Introduction
Embark on an exciting journey into the world of effortless machine learning with “Query2Model”! This innovative blog introduces a user-friendly interface where complex tasks are simplified into plain language queries. Explore the fusion of natural language processing and advanced AI models, transforming intricate tasks into straightforward conversations. Join us as we delve into the HuggingChat chatbot, develop end-to-end model training pipelines, leverage AI-powered chatbots for streamlined coding, and unravel the future implications of this groundbreaking technology.
Learning Objectives
- Immerse yourself in the world of HuggingChat, a game-changing AI chatbot redefining user interaction.
- Navigate the intricacies of model training pipelines effortlessly using intuitive natural language queries.
- Explore the horizon of AI chatbot technology, uncovering its future implications and potential advancements.
- Discover innovative prompt engineering techniques for seamless code generation and execution.
- Embrace the democratization of machine learning, empowering users with accessible interfaces and automation.
This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Table of contents
What is HuggingChat?
Hugging Chat is an open-source AI-powered chatbot that has been designed to revolutionize the way we interact with technology. With its advanced natural language processing capabilities, Hugging Chat offers a seamless and intuitive conversational experience that feels incredibly human-like. One of its key strengths lies in its ability to understand and generate contextually relevant responses, ensuring that conversations flow naturally and intelligently. Hugging Chat’s underlying technology is based on large language models, which have been trained on vast amounts of text data, enabling it to grasp a wide range of topics and provide informative and engaging responses.

It can assist users in generating code snippets based on their prompts, making it an invaluable tool for developers and programmers. Whether it’s providing code examples, explaining syntax, or offering solutions to various challenges, Hugging Chat’s code generation feature enhances its versatility and utility. Additionally, Hugging Chat prioritizes user privacy and data security, ensuring confidential and secure conversations. It adheres to ethical AI practices, refraining from storing user information or conversations, thus providing users with peace of mind and control over their personal data.
Unofficial HuggingChat Python API is available here.
What is Pipeline?
A pipeline refers to a sequence of data processing components arranged in a specific order. Each component in the pipeline performs a particular task on the data, and the output of one component becomes the input of the next. Pipelines are commonly used to streamline the machine learning workflow, allowing for efficient data preprocessing, feature engineering, model training, and evaluation. By organizing these tasks into a pipeline, it becomes easier to manage, reproduce, and deploy machine learning models.
The pipeline is as follows:
- Text Query: User queries the system with all the requirements specified
- Request: Query is restructured and the request is sent to HuggingChat API(unofficial)
- HuggingChatAPI: Processes the query and generates relevant code
- Response: Generated code is received by user as response
- Execution: Resultant Python code is executed to get desired output
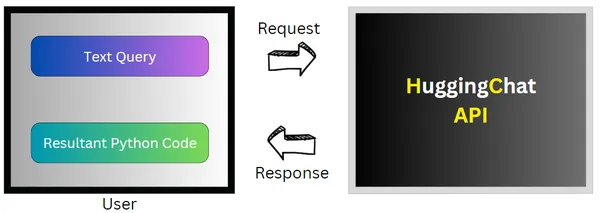
Step-by Step Implementation of Query2Model
Let us now look into the step by step implementation of Query2Model:
Step1. Import Libraries
Let us start by importing the following libraries:
- sklearn: versatile machine learning library in Python, offering a comprehensive suite of tools for data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and deployment.
- pandas: powerful data manipulation and analysis library in Python, designed to simplify the handling of data efficiently.
- hugchat: unofficial HuggingChat Python API, extensible for chatbots etc.
!pip install hugchat
import sklearn
import pandas as pd
from hugchat import hugchat
from hugchat.login import LoginStep2. Defining Query2Model Class
Formatting prompt is used to structure the output in desired format. It consists of several guidelines such as printing results if needed, including indentations, ensuring error-free code, etc., to ensure the output from the chatbot contains only executable code without errors when passed to the exec() function.
#formatting_prompt is to ensure that the response contains only the required code
formatting_prompt = """Error-free code
Store the variable names in variables for future reference.
Print the result if required
Code should be well indented with spaces, etc., should not contain importing libraries, comments.
No loops.
Output should be executable without errors when it is passed to exec() function"""The Query2Model class is a tool for executing user queries within a specific environment. It requires the user’s email and password for authentication, sets a cookie storage directory, and initializes a Login object. After successful authentication, it retrieves and saves cookies, initializing a ChatBot object for interaction. The execute_query() method executes user queries, returning the result as a string.
class Query2Model:
def __init__(self, email, password):
self.email = email
self.password = password
self.cookie_path_dir = "./cookies/"
self.sign = Login(EMAIL, PASSWD)
self.cookies = sign.login(cookie_dir_path=cookie_path_dir, save_cookies=True)
self.chatbot = hugchat.ChatBot(cookies=cookies.get_dict())
# function to execute the user's query
def execute_query(self, query):
query_result = self.chatbot.chat(query+formatting_prompt)
exec(str(query_result))
return str(query_result)User needs to provide the login credentials of HuggingFace account for authentication
user = Query2Model(email="email", password="password")Step3. Data Preparation and Preprocessing
Query includes path to the dataset(here the dataset is present in current working directory), the variable to store it upon reading, and to display the first 5 rows.
query= r"""Read the csv file at path: iris.csv into df variable and display first 5 rows"""
output_code= user.execute_query( query )
print(output_code, sep="\n")
Separating the input features(X) and label(y) into separate dataframes. Features includes sepal length& width, petal length& width which represent the characteristics of iris flower. Label denotes which species the flower belongs to.
query= r"""Store 'SepalLengthCm', 'SepalWidthCm', 'PetalLengthCm', 'PetalWidthCm' in X
and 'Species' in y"""
output_code= user.execute_query( query )
print(output_code, sep="\n")
Dividing 80% of data for training and 20% of data for testing with a random state of 111
query= r"""Divide X, y for training and testing with 80-20% with random_state=111"""
output_code= user.execute_query( query )
print(output_code, sep="\n")
Applying standard scaler technique to normalize the data. It transforms the data by removing the mean and scaling it to unit variance, ensuring that each feature has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
query= r"""Apply standard scaler"""
output_code= user.execute_query( query )
print(output_code, sep="\n")
Step4. Model Training and Evaluation
Query contains instructions to train a random forest classifier, display it’s accuracy, and finally to save the trained model for futuristic tasks. As any hyperparameters are not specified in the query, it considers default ones.
Random Forest: Random forest algorithm operates by constructing multiple decision trees during training and outputs the mode of the classes or mean prediction of the individual trees for regression tasks.
query= r"""Train a random forest classifier, print the accuracy, and save in .pkl"""
output_code= user.execute_query( query )
print()
print(output_code, sep="\n")
After successfully training the model, we perform querying to check the output based on provided input features.
query= r"""Load the model, and predict ouput for SepalLength= 5.1, SepalWidth= 3.5, PetalLength= 1.4, and PetalWidth= 0.2"""
output_code= user.execute_query( query )
print()
print(output_code, sep="\n")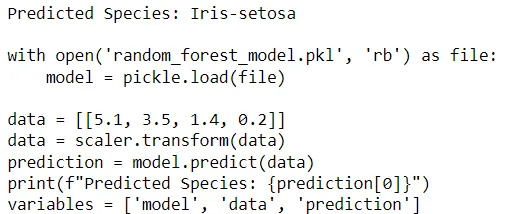
Future Implications
- Democratization of Programming: “Query2Model” could democratize programming by lowering the barrier to entry for beginners, enabling individuals with limited coding experience to harness the power of machine learning and automation.
- Increased Productivity: By automating the code generation process, “Query2Model” has the potential to significantly enhance productivity, allowing developers to focus more on problem-solving and innovation rather than routine coding tasks.
- Advancement of Natural Language Processing: The widespread adoption of such tools may drive further advancements in natural language processing techniques, fostering a deeper integration between human language and machine understanding in various domains beyond programming which lead to the futuristic development of Large Action Models(LAMs).
Conclusion
“Query2Model” represents an innovative solution for automating the process of generating and executing code based on user queries. By leveraging natural language input, the pipeline streamlines the interaction between users and the system, allowing for seamless communication of requirements. Through integration with the HuggingChat API, the system efficiently processes queries and generates relevant code, providing users with timely and accurate responses. With its ability to execute Python code, “Query2Model” empowers users to obtain desired outputs effortlessly, enhancing productivity and convenience in the realm of code generation and execution. It is highly beneficial to beginners as well as working professionals.
Key Takeaways
- HuggingChat, an AI-powered chatbot, revolutionizes user interaction by simplifying complex tasks into natural language queries, enhancing accessibility and efficiency.
- Query2Model facilitates seamless model training pipelines, enabling users to navigate machine learning workflows effortlessly through intuitive natural language queries.
- Developers can customize chatbots like HuggingChat for code generation tasks, potentially reducing development time and enhancing productivity.
- Prompt engineering techniques leverage the outputs of large language models (LLMs), such as GPT, to generate desirable code snippets efficiently and accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. HuggingChat streamlines machine learning tasks by allowing users to interact with the system through natural language queries, eliminating the need for complex programming syntax and commands.
A. Yes, users can tailor HuggingChat’s functionality to suit various code generation tasks, making it adaptable and versatile for different programming needs.
A. Query2Model empowers users by providing a user-friendly interface for building and training machine learning models, making complex tasks accessible to individuals with varying levels of expertise.
A. AI-powered chatbots have the potential to democratize programming by lowering the barrier to entr. It increase developer productivity by automating repetitive tasks, and drive advancements in natural language processing techniques.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.




