Introductions
Numbers are at the heart of every spreadsheet, but precision and clarity often require more than raw data. Enter the ROUND function in Microsoft Excel—a versatile tool transforming numerical data into precise, readable, and professional results. Whether you’re fine-tuning financial calculations, performing detailed data analysis, or simply presenting information more clearly, the ROUND function is your go-to solution for making numbers work for you.
Overview
- The ROUND function in Excel is a versatile tool for precise number formatting. It has various applications in financial calculations and data presentation.
- ROUND’s syntax, use cases, and rounding rules are explained, along with advanced usage tips and common pitfalls to avoid.
- The article covers alternatives to ROUND, best practices, and the importance of understanding various Excel functions for productivity and data analysis.
- Excel functions, including ROUND, are crucial for efficiency, accuracy, data analysis, and professional development across multiple industries.
Table of contents
Round Functions
In Excel, round functions are used to round numbers to a specified number of digits:
Syntax: The basic syntax of the ROUND function is:
=ROUND(number, num_digits)Explanations
- “number” is the value you want to round
- “num_digits” specifies the number of digits to which you want to round the number
Use Cases of Round Function in Excel
Here are the use cases of Round Function:
- Positive num_digits: When num_digits is positive, Excel rounds to the specified number of decimal places. Example: =ROUND(3.14159, 2) returns 3.14.
- Zero num_digits: When num_digits is zero, Excel rounds to the nearest integer. Example: =ROUND(3.14159, 0) returns 3.
- Negative num_digits: When num_digits is negative, Excel rounds to the left of the decimal point. Example: =ROUND(3141.59, -2) returns 3100.
- Rounding rules:
- If the digit to the right of the rounding digit is less than 5, Excel rounds down.
- If the digit to the right of the rounding digit is 5 or greater, Excel rounds up.
- This consistent rounding approach ensures accuracy in calculations and data representation.
- Compatibility: The ROUND function is available in all versions of Excel, making it a universally applicable tool.
| Formula | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
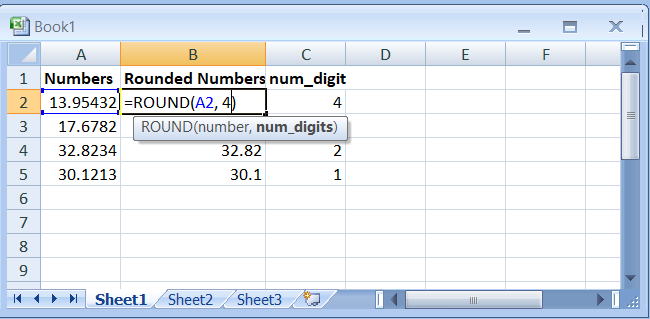
| =ROUND(13.95432, 4) | Round to four decimal places | 13.9543 |
| =ROUND(17.6782, 3) | Round to three decimal places | 17.678 |
| =ROUND(32.8234,2) | Round to two decimal places | 32.82 |
| =ROUND(30.1213, 1) | Round to one decimal place | 30.1 |
Let’s see how these work on Excel:
- We have listed the data in the numbers column after that, rounded numbers, and then num_digit
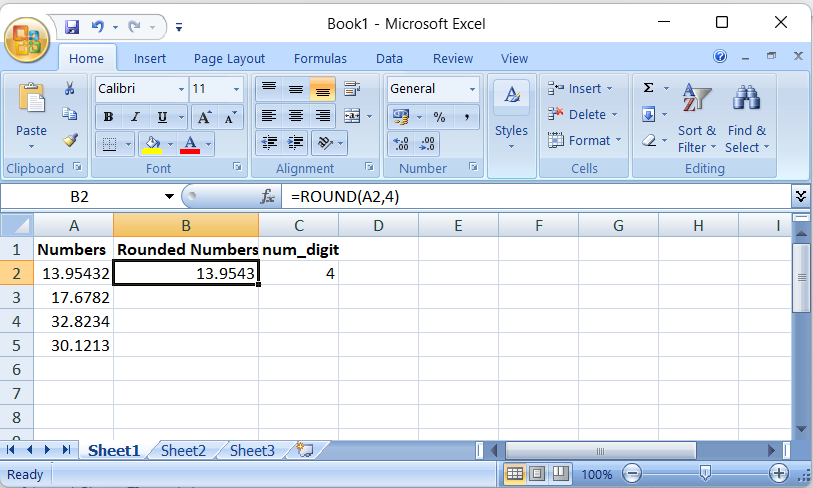
- Now round the number of digits to which you want to round the number, apply the formula – ROUND(A2,4)
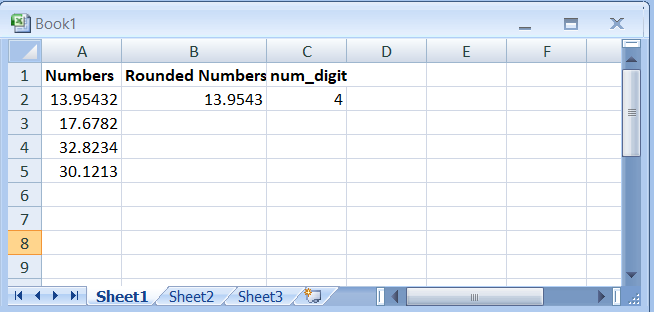
- Here are the all-rounded numbers
Also read: Microsoft Excel for Data Analysis
Advanced Usage and Common Pitfalls of Round Function in Excel
Here are the advanced usages of the Round Function:
- Combining with other functions: ROUND can be nested within other functions for complex calculations. Example:
=SUM(ROUND(A1:A10, 2))rounds each number in the range before summing. - Financial applications: In financial modeling, ROUND is often used to ensure accuracy in calculations involving currency. Example:
=ROUND(B2*1.0825, 2)could be used to calculate sales tax and round to cents. - Avoiding floating-point errors: ROUND can help mitigate issues with Excel’s floating-point arithmetic. Example:
=ROUND(0.1+0.2, 10)ensures that 0.1+0.2 equals exactly 0.3
Common Pitfalls:
Here are the common Pitfalls:
- Overuse: Excessive rounding can lead to a loss of precision in calculations. Use judiciously.
- Confusion with ROUNDUP and ROUNDDOWN: Unlike ROUND, ROUNDUP always rounds away from zero, while ROUNDDOWN always rounds toward zero.
- Display vs. Actual Value: ROUND changes the actual value, not just the display format.
Also read: A Comprehensive Guide on Advanced Microsoft Excel for Data Analysis
Alternatives and Best Practices to ROUND Function
Here are the alternatives and best practices:
Alternatives to ROUND:
- MROUND: Rounds to the nearest multiple of a specified number.
- CEILING and FLOOR: Round up or down to the nearest specified multiple.
- INT: Rounds down to the nearest integer.
- TRUNC: Truncates a number to a specified number of digits.
Best Practices:
- Document your use of ROUND in complex formulas to ensure clarity.
- Consider using named ranges to make formulas with ROUND more readable.
- Be consistent in your rounding approach across a spreadsheet or workbook.
Why You Should Know About Different Functions in Excel?
1. Efficiency and Productivity
- Automation: Excel functions allow you to automate repetitive tasks, saving you time and reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Quick Calculations: Functions enable you to perform complex calculations swiftly, which would otherwise take considerable time if done manually.
2. Data Analysis
- Advanced Analysis: Functions such as VLOOKUP, INDEX, and MATCH can help you analyze large datasets and extract meaningful insights.
- Statistical Analysis: Functions like AVERAGE, MEDIAN, and STDEV are essential for performing statistical analyses and understanding data trends.
3. Accuracy
- Precision: Functions ensure accurate calculations, reducing the risk of human error with manual computations.
- Consistency: Using functions ensures that calculations are done consistently across the entire dataset.
4. Better Data Presentation
- Formatting: Functions like TEXT, CONCATENATE, and ROUND help present data in a more readable and professional format.
- Visualization: Functions can assist in preparing data for visualization tools within Excel, such as charts and graphs, making it easier to communicate insights.
5. Problem-Solving
- Versatility: Excel functions can be combined in various ways to solve complex problems and perform multifaceted analyses.
- Custom Solutions: By understanding different functions, you can tailor solutions to specific problems or needs, enhancing your ability to handle diverse tasks.
6. Professional Development
- Skill Enhancement: Proficiency in Excel functions is valuable in many professions, enhancing your resume and career prospects.
- Decision-Making: Knowledge of Excel functions empowers you to make informed decisions based on accurate data analysis.
7. Financial Management
- Budgeting: Functions are essential for creating and managing budgets, forecasting financial performance, and conducting financial analysis.
- Investment Analysis: Functions like NPV and IRR are critical for evaluating investment opportunities and financial planning.
8. Versatile Applications
- Wide Usage: Excel functions are used across various industries, from finance and marketing to engineering and science, making them universally applicable skills.
- Problem Solving: Whether you manage personal finances, conduct research, or run a business, knowing Excel functions can help you solve many problems efficiently.
By mastering different Excel functions, you unlock the full potential of this powerful tool, enhancing your productivity, accuracy, and ability to analyze and present data effectively.
Conclusion
The ROUND function in Excel is a powerful tool for managing numerical precision, crucial for financial calculations and data analysis. Understanding its usage enhances Excel proficiency. ROUND exemplifies Excel’s numerous functions that boost productivity and accuracy. While mastering these functions improves work efficiency and decision-making, it’s important to use ROUND judiciously, considering its limitations and alternatives. Proper application of ROUND and other Excel functions unlocks the software’s full potential, enabling more efficient and insightful data management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. The ROUND function in Excel rounds a number to a specified number of digits. This helps achieve precision and clarity in numerical data, making it more readable and professional.
Ans. The basic syntax of the ROUND function is:=ROUND(number, num_digits)
Ans. Here are the differences:
a. ROUND: Rounds a number to a specified number of digits, rounding up if the next digit is 5 or greater and down if it’s less than 5.
b. ROUNDUP: Always rounds a number up, away from zero, to a specified number of digits.
c. ROUNDDOWN: Always rounds a number down, towards zero, to a specified number of digits.
Ans. Yes, the ROUND function can be combined with other functions to perform more complex calculations. For example, you can nest ROUND within a SUM function to round each number in a range before summing them:=SUM(ROUND(A1:A10, 2))
Ans. Here are the common pitfalls to avoid:
a. Overuse: Excessive rounding can lead to a loss of calculation precision.
b. Confusion with other rounding functions: Determine the differences between ROUND, ROUNDUP, and ROUNDDOWN to avoid incorrect results.
c. Display vs. actual value: Remember that ROUND changes the actual value, not just the display format, which can affect subsequent calculations.





