In modern Python development, securely managing configuration settings, API keys, and sensitive data is essential. This is where .env files come into play. .env files provide a structured and secure way to manage environment variables, ensuring that your sensitive data is not hardcoded into the source code. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into creating and using .env files in Python.

Table of contents
What is a .env File in Python?
A .env file is a simple text file containing key-value pairs representing configuration settings. These files are widely used to store sensitive data like API keys, database credentials, and application configurations. By using .env files, developers can separate sensitive information from the codebase, simplifying management across different environments (e.g., development, staging, production).
Why Use .env Files in Python?
- Security: Keeps sensitive data out of your codebase.
- Portability: Enables easy sharing of configurations across different systems.
- Flexibility: Simplifies managing different environments without changing code.
- Readability: Organizes configurations in a clean, structured manner.
Setting Up and Using .env Files in Python
Step 1: Create the .env File
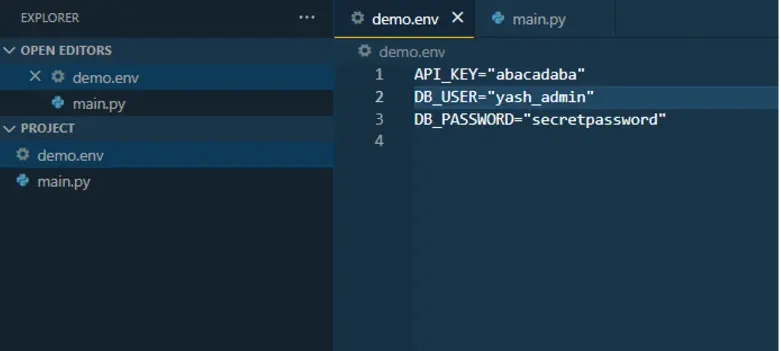
Create a file named .env in the root directory of your project. Add your key-value pairs to this file.
Note: In Linux and macOs, we can use the “touch .env” command in the terminal to create the file.
Also touch .env can be used if the user wants to create it using command prompt which is not required if the user is using vs code or pycharm in macos
Step 2: Install the python-dotenv Library
The python-dotenv library is a popular choice for loading .env files into Python projects. Install it using
pip install python-dotenv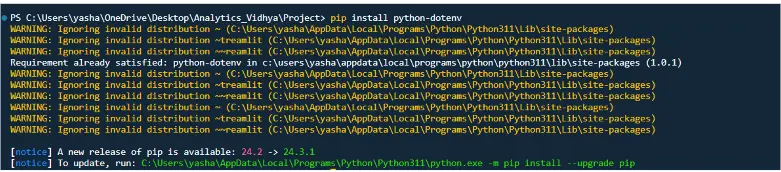
Step 3: Load Variables from the .env File
In your Python code, use python-dotenv to load the variables
You can mention the path of the .env file using the load_dotenv() method.
E.g. load_dotenv(:C/projects)
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# Load variables from .env file
load_dotenv()
# Access the variables
api_key = os.getenv("API_KEY")
user = os.getenv("DB_USER")
password = os.getenv("DB_PASSWORD")
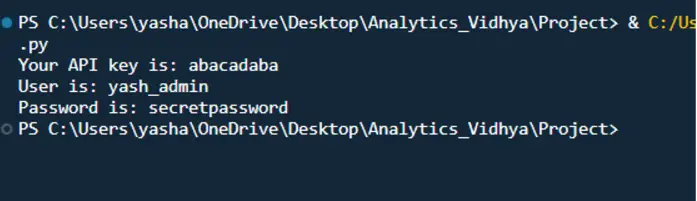
print(f"Your API key is: {api_key}")
print(f"User is: {user}")
print(f"Password is: {password}")
Best Practices for Using .env Files
- Exclude from Version Control: Add .env to your .gitignore file to prevent accidental commits.
- Use Descriptive Names: Ensure variable names are clear and consistent.
- Avoid Hardcoding Defaults: Rely on .env for sensitive data instead of hardcoding fallback values.
- Provide a .env.example: Share a sample file (without sensitive data) with collaborators to clarify the required structure.
Conclusion
Using .env files in Python is a best practice for securely managing sensitive information, such as API keys, database credentials, and other configuration settings. By leveraging the python-dotenv library, developers can easily load these variables into their projects, ensuring a clear separation between sensitive data and the codebase.
This approach enhances security, improves portability, and allows for seamless configuration across different environments, such as development, staging, and production. Following best practices like excluding .env files from version control, using descriptive variable names, and providing a .env.example file can further streamline collaboration and reduce the risk of exposing sensitive data.
Whether you’re building a small project or a large-scale application, incorporating .env files into your workflow ensures an organized and secure way to handle project configurations.
If you are looking for Python course online then explore: Introduction to Python
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. A .env file is used to store environment variables such as API keys, database credentials, and other sensitive information securely. It helps keep this data separate from the source code, improving security and organization.Ans.
Ans. .env files often contain sensitive information like passwords or API keys. Including them in version control could expose this information to unauthorized users. Use a .gitignore file to prevent .env files from being committed to repositories.
Ans. The python-dotenv library makes it easy to load variables from a .env file into your Python application. It simplifies the process of managing environment variables and reduces the risk of hardcoding sensitive information.





