Nvidia’s annual GPU Technology Conference (GTC) has long been a highlight for the AI community. At this year’s event, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang unveiled a roadmap of new products and innovations aimed at scaling up artificial intelligence. This included next‐generation AI chips – Blackwell Ultra, Vera Rubin, etc., accelerated inferencing software, and even future breakthroughs in robotics. Yet, despite the fanfare, Nvidia’s stock price experienced a notable decline. In this article, we dissect the key AI advancements presented at GTC 2025 and explore the market’s cautious reaction.
Table of Contents
Nvidia’s Latest Announcements at GTC 2025
First, let’s explore some of the upcoming innovations announced by Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang at the GTC 2025 event.
Next-Generation AI Chips: Blackwell Ultra and Beyond
At the event, Nvidia revealed a series of chip advancements that will power the next wave of AI innovation. The company introduced its Blackwell Ultra GPUs, designed to deliver exponential improvements in inference performance and energy efficiency. Along with it, Nvidia also announced its GB300 superchip, which combines two Blackwell Ultras with the company’s Grace central processing unit (CPU).

Building on this, the roadmap extends to the upcoming Vera Rubin chips scheduled for release in the second half of 2026 and Vera Rubin Ultra in 2027. These chips promise higher data throughput and enhanced processing capabilities, crucial for training and running increasingly complex AI models. Vera Rubin will have 3.3 times the performance of Nvidia’s Grace Blackwell system, with 144 graphics processing units. Its follow up, Vera Rubin Ultra, will be an even more massive system with 14.4 times the performance of Grace Blackwell, and 576 GPUs.
Additionally, a successor architecture, codenamed Feynman, is also slated for launch in 2028. This underscores Nvidia’s commitment to a yearly cadence of innovation in the AI hardware space.
AI-Optimized Computing and Networking Technologies
Nvidia is also democratizing AI compute power with the launch of DGX Personal AI Supercomputers. These desktop systems are designed in collaboration with partners like Dell, Lenovo, and HP. Through this launch Nvidia aims to bring supercomputing capabilities to AI researchers and developers at a more accessible scale.

Complementing these, are new networking technologies, such as the Spectrum‑X and Quantum‑X silicon photonics switches. These products integrate optical communication with Nvidia’s accelerated compute platforms to enable faster, more energy‑efficient data transfer between thousands of GPUs in modern AI data centers.
Software Platforms for AI Inference
Another highlight unveiled at the event was Nvidia Dynamo – an open‑source software system designed to optimize AI inference. Dubbed “the operating system of an AI factory,” Dynamo aims to scale reasoning models efficiently by dynamically distributing workloads across GPUs. This improvement is pivotal as AI applications shift from mere generation to complex reasoning and decision‑making tasks.

Advancements in Robotics and Agentic AI
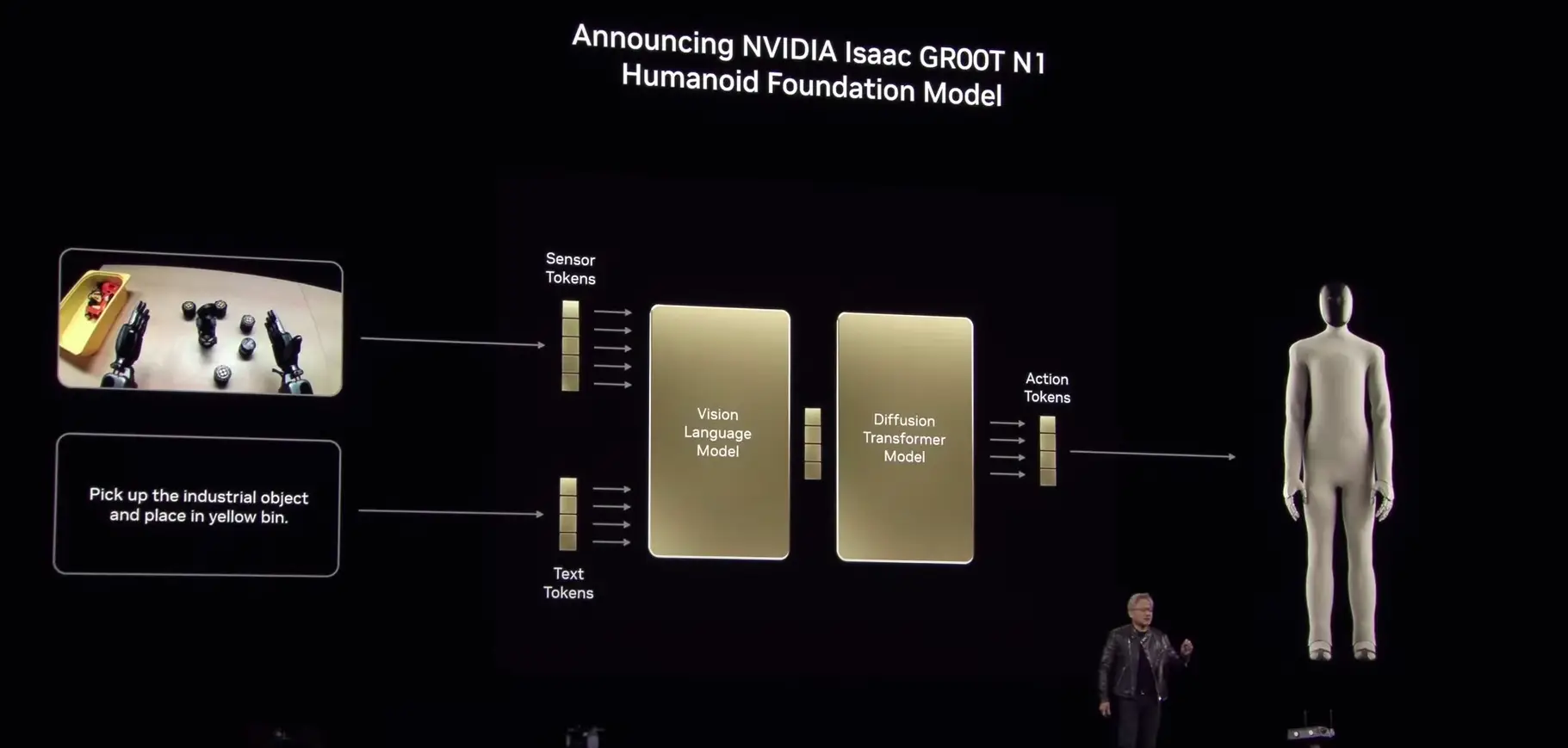
Nvidia pushed the boundaries beyond traditional data center applications by addressing robotics and physical AI at GTC 2025. One standout announcement was the introduction of the Isaac GR00T N1 foundation model for humanoid robots. This new model is designed with a dual‑system architecture inspired by human cognition – featuring fast “System 1” reflexes and a slower “System 2” reasoning process.
With GR00T N1, Nvidia aims to accelerate the development of adaptable, generalist robotic platforms. Early demonstrations of the model showcased a robot autonomously executing tasks such as tidying up. This hints at a future where robots may transition from tools to intelligent learning companions.
Promising Technological Partnerships
At the event, Nvidia announced its collaborations with Disney Research and Google DeepMind, further emphasizing its vision of integrating robotics with AI. These partnerships aim to develop advanced physics engines (e.g., the Newton engine) and simulation frameworks that will pave the way for real‑world deployment of intelligent robotics across industries.
During his keynote, Huang also revealed Nvidia’s partnership with General Motors (GM) to help them build their first fleet of self-driving cars.

Also Read: 4 Major Updates from NVIDIA CES 2025 – Day 1
The Stock Market Reaction to GTC 2025
Despite Jensen Huang’s GTC keynote speech being loaded with an impressive product roadmap, Nvidia’s stock price fell significantly following the announcements. The stock, which was down by nearly 1% in anticipation of Huang’s keynote, ended the day with a 3.4% dip, as its annual GTC event failed to impress investors. Shares of General Motors also closed with around 1% dip following the announcements.

Now, there are several factors that contributed to this counterintuitive market response, some of which include:
- Incremental Growth & Revenue Timing: Analysts see the new AI chips and software as incremental upgrades rather than major revenue drivers, raising concerns about their short-term financial impact.
- Competitive & Geopolitical Pressures: Cost-effective alternatives from startups like DeepSeek challenge NVIDIA’s pricing power, while trade restrictions and geopolitical tensions add uncertainty.
- Investor Concerns on AI Spending: Despite AI’s potential, high infrastructure costs for AI data centers raise doubts about immediate earnings growth.
The launch of the Chinese AI model DeepSeek-R1 had caused a dip in Nvidia stock prices earlier this year. New Federal restrictions and regulations on the export of AI chips has also taken a jab at Nvidia’s prices. And now with the GTC announcements not panning out too well, short‑term market sentiment remains cautious, hoping Nvidia’s current stock price correction is temporary.
The Future of Nvidia: Is it Headed in the Right Direction?
For the AI community and industry watchers, Nvidia’s GTC 2025 provides a fascinating glimpse into the future of AI infrastructure. The company’s roadmap – featuring a rapid cadence of chip launches, new inference software, and innovations in robotics – positions it as a key enabler of next‑generation AI.
However, the mixed reaction in the stock market underscores an important lesson: technological prowess alone does not guarantee immediate financial gains. Investors are waiting for concrete evidence that these innovations will surely convert into robust revenue streams.
Nvidia’s developments do show a bright future for those tracking the AI revolution. However, the journey from technological breakthroughs to market impact is often measured in years rather than months. And so, only time can tell if Nvidia can navigate the broader economic dynamics that influence technology investments.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s GTC 2025 keynote showcased a vision of a future where AI is more powerful, interconnected, and embodied in intelligent machines. From next‑generation chips like Blackwell Ultra and Vera Rubin to transformative robotics models such as Isaac GR00T N1, the company is laying the groundwork for significant advances in AI. Yet, the stock market’s cautious reaction serves as a reminder that even industry-leading innovations must ultimately prove their financial viability. For AI enthusiasts and practitioners, these announcements offer both a glimpse into the future of AI and a challenge to bridge the gap between breakthrough technology and market success.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Nvidia introduced next-gen AI chips like Blackwell Ultra, Vera Rubin, and GB300 at the GTC 2025 event. It also gave a glimpse at new inference software, AI-optimized networking, and advancements in robotics.
A. Investors saw the updates as incremental rather than groundbreaking, with concerns over revenue timing, rising competition, and geopolitical challenges. This lead to a significant dip in Nvidia’s stock price.
A. Vera Rubin, said to be launched in 2026, is an AI chip that will have 3.3 times the performance of Nvidia’s Grace Blackwell system, with 144 graphics processing units. Its successor, Vera Rubin Ultra, to follow in 2027, will be an even more massive system with 14.4 times the performance of Grace Blackwell, and 576 GPUs.
A. Dynamo optimizes AI reasoning by dynamically distributing workloads across GPUs, making AI systems more efficient and scalable.
A. Nvidia’s Isaac GR00T N1 is a foundation model for humanoid robots. It aims to create adaptable AI-driven robots with advanced reasoning abilities.
A. Nvidia’s Feynman architecture, renowned physicist Richard Feynman, is its upcoming next-generation AI chip platform. It is slated for release in 2028, following Vera Rubin and Vera Rubin Ultra.
A. With yearly chip updates, AI computing advancements, and strategic partnerships, Nvidia aims to stay at the forefront of the AI revolution despite market uncertainties.







