential data science tools such as R Studio, Jupyter Notebook, and GitHub.
- Consider advanced tools like AWS and Azure.
Data Science Project Planning Basics
- Learn project planning, including problem understanding, dataset exploration, model selection, and evaluation.
- Organize and structure your projects effectively for increased productivity.
Domain Knowledge
- Depending on your interests, dive into domain-specific knowledge. For example, if you’re interested in healthcare data, understand healthcare systems and terminology.
Big Data and Cloud Computing
- Explore technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP) for handling large datasets.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- If interested in text data, learn NLP techniques and libraries like NLTK and spaCy.
Deep Learning
- Delve into neural networks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and frameworks like Keras and TensorFlow.
Data Ethics and Privacy
- Understand the ethical implications of data science and privacy regulations like GDPR.
Resource List
- Statistics 101 Ebook
- Introduction to Business Analytics
- Introduction to AI and ML
- Pandas for Data Analysis in Python
- Introduction to NLP
- Data Science Hacks, Tips and Tricks
- Getting Started with Git and Github
- Introduction to Python
Click here to explore the entire resource list for free!
Conclusion
following a structured data science curriculum is like having a reliable map for your learning journey. It helps you acquire essential knowledge and skills efficiently while building a strong foundation. It also prepares you for the workforce and equips you with the ability to keep learning as the field evolves.
If you’re ready to take your data science skills to the next level, consider joining our BlackBelt AI/ML Program. It’s designed to boost your expertise and empower you to excel in challenging data science projects. Your future in data science begins here. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to advance your career. Join us now!
Frequently Asked Questions
A. To become a data scientist, you’ll need resources like relevant courses, books, online tutorials, access to data, programming languages like Python or R, and analytical tools.
A. A: The four types of data science are descriptive (summarizing data), diagnostic (explaining data patterns), predictive (forecasting trends), and prescriptive (providing recommendations).
A. Yes, you can self-study data science through online courses, tutorials, books, and practice with real-world datasets. Many resources are available for self-learners.





