These days, even the tiniest update from AI companies gets hyped like a major breakthrough. Is that true for Meta? I wouldn’t say so. They skipped the drama and just dropped not one, but 3 new models in one go as the “Llama 4 herd.” The Llama 4 models – Scout, Maverick, and Behemoth – are each built with a clear purpose, from lightweight deployment to enterprise-level reasoning. And the best part? Two of them are available to the public right now! In this blog, we’ll learn how to access Meta’s Llama 4 models and explore their capabilities, features, benchmark results, and real-world performance against other top models.
Table of Contents
The Llama 4 Models: Scout, Maverick, and Behemoth
Meta’s Llama 4 herd: Scout, Maverick, and Behemoth, are a group of highly efficient, open-source & multi-modal models. In a time when companies like OpenAI, Google, and X.com are building increasingly large but closed models, Meta has chosen a different route: making powerful AI open and accessible. In fact, Llama 4 Maverick crossed the 1400 benchmark on the LMarena, beating models like GPT 4o, DeepSeek V3, Gemini 2.0 Flash, and more! Equally notable is the 10 million token context length supported by these models, which is the longest of any open-weight LLM to date. Let’s look at each of these models in detail.

Llama 4 Scout: Small, Fast, and Smart
Scout is the most efficient model in the Llama 4 family. It is a fast and lightweight model, ideal for developers and researchers who don’t have access to large GPU clusters.
Key Features of Llama 4 Scout:
- Architecture: Scout uses a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture with 16 experts, activating only 2 at a time, which results in 17B active parameters from a total of 109B. It supports a 10 million token context window.
- Efficiency: The model runs efficiently on a single H100 GPU using Int4 quantization, making it an affordable high-performance option.
- Performance: Scout outperforms peer models such as Gemma 3, Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite, and Mistral 3.1 in benchmark tests.
- Training: It has been pre-trained in 200 languages 100 of which include over a billion tokens each and trained on diverse image and video data, supporting up to 8 images in a single prompt.
- Application: Thanks to advanced image region grounding, it delivers precise visual reasoning. This makes it ideal for applications such as long-context memory chatbots, code summarization tools, educational Q&A bots, and assistants optimized for mobile or embedded systems.
Llama 4 Maverick: Strong and Reliable
Maverick is the flagship open-weight model. It is designed for advanced reasoning, coding, and multimodal applications. While it is more powerful than Scout, it maintains efficiency using the same MoE strategy.
Key Features of Llama 4 Maverick:
- Architecture: Maverick uses a Mixture of Experts architecture with 128 routed experts and a shared expert, activating only 17B parameters out of a total of 400B during inference. It is trained using an early fusion of text and image inputs and supports up to 8 image inputs.
- Efficiency: The model runs efficiently on a single H100 DGX host or can be scaled across GPUs.
- Performance: It achieves an ELO score of 1417 on the LMSYS Chatbot Arena, outperforming GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash, while also matching DeepSeek v3.1 in reasoning, coding, and multilingual capabilities.
- Training: Maverick was built with cutting-edge techniques such as MetaP hyperparameter scaling, FP8 precision training, and a 30 trillion token dataset. It delivers strong image understanding, multilingual reasoning, and cost-efficient performance that surpasses the Llama 3.3 70B model.
- Applications: Its strengths make it ideal for AI pair programming, enterprise-level document understanding, and educational tutoring systems.
Llama 4 Behemoth: The Teacher Model
Behemoth is Meta’s largest model to date. It isn’t available for public use, but it played a vital role in helping Scout and Maverick become what they are today.
Key Features of Llama 4 Behemoth:
- Architecture: Behemoth is Meta’s largest and most powerful model, using a Mixture of Experts architecture with 16 experts and activating 288B parameters out of nearly 2 trillion during inference. It is natively multimodal and excels in reasoning, math, and vision-language tasks.
- Performance: Behemoth consistently outperforms GPT-4.5, Claude Sonnet 3.7, and Gemini 2.0 Pro on STEM benchmarks like MATH-500, GPQA Diamond, and BIG-bench.
- Role: It plays a key role as a teacher model, guiding Scout and Maverick through co-distillation with a novel loss function that balances soft and hard supervision.
- Training: The model was trained using FP8 precision, optimized MoE parallelism for 10x speed gains over Llama 3, and a new reinforcement learning strategy. This included hard prompt sampling, multi-capability batch construction, and sampling from a variety of system instructions.
Though not publicly available, Behemoth serves as Meta’s gold standard for evaluation and internal distillation.
How to Access the Llama 4 Models?
You can start using Llama 4 today through multiple easy-to-use platforms, depending on your goals—whether it’s research, application development, or just testing out capabilities.
- llama.meta.com: This is Meta’s official hub for Llama models. It includes model cards, papers, technical documentation, and access to the open weights for both Scout and Maverick. Developers can download the models and run them locally or in the cloud.
- Hugging Face: Hugging Face hosts the ready-to-use versions of Llama 4. You can test models directly in the browser using inference endpoints or deploy them via the Transformers library. Integration with common tools like Gradio and Streamlit is also supported.
- Meta Apps: The Llama 4 models also power Meta’s AI assistant available in WhatsApp, Instagram, Messenger, and Facebook. This allows users to experience the models in real-world conversations, directly within their everyday apps.
- Web Page: You can directly access the latest Llama 4 models using the web interface.
Llama 4 Models: Let’s Try!
It’s super easy to try the latest Llama 4 models across any of Meta’s apps or the web interface. Although it isn’t specifically mentioned in any of those, regarding which model -out of Scout, Maverick, and Behemoth – is used in the background. As of now, Meta AI hasn’t provided a choice to choose the model that you wish to work with on its apps or interface. Nonetheless, I’ll test the Llama 4 model for three tasks: Creative Planning, Coding, and Image Generation.
Task 1: Creative Planning
Prompt: “Create a Social Media content strategy for a Shoe Brand – Soles to help them engage with the Gen z audience”
Output:

Observation
- Llama 4 models are very fast! The model quickly maps put a detailed yet concise plan for the social media strategy.
- In the web interface, you can’t currently upload any files or images.
- Also, it doesn’t support web search or canvas features yet.
Task 2: Coding
Prompt: ”Write a python program that shows a ball bouncing inside a spinning pentagon, following the laws of Physics, increasing its speed every time it bounces off an edge.”
Output:
Observation
- The code it generated had errors.
- The model quickly processes the requirement but yet is not great when it comes to accuracy.
Task 3: Image Generation
Prompt: “Create an image of a person working on a laptop with a document open in the laptop with the title “llama 4”, the image should be taken in a way the screen of the person is visible, the table on which the laptop is kept has a coffee mug and a plant”
Output:
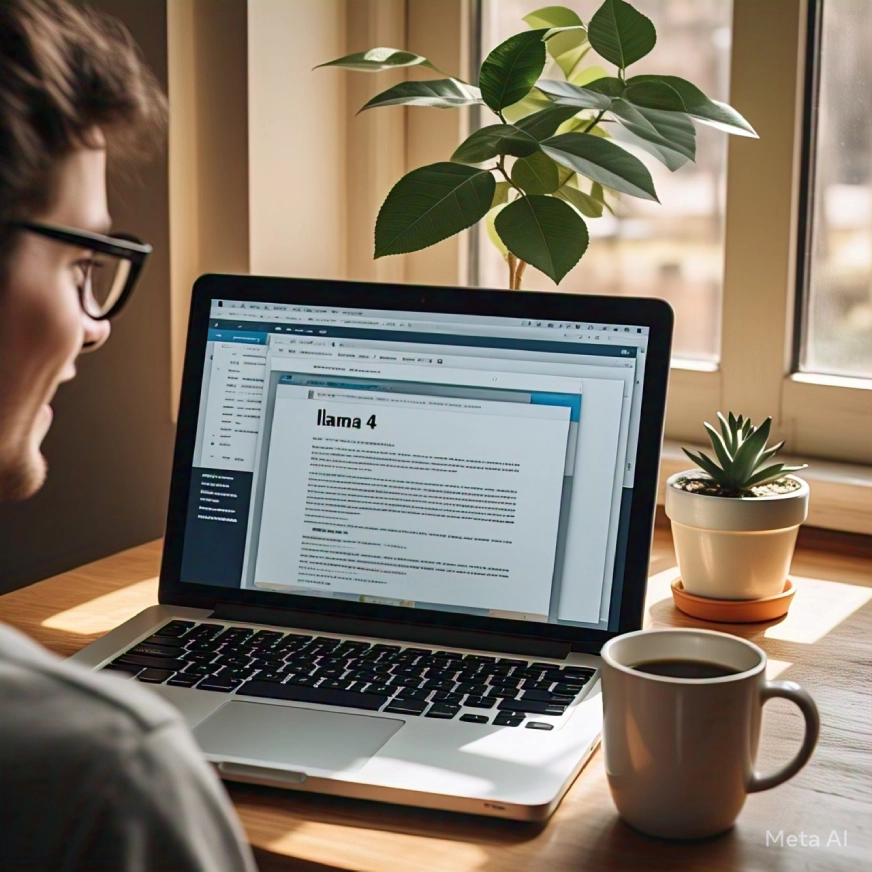

Observation
- It generated 4 images! Out of those, I found the above image to be the best.
- You also get the option to “Edit” and “Animate” the images that you have generated.
- Editing allows you to rework certain sections of an image while Animating allows you to create a gif of the image.
Training and Post-Training of Llama 4 Models
Meta used a structured two-step process: pre-training and post-training, incorporating new techniques for better performance, scalability, and efficiency. Let’s break down the whole process:
Pre-Training Phase
Pre-training is the foundation for a model’s knowledge and ability. Meta introduced several innovations in this stage:
- Multimodal Data: Llama 4 models were trained on over 30 trillion tokens from diverse text, image, and video datasets. They’re natively multimodal, meaning they handle both language and vision from the start.
- Mixture of Experts (MoE): Only a subset of the model’s total parameters is active during each inference. This selective routing allows massive models like Maverick (400B total parameters) and Behemoth (~2T) to be more efficient.
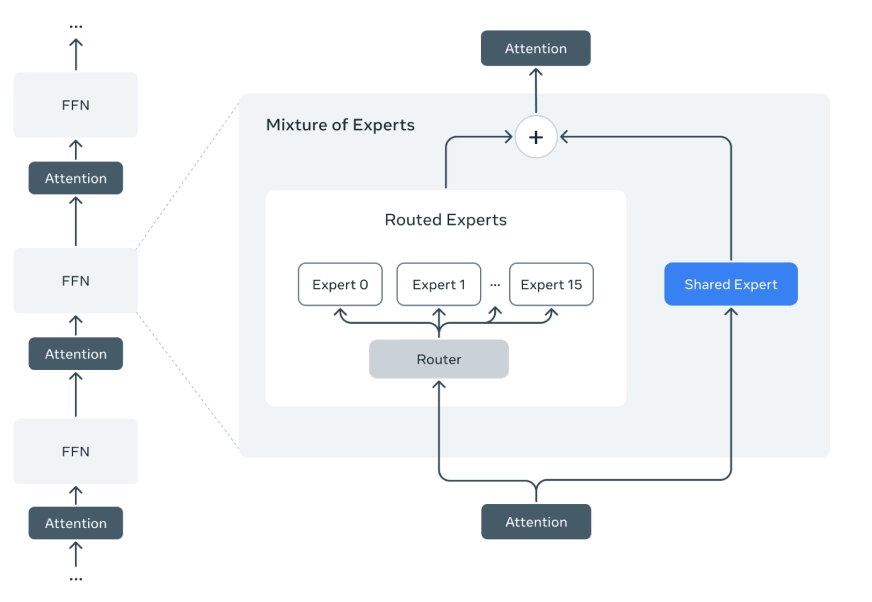
- Early Fusion Architecture: Text and vision inputs are jointly trained using early fusion, integrating both into a shared model backbone.
- MetaP Hyperparameter Tuning: This new technique lets Meta set per-layer learning rates and initialization scales that transfer well across model sizes and training configurations.
- FP8 Precision: All models use FP8 for training, which increases computing efficiency without sacrificing model quality.
- iRoPE Architecture: A new approach using interleaved attention layers without positional embeddings and inference-time temperature scaling, helping Scout generalize to extremely long inputs (up to 10M tokens).
Post-Training Phase
After training the base models, the team fine-tuned them using a carefully crafted sequence:
- Lightweight Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT): Meta filtered out easy prompts using Llama models as judges and only used harder examples to fine-tune performance on complex reasoning tasks.
- Online Reinforcement Learning (RL): They implemented continuous RL training using hard prompts, adaptive filtering, and curriculum design to maintain reasoning, coding, and conversational capabilities.
- Direct Preference Optimization (DPO): After RL, they applied lightweight DPO to fine-tune specific corner cases and response quality, balancing helpfulness and safety.
- Behemoth Codistillation: Behemoth acted as a teacher by generating outputs for training Scout and Maverick. Meta even introduced a novel loss function to dynamically balance soft and hard supervision targets.
Together, these steps created models that aren’t just large, they’re deeply optimized, safer, and more capable across a wide range of tasks.
Also Read: What are Open Source and Open Weight Models?
Meta Llama 4 Benchmark Performance
Meta has shared detailed benchmark results for all three Llama 4 models, reflecting how each performs based on its design goals and parameter sizes. They also outperform leading models in several newly introduced benchmarks that are particularly challenging and comprehensive.
Llama 4 Scout
Scout, despite being the smallest in the family, performs remarkably well in efficiency-focused evaluations:
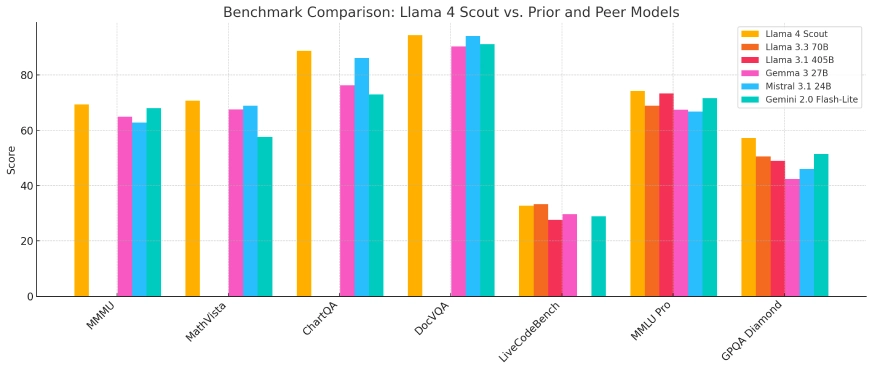
- ARC (AI2 Reasoning Challenge): Scores competitively among models in its size class, particularly in commonsense reasoning.
- MMLU Lite: Performs reliably on tasks like history, basic science, and logical reasoning.
- Inference Speed: Exceptionally fast, even on a single H100 GPU, with low latency responses in QA and chatbot tasks.
- Code Generation: Performs well for simple to intermediate programming tasks, making it useful for educational coding assistants.
- Needle-in-a-Haystack (NiH): Achieves near-perfect retrieval in long-context tasks with up to 10M tokens of text or 20 hours of video, demonstrating unmatched long-term memory.
Llama 4 Maverick
Maverick is built for performance, and it delivers across the board:
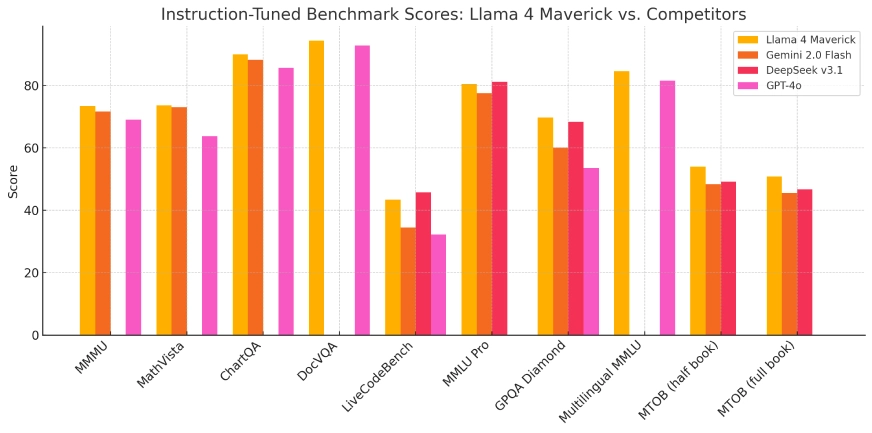
- MMLU (Multitask Language Understanding): Outperforms GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Flash, and Claude 3 Sonnet in knowledge-intensive tasks.
- HumanEval (Code Generation): Matches or surpasses GPT-4 in generating functional code and solving algorithmic problems.
- DROP (Discrete Reasoning Over Paragraphs): Shows strong contextual understanding and numerical reasoning.
- VQAv2 (Visual Question Answering): Excels at answering image-based queries accurately, showcasing Maverick’s strong vision-language abilities.
- Needle-in-a-Haystack (NiH): Successfully retrieves hidden information across long documents up to 1M tokens, with near-perfect accuracy and only a few misses at extreme context depths.
Llama 4 Behemoth
Behemoth is not available to the public but serves as Meta’s most powerful evaluation benchmark. It is used to distill and guide the other models:
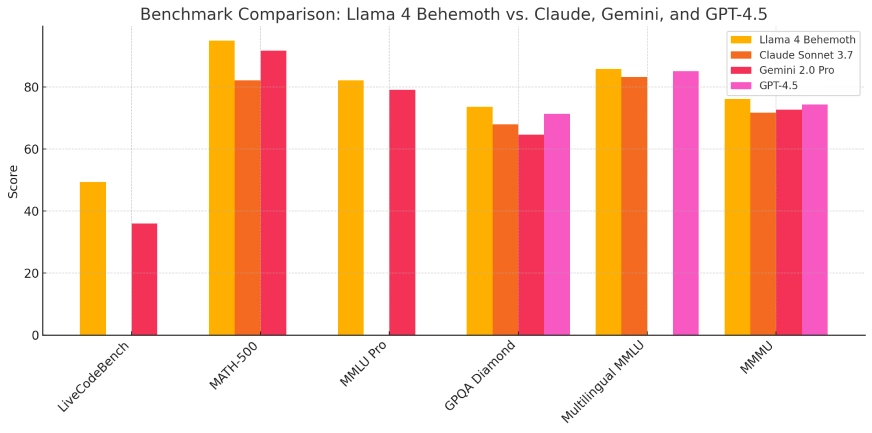
- Internal STEM Benchmarks: Tops internal Meta tests in science, math, and reasoning.
- SuperGLUE and BIG-bench: Achieves top scores internally, reflecting cutting-edge language modeling capability.
- Vision-Language Integration: Shows exceptional performance on tasks requiring combined text and image understanding, often surpassing all known public models.
These benchmarks highlight how each model excels in its role: Scout delivers speed and efficiency, Maverick handles power and general-purpose tasks, and Behemoth serves as a research-grade teacher model for distillation and evaluation.
Comparing the Llama 4 Models
While all the three models come with their own features, here is a brief summary that can help you find the right Llama 4 model for your task:
Conclusion
With the Llama 4 release, Meta is doing more than just keeping up it’s setting a new standard. These models are powerful, efficient, and open. Developers don’t need huge budgets to work with top-tier AI anymore. From small businesses to big enterprises, from classrooms to research labs Llama 4 puts cutting-edge AI into everyone’s hands. In the growing world of AI, openness is no longer a side story; it’s the future. And Meta just gave it a powerful voice.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Scout is a lightweight, fast, and efficient model suitable for devices with limited compute. Maverick is the flagship model built for coding, reasoning, and enterprise applications. Behemoth is Meta’s largest internal model used for training and benchmarking but is not publicly available.
A. Yes, Scout and Maverick are open-weight models available to the public. Behemoth is not open for public use but serves as a teacher model for internal training and distillation.
A. You can access Llama 4 Scout and Maverick via llama.meta.com, on Hugging Face, or through Meta’s apps like WhatsApp and Instagram via the Meta AI assistant.
A. Yes, all Llama 4 models are natively multimodal and can process up to 8 images per prompt, offering advanced visual reasoning capabilities.
A. No, Meta hasn’t provided an option to choose between Scout, Maverick, or Behemoth within its apps or web interface. The specific model used in the background is not disclosed.
A. Scout and Maverick support a context window of up to 10 million tokens, the highest among any open-weight LLMs to date.
A. Llama 4 Maverick has outperformed GPT-4o and Gemini 2.0 Flash in several benchmark tests, especially in coding, reasoning, and multilingual tasks. Scout also beats similar-sized models in speed and retrieval accuracy.





